Present in english
Anuncio

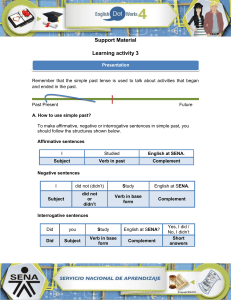
Simple Present Use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do. Subject + Verb + complement We use the present tense: Affirmative Sentences. • I talk • You walk • He eats • We learn For facts or Generalizations • My boyfriend lives near to my home • We come from the beach • A dog has an empty plate For habits. (frequency adverbs) • I get up late every day. • He never eats vegetables • They hardly ever talks with their parents Imperative • Open the window. • • • Eat the vegetables. Don't cry Call your mother. Events in the near feature • The train leaves tonight at 6 PM. • The party starts at 10 o'clock. • When does class begin tomorrow? Negative Sentences Subject + auxiliary verb (do) + negative auxiliary (not) + verb • They do not eat • I dont talk • You do not walk Interrogative Sentences Auxiliary verb (do) + subject + verb • Do you want? • Does he love? • Do they learn? Present Continuous We use the Present continuous to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now but is in process of doing a longer action which is in progress however; we might not be doing it at this exact second. Subject + auxiliary verb to be + gerund (ing) + complement We use the present tense: Affirmative Sentences Something is happening now. • I am eating • You are running • They are learning Activities happening in the near future, especially for planned future events. • Polly is coming for dinner tomorrow. • I am studying for the exam in an hour. • I am going to the party tonight. To say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second. • I am studying to become a lawyer. • You are working to buy a home. • He is saving money to travel to Spain Negative Sentences Subject + auxiliary verb ("to be") + auxiliary negative ("not") + gerund ("-ing"). • I'm not talking • He's not eating • They're not learning Interrogative Sentences Auxiliary verb ("to be") + subject + gerund ("-ing")? • Are you sleeping? • Is he walking? • Are they learning? Present Perfect We use present perfect simple expresses an action that is still going on or that stopped recently, but has an influence on the present. Subject + auxiliary verb (have/has) + past participle Affirmative Sentences • I have studied. • He has written a letter to María. • They have eaten. We use present perfect to describe an experience • I have never flown in a plane. • He has worked in many different schools. • We have been in Europe. We often use the Present Perfect to talk about change that has happened over a period of time. • My english has really improved since I moved to USA • He has become more timid in his old age. • You have grown since the last time I saw you. We often use the Present Perfect to list the accomplishments of individuals and humanity. You can not mention a specific time. • Man has walked on the Moon. • Our son has learned how to read. • Doctors have cured many deadly diseases. We use the present perfect for actions that have not yet happened, in these cases indicates that we are still waiting for action, we can use adverbs "yet" and "still" • The plane hasn't arrived yet • The rain hasn't stopped. • You haven't finished your homework yet? We also use the Present Perfect to talk about several different actions which have occurred in the past at different times. Present Perfect suggests the process is not complete and more actions are possible. • I have had four quizzes and five tests so far this semester. • We have had many major problems while working on this project. • I love New York! I have been there 5 times already and I can't wait to go back Negative Sentences Subject + auxiliary verb (have/has) + not + past participle +complement • I haven't talked to Peter • She hasn't gone to work. • They haven't learned English. Interrogative Sentences Auxiliary verb (have/has) + subject + past participle + complement • Has she gone to work?? • Have they learned English? • Have you been to London?