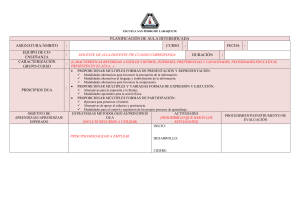
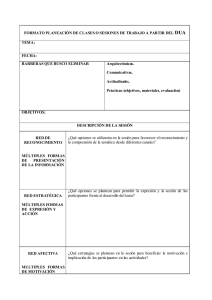
Универсальный дизайн для обучения (UDL) - этомодель, которая по результатам образовательная практика и исследования, теорииобучения, технологий и достижений в нейробиология, сочетает в себе взгляд и фокус включая обучение с предложениями по его применение на практике. Начиная с концепции универсальный дизайн, он организован вокруг трех групп нейронных сетей аффективных, распознающих и стратегический - и предлагает три принципа, связанные с они: обеспечивают несколько форм участия, множественные формы представления информации и множественные формы действия и выражения обучения. DUA основывается на разнообразии с самого началадидактическое планирование и старается, чтобы все у студентов есть возможность учиться. Облегчает учителя - основа для обогащения и повышения гибкости разработка учебной программы, снижение потенциальных барьеров ипредоставить возможности обучения для всех студенты. Таким образом, потенциал признан этой теоретико-практической модели, чтобы способствовать достичь Цели устойчивого развития (SDG4) Повестки дня до 2030 года: «Гарантировать образование инклюзивный и качественный и продвигать возможности для обучение для всех ». The Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a model that, based on the results of educational practice and research, learning theories, technologies and advances in neuroscience, combines an inclusive view and approach to teaching with proposals for its application in practice. Starting from the concept of universal design, it is organized around three groups of neural networks - affective, recognition and strategic - and proposes three principles linked to them: providing multiple forms of involvement, multiple forms of information representation and multiple forms of action and expression of learning. The DUA starts from diversity from the beginning of didactic planning and tries to ensure that all students have opportunities to learn. It provides teachers with a framework to enrich and make curriculum design more flexible, reduce potential barriers, and provide learning opportunities for all students. Therefore, the potential of this theoretical and practical model is recognized to contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG4) of the 2030 Agenda: "Guarantee inclusive and quality education and promote learning opportunities for all." The DUA helps account for student variability by suggesting flexibility in objectives, methods, materials, and assessment that allow educators to meet these varied needs. The curriculum that is created following the DUA framework is designed, from the beginning, to meet the needs of all students, making subsequent changes, as well as the cost and time associated with them, unnecessary. The DUA proposes information access strategies for students, as well as the way in which we are going to request jobs or activities and, of course, the mechanisms that motivate them to do them from home. ASPECTS TO CONSIDER Objectives: they must recognize the diversity of the students, allowing more options to achieve mastery of the content. Methods: The DUA provides us with ideas such as those exemplified above for and their use and adjustment are based on continuous observation of student progress. Materials: the hallmark of DUA is that the materials are variable and flexible, that they offer the contents in different media as well as taking into account the participation, interest and motivation of the students. Evaluation: within the framework of the DUA, it is expected that the evaluation can guide the learner, giving the possibility to use supports or scaffolds that adapt to the variability of students. El Diseño Universal para el Aprendizaje (DUA) es un modelo que, fundamentado en los resultados de la práctica y la investigación educativa, las teorías del aprendizaje, las tecnologías y los avances en neurociencia, combina una mirada y un enfoque inclusivo de la enseñanza con propuestas para su aplicación en la práctica. Partiendo del concepto de diseño universal, se organiza en torno a tres grupos de redes neuronales –afectivas, de reconocimiento y estratégicas– y propone tres principios vinculados a ellas: proporcionar múltiples formas de implicación, múltiples formas de representación de la información y múltiples formas de acción y expresión del aprendizaje. El DUA parte de la diversidad desde el comienzo de la planificación didáctica y trata de lograr que todo el alumnado tenga oportunidades para aprender. Facilita a los docentes un marco para enriquecer y flexibilizar el diseño del currículo, reducir las posibles barreras y proporcionar oportunidades de aprendizaje a todos los estudiantes. Por todo ello se reconoce el potencial de este modelo teórico-práctico para contribuir a lograr el Objetivo de Desarrollo Sostenible (ODS4) de la Agenda 2030: «Garantizar una educación inclusiva y de calidad y promover oportunidades de aprendizaje para todos». El DUA ayuda a tener en cuenta la variabilidad de los estudiantes al sugerir flexibilidad en los objetivos, métodos, materiales y evaluación que permitan a los educadores satisfacer dichas necesidades variadas. El currículum que se crea siguiendo el marco del DUA es diseñado, desde el principio, para atender las necesidades de todos los estudiantes, haciendo que los cambios posteriores, así como el coste y tiempo vinculados a los mismos sean innecesarios El DUA propone estrategias de acceso a la información para los estudiantes, así como la manera en que vamos a solicitarles trabajos o actividades y por supuesto, los mecanismos que los motiven para realizarlas desde sus hogares. ASPECTOS A TENER EN CUENTA Objetivos: deben reconocer la diversidad del alumnado, permitiendo más opciones para alcanzar el dominio de los contenidos. Métodos: el DUA nos proporciona ideas como las ejemplificadas anteriormente para y su uso y ajuste se basan en la observación continua del progreso de los estudiantes. Materiales: el sello de DUA es que los materiales sean variables y flexibles, que ofrezcan los contenidos en distintos medios además de tener en cuenta la participación, interés y motivación del alumnado. Evaluación: en el marco del DUA, se espera que la evaluación pueda guiar al aprendiz, dando la posibilidad usar apoyos o andamiajes que se adapten a la variabilidad de estudiantes.