SOLAR SYSTEM
Anuncio
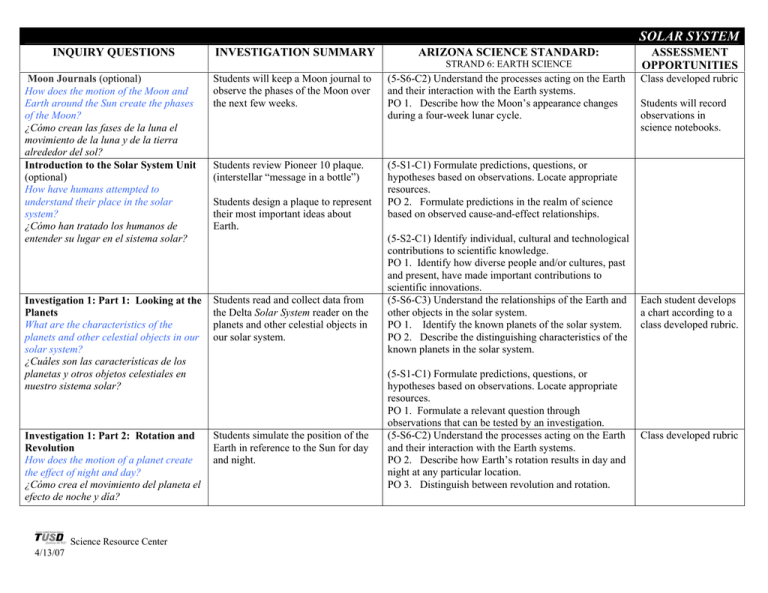
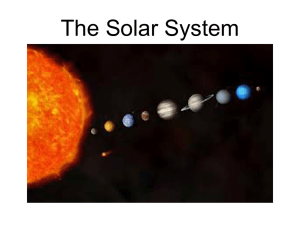
SOLAR SYSTEM INQUIRY QUESTIONS INVESTIGATION SUMMARY ARIZONA SCIENCE STANDARD: STRAND 6: EARTH SCIENCE Moon Journals (optional) How does the motion of the Moon and Earth around the Sun create the phases of the Moon? ¿Cómo crean las fases de la luna el movimiento de la luna y de la tierra alrededor del sol? Introduction to the Solar System Unit (optional) How have humans attempted to understand their place in the solar system? ¿Cómo han tratado los humanos de entender su lugar en el sistema solar? Students will keep a Moon journal to observe the phases of the Moon over the next few weeks. (5-S6-C2) Understand the processes acting on the Earth and their interaction with the Earth systems. PO 1. Describe how the Moon’s appearance changes during a four-week lunar cycle. Students review Pioneer 10 plaque. (interstellar “message in a bottle”) (5-S1-C1) Formulate predictions, questions, or hypotheses based on observations. Locate appropriate resources. PO 2. Formulate predictions in the realm of science based on observed cause-and-effect relationships. Investigation 1: Part 1: Looking at the Planets What are the characteristics of the planets and other celestial objects in our solar system? ¿Cuáles son las características de los planetas y otros objetos celestiales en nuestro sistema solar? Students read and collect data from the Delta Solar System reader on the planets and other celestial objects in our solar system. Investigation 1: Part 2: Rotation and Revolution How does the motion of a planet create the effect of night and day? ¿Cómo crea el movimiento del planeta el efecto de noche y día? Students simulate the position of the Earth in reference to the Sun for day and night. Science Resource Center 4/13/07 Students design a plaque to represent their most important ideas about Earth. (5-S2-C1) Identify individual, cultural and technological contributions to scientific knowledge. PO 1. Identify how diverse people and/or cultures, past and present, have made important contributions to scientific innovations. (5-S6-C3) Understand the relationships of the Earth and other objects in the solar system. PO 1. Identify the known planets of the solar system. PO 2. Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the known planets in the solar system. (5-S1-C1) Formulate predictions, questions, or hypotheses based on observations. Locate appropriate resources. PO 1. Formulate a relevant question through observations that can be tested by an investigation. (5-S6-C2) Understand the processes acting on the Earth and their interaction with the Earth systems. PO 2. Describe how Earth’s rotation results in day and night at any particular location. PO 3. Distinguish between revolution and rotation. ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Class developed rubric Students will record observations in science notebooks. Each student develops a chart according to a class developed rubric. Class developed rubric SOLAR SYSTEM INQUIRY QUESTIONS Investigation 2: The Moon How does the motion of the Moon and Earth around the Sun create the phases of the Moon? ¿Cómo crea la fases de la luna el movimiento de la luna y la tierra alrededor de la luna? Investigation 3: Part 1: Objects in the Sky (optional) What are the characteristics of the other celestial objects in our solar system? ¿Cuáles son las características de los otros objetos celestiales en nuestro sistema solar? Investigation 3: Part 2: Gravity How does the force of gravity affect objects? ¿Cómo afecta la fuerza de la gravedad a los objetos? Investigation 3: Part 3: Celestial Motion Why do some celestial objects appear to move in a way that is different from their real motion? ¿Porqué parece que algunos objetos celestiales se mueven en forma diferente de su movimiento verdadero? Investigation 4: Space Exploration Research What efforts have humans made to explore space? ¿Que esfuerzos han hecho los humanos para explorar el espacio? Science Resource Center 4/13/07 INVESTIGATION SUMMARY ARIZONA SCIENCE STANDARD: STRAND 6: EARTH SCIENCE ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Students understand through a simulation what causes the phases of the Moon. (5-S6-C2) Understand the processes acting on the Earth and their interaction with the Earth systems. PO 1. Describe how the Moon’s appearance changes during a four-week lunar cycle. Student notebook page “Moon Phases Posttest” Students will read about other celestial objects in the Delta Science readers, take notes and discuss findings. They will play “Solar System Bingo” from their collected data. (5-S6-C3) Understand the relationships of the Earth and other objects in the solar system. PO 3. Describe various objects in the sky (e.g., asteroids, comets, stars, meteors/shooting stars). Teacher observation and review of student notebooks. Students will understand that the force of gravity between objects depends on mass. They will relate the force of gravity between a planet and a person to the force of gravity between the sun and other objects in the solar system. Students will learn the difference between real and apparent motion. (5-S6-C2) Understand the processes acting on the Earth and their interaction with the Earth systems. PO 4. Describe the role of gravity as an attractive force between celestial objects. Student letter (5-S6-C3) Understand the relationships of the Earth and other objects in the solar system. PO 4. Describe the change in position and motion of the following objects in the sky over time: • real motion – Moon, planets • apparent motion (due to the motion of the Earth) – Sun, Moon, stars Explanatory response to writing prompt. Students will research efforts to explore space and write a letter to the Hall of Recognition on the importance of their chosen event. (5-S6-C3) Understand the relationships of the Earth and other objects in the solar system. PO 6. Describe efforts to explore space (e.g., Apollo missions, space shuttles, Hubble space telescope, space probes). Research and student letter to Hall of Recognition