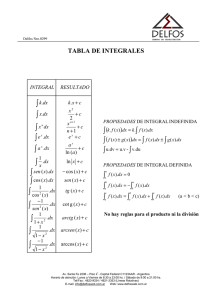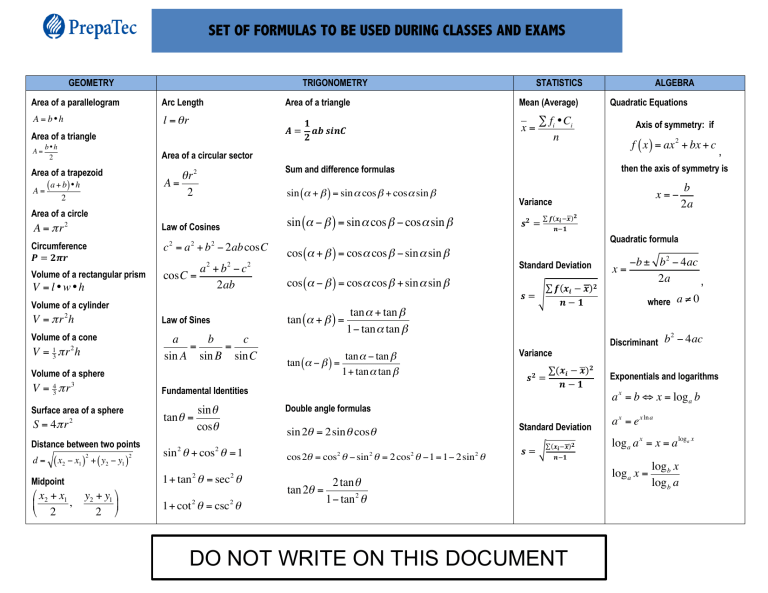
SET OF FORMULAS TO BE USED DURING CLASSES AND EXAMS GEOMETRY TRIGONOMETRY Area of a parallelogram Arc Length A = b•h l = θr Area of a triangle 𝑨= Area of a triangle A= b•h 2 x= Quadratic Equations ∑ fi •Ci n Axis of symmetry: if f ( x ) = ax 2 + bx + c ( a + b) • h 2 sin (α + β ) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β sin (α − β ) = sin α cos β − cos α sin β A = π r2 Law of Cosines Circumference 𝑷 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓 c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cosC 2 Volume of a rectangular prism V = l •w•h 2 a +b −c cosC = 2ab 2 Volume of a cylinder V = π r 2h Law of Sines Volume of a cone a b c = = sin A sin B sinC 2 V = πr h 1 3 Volume of a sphere V = 43 π r 3 S = 4π r tan θ = 2 Distance between two points 2 ( x2 − x1 ) + ( y2 − y1 ) 2 2 sin θ cosθ 2 sin θ + cos θ = 1 1+ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ Midpoint ! x2 + x1 , # " 2 𝒔𝟐 = y2 + y1 $ & 2 % 1+ cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ b 2a ∑ 𝒇(𝒙𝒊 3𝒙)𝟐 𝒏3𝟏 cos (α − β ) = cos α cos β + sin α sin β tan α + tan β tan (α + β ) = 1− tan α tan β tan (α − β ) = tan α − tan β 1+ tan α tan β Standard Deviation ∑ 𝒇(𝒙𝒊 − 𝒙)𝟐 𝒔=5 𝒏−𝟏 cos 2θ = cos2 θ − sin 2 θ = 2 cos2 θ −1 = 1− 2sin 2 θ tan 2θ = −b ± b 2 − 4ac 2a , where a ≠ 0 Discriminant b − 4ac Variance 𝒔𝟐 = ∑(𝒙𝒊 − 𝒙)𝟐 𝒏−𝟏 Exponentials and logarithms a x = b ⇔ x = log a b Double angle formulas sin 2θ = 2sin θ cosθ x= 2 Fundamental Identities Surface area of a sphere x=− Variance Quadratic formula cos (α + β ) = cos α cos β − sin α sin β , then the axis of symmetry is Sum and difference formulas θr2 A= 2 Area of a circle d= Mean (Average) ALGEBRA Area of a circular sector Area of a trapezoid A= 𝟏 𝒂𝒃 𝒔𝒊𝒏𝑪 𝟐 STATISTICS Standard Deviation ∑(𝒙𝒊 3𝒙)𝟐 𝒔=7 a x = e x ln a log a a x = x = a loga x 𝒏3𝟏 2 tan θ 1− tan 2 θ DO NOT WRITE ON THIS DOCUMENT log a x = log b x log b a CALCULUS MATHEMATICS FOR DECISION MAKING Addition rule for probabilities Derivative % f ( x + h) − f ( x ) ( dy y = f ( x) ⇒ = f " ( x ) = Lim ' * h→0 dx h & ) 𝑓(𝑥) 𝑓′(𝑥) f ! ( x ) = nx n−1 f ( x) = x n y = un y = uv y= u v y = ln u vu! − uv! v2 y! = u! u y = sin (u) y = cos (u) y! = −u! sin (u) y = tan (u) y! = u! sec 2 (u) y=e y = cot (u) y! =− u'csc (u) ∫ sec (u) du = ln sec (u) + tan (u) +C y = sec (u) y! = u'sec (u) tan (u) ∫ csc (u) du = ln csc (u) − cot (u) + C y = csc (u) 2 y! =− u'csc (u) cot (u) s= 1+ "# f ! ( x )$% dx a Average y value 1 b−a A= Permutations n! , (n − r)! Combinations n Cr = n! r!(n − r)! : : 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑥) = 𝜎 T = K(𝑥M − 𝑥̅ )T ∗ 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) 𝐸(𝑋) = 𝜇 = K 𝑥M 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) MOA MOA = 𝐸(𝑥 T ) − 𝜇T 𝑆𝐷(𝑋) = 𝜎 = Y𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) Binomial distribution #n& or P(X = k) = % ( p k ⋅ (1− p)n−k $k ' P(X = x) = n Cx ⋅ p x ⋅ (1− p)n−x E(X) = np , σ 2 = Var(X) = npq = np(1− p) , σ = SD(X) = npq Standard z-score (Normal distribution) 𝑧= Contrast value or t statistic for Tscore, Z-score and Paired sample T-test c [̅ 3\ [̅ 3\ b 𝑡=_ 𝑧=] 𝑡 = de [̅ 3\ ] a √: a √: ∫ f ( x ) dx E = Zα /2 σ n _ so that _ E = tα /2 x− E < µ < x+ E s n _ _ so that x − E < µ < x+ E i 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑥) = 𝜎 T = g (𝑥 − 𝜇)T 𝑓(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 = 𝐸(𝑥 T ) − 𝜇T 𝐸(𝑋) = 𝜇 = g 𝑥𝑓(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 j i j j Simple Interest Compound Interest A = P(1+ rt) ! r$ A = P #1+ & " n% a ∫ f √: Confidence intervals, where E is the margin of error 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑥 ) = g 𝑥 T 𝑓(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 − 𝜇T 𝑆𝐷(𝑋) = 𝜎 = Y𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) f ( x ) dx b , I = Prt nt Annuities Ordinary 2 V = π ∫ !" f ( x )#$ dx a Integration by parts Pr = Expected value, variance and standard deviation of a discrete random variable a Volume n b b Area under the curve Counting Techniques Expected value, variance and standard deviation of a continuous random variable 2 ∫ P(A ∩ B) P(B) P(A B) = i b Arc Length Conditional Probability 2 2 y! = u!eu y! = u! cos (u) u 𝑛 ≠ −1 ∫ sin (u) du = −cos (u) + C ∫ cos (u) du = sin (u) + C ∫ sec (u) du = tan (u) + C ∫ csc (u) du = −cot (u) + C ∫ sec (u) tan (u) du = sec (u) + C ∫ csc (u) cot (u) du = −csc (u) + C ∫ tan (u) du = − ln cos (u) + C ∫ cot (u) du = ln sin (u) + C 𝑦´ = 𝑛 ∙ 𝑢´ ∙ 𝑢:3A y! = vu! + uv! y! = <=>? ∫ 𝑢: 𝑑𝑢 = :@A + 𝐶, 1 ∫ u du = ln u + C ∫ eu du = eu + C P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B) ∫ u dv = uv − ∫ v du A= R ((1+ i)n −1) i Anticipated A = R(1+ i) , P= R (1− (1+ i)−n ) i ((1+ i)n −1) i R (1− (1+ i) −n Deferred: Ordinary P= (1− (1+ i) ) −n , P = R(1+ i) i ) (1+ i) −K i