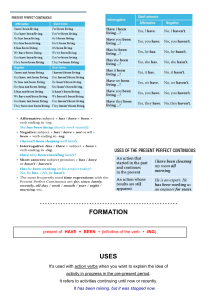
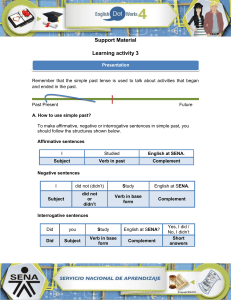
Daniel Felipe Michael Teacher we are going to expose is a review of the topics that we are going to deal with in the game PRESENTATION ENGLISH First diapositive: Hello, today we will present you the simple tenses both in the past, present and future. Our group is made up of: Second diapositive: First we have to remember what regular and irregular verbs are and how they are used. Regular Verbs: Regular English verbs create the past simple and past participle by adding -ed to the base form As we can see in example one. If the verb ends in a consonant and -y, we change the -y to -i and add -ed..As we can see in example two If a verb ends in -e, we just add -d. As we can see in example tree Irregular verbs: There are about twelve irregular verbs in English. We can divide these into four types: 1. 2. 3. 4. Verbs that have the same basic form, simple past and past participle Verbs that have the same past simple and past participle Verbs that have the same base form and past participle Verbs that have a base form, past simple, and different past participle For example, as we can see in the table the four types of irregular verbs Third Diapositive: Simple past: The past simple is used to talk about a specific action that started and ended in the past. In its negative and interrogative form, the auxiliary DID is used. Forth Diapositive We will start with the affirmative sentences, their structure is: First the pronoun, then the verb must go, remember that this must be in the past and lastly the complement. For example. I PLAYED IN THE PARK In its negative form, the pronoun comes first, followed by the auxiliary DID with the not, then the verb and the complement. For example, (SHE DIDENT SLAP IN DE BED), as we can tell, the auxiliary did is combined with the not, leaving a single word as didn't. In the interrogative form its structure is: the auxiliary did first, followed by the pronoun plus the verb and the complement, finally it must go is question mark. For example, (DED WE DRANK BEER THE FRAIDAY) FIVE DIAPOSITIVE Simple present: The present simple is used to talk about things that happen regularly. SIX DIAPOSITIVE We will have to take into account some observations to go through the structure of the sentences of the present simple The first observation is In the present simple it is important to note that in negative and interrogative sentences, the auxiliary (DO) is used in the pronouns (I, YOU, WE, TH) EY) and the auxiliary (DOES) is used in the pronouns (SHE, HE, IT). The second observation is that In affirmative sentences, (es) S is added to the end of the verb if the pronoun is (SHE, HE, IT). SEVEN DIPOSITIVE We will start with the affirmative sentences, their structure is: First the pronoun then the verb and take into account if it has the letter (s) and finally the complement For example. SHE READS THE NEWSPAPER EVERY DAY In its negative form the pronoun comes first, followed by the auxiliary (DO) or (DOES) then the verb and the complement. BY EXAMPLE HE DOESN'T ENJOY HIS ENGLISH CLASS As we can see, the auxiliary did is combined with the no, leaving a single word In the interrogative form its structure is: the auxiliary did first, followed by the pronoun plus the verb and the complement, finally the question mark must go. for example: DO THEY SMOKE A LOT? DIAPOSITIVE EIGHT FUTURE IN THE SIMPLE FUTURE is to say something that is going to happen and you must use (going to) or (will) In going to it is generally used to talk about plans or intentions and premeditated decisions to be made in the future. And Will It is used to talk about the future. It is generally used to talk about spontaneous decisions or events that could happen in the future Dipositive nine We will start with the affirmative sentences, their structure is: First the pronoun, with the verb to be, then going to continues with the verb and ends with the complement FOR EXAMPLE: HE IS GOING TO VISIT HER NEXT WEEK we must use in the negative form first the pronoun with the verto to be with the not continuous going to more the verb and the complement FOR EXAMPLE YOU ARE NOT GOING TO TO TRAVEL WITH HIM in the interrogative form the verb to be comes first followed by going to continues the verb and ends with the complement and question mark FOR EXAMPLE AM I GOING TO SEE YOU TOMORROW? DIPOSITIVE TEN We start with the affirmative sentences, their structure is: First the pronoun, then the auxiliary will followed by the verb and the complement For example: SHE WILL LIKE TO SIT IN THE SUN we must use for a negative form first the pronoun followed by the negative auxiliary won´t and ends with the complement the auxiliary must change because in negative form it must be written in another way for example, HE WON'T GIVE YOU THE MONEY TOMORROW and in the interrogative form it is structured is: first the auxiliary will, then the pronoun, continues with the verb and ends with the complement for example WILL SHE PLAY THE PIANO? Thank you