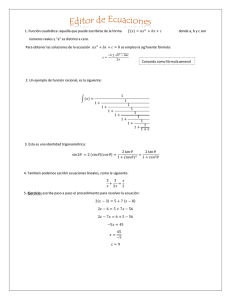
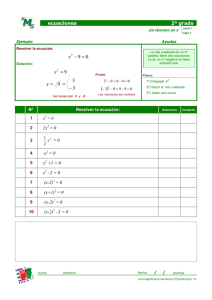
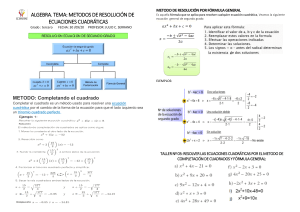
ECUACIONES
CUADRÁTICAS
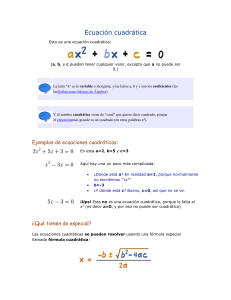
ECUACIONES CUADRÁTICAS
Una ecuación cuadrática o también llamada
ecuación de segundo grado tiene la
siguiente forma: 𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒃𝒙 + 𝒄 = 𝟎,
un polinomio de segundo grado. Además,
consiste en una sola variable (x) y tres
términos ((a, b, c) ∈ 𝑅)
I. Métodos para desarrollar
1. Por factorización
𝒙𝟐 + 𝟒𝒙 − 𝟓 = 𝟎
𝑥
+5
𝑥
−1
𝑥+5 𝑥−1 =0
Igualando cada factor a cero:
𝑥 + 5 = 0 → 𝑥 = −5
𝑥−1=0 →𝑥 =1
C.S. = {-5,1}
2. Por fórmula general cuadrática
𝑿=
−𝒃 ± 𝒃2 − 4𝒂𝒄
2𝒂
𝑥2 =
−4 − 42 − 4 1 (−5)
2(1)
𝑥2 =
−4 − 16 + 20
2
𝒙2 + 4𝒙 − 5 = 0
𝑥1 =
𝑥1 =
−4 +
42
− 4 1 (−5)
2(1)
−4 + 16 − 4(−5)
2
𝑥2 =
−4 − 36
2
𝑥2 =
𝑥1 =
−4 + 16 + 20
2
𝑥1 =
−4 + 36
2
𝑥1 =
−4+6
2
=1
−4 − 6
2
𝑥2 = −5
Además, se debe de analizar el
discriminante:
∆= 𝒃𝟐 − 𝟒𝒂𝒄
3. Método de raíz cuadrada: consiste en
despejar la variable x o la variable
involucrada.
i.
Si: ∆= 𝒃𝟐 − 𝟒𝒂𝒄 > 𝟎
→ Las raíces 𝑥1 y 𝑥2 son reales y
diferentes
i.
Si: ∆= 𝒃𝟐 − 𝟒𝒂𝒄 = 𝟎
→ Las raíces 𝑥1 y 𝑥2 son iguales
i.
25x2 – 121 = 0
25x2 = 121
x2 = 121/25
x = ±√
𝟐
Si: ∆= 𝒃 − 𝟒𝒂𝒄 < 𝟎
→ Las raíces 𝑥1 y 𝑥2 son complejas
y conjugadas
x=±
121
25
11
5
4. Completando cuadrado:
Extraemos raíz cuadrada de
ambos miembros y tenemos
X2 + 8x – 48 = 0
x2 + 8x = 48
8 dividido entre 2 →
(42
8
2
=4
= 16)
x2 + 8x + 16 = 48 + 16
x2 + 8x + 16 = 64
Factorizamos:
(x + 4) (x + 4) = 64
(x + 4)2 = 64
x+4=8
x=8−4
x=4