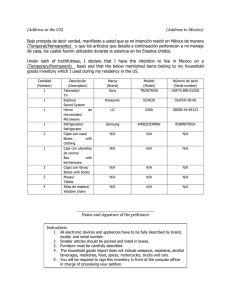
table of english tenses
Anuncio

TABLE OF ENGLISH TENSES TENSE PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS FORM USE SIGNAL WORDS A: I / You / We / They eat He / She / It eats N: I / You / We / They don't eat He / She / It doesn't eat Q: Do I / You / We / They eat? Acciones rutinarias: I watch TV every night Con hechos o verdades generales: Water boils at 100 Cº Con situaciones permanentes: I work as a waiter in a restaurant Acciones futuras con horarios de trenes, aviones, etc. My train leaves at 5.30 Con verbos que no suelen ir en presente continuo: know, like, hate, want, love, need, belong, mean, understand, remember, prefer… Con acciones que ocurren en el momento de hablar: We're studying the verbs now. Adverbios de frecuencia: always, often, usually, generally, seldom, never… A: I am eating He / She / It is eating We / You / They are eating N: I am not eating He / She / It isn't eating We / You / They aren't eating Q: Am I eating? Is He / She / It eating? Are We / You / They eating? Con acciones que están ocurriendo temporalmente: My brother is working hard this year. Con acciones habituales que causan irritación al hablante: They are always complaining about the same thing. Con acciones futuras planeadas y confirmadas (fecha): She's visiting the doctor tomorrow morning. * El presente continuo no se suele utilizar con los siguientes verbos: know, like, want, hate, love, need, belong mean, understand, believe, remember, prefer; aunque algunos de estos verbos pueden aparecer en forma continua con un sentido diferente Every day/ week/ month… Once / Twice / Three times… a week/ day / month/ year… Now, right now At present, at the moment, in this moment, …. These days, this year/ month/ week…, nowadays Tonight, tomorrow, next week / month…, in a minute, in a couple of days… TENSE PAST SIMPLE FORM USE SIGNAL WORDS A: He watched / He ate Con acciones pasadas que tuvieron lugar en un momento determinado: We didn't watch TV last night Narrar hechos pasados secuenciados I went to the doctor and later I came home While N: He didn't watch / He didn't eat Q: Did he watch? / Did he eat? PAST CONTINUOUS A: I / He / She / It was eating We / You / They were eating N: I / He / She / It wasn't eating We / You / They weren't eating Q: Was I / He / She / It eating? Were We / You / They eating? Normalmente, después de las siguientes expresiones: I wish, If only, as if, as though, would rather, would sooner, it's time…. Para expresar una acción incompleta que estaba ocurriendo en el pasado. (acción larga): Last week, we were working in a science project. Para señalar que una acción larga estaba teniendo lugar en el pasado cuando fue interrumpida por otra breve: We were watching TV, when suddenly the TV set broke down. Para indicar que 2 ó + acciones largas estaban ocurriendo simultáneamente en el pasado: While I was cooking dinner, he was laying the table. Para indicar acciones repetidas y monótonas en el pasado indicando cierta queja: The children were always screaming. Para descripciones y especificaciones: People were walking, the sun was shining, the birds…. While TENSE PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE FORM USE SIGNAL WORDS A: I / You / We / They have eaten He / She / It has eaten N: I / You / We / They haven't eaten He / She / It hasn't eaten Q: have I / You / We / They eaten? Para hablar de acciones que ocurrieron en el pasado pero llegan o tienen importancia en el presente: I have found a wallet in the street. Con el superlativo: She's the most intelligent person I have ever met. Already (AF)…ya Yet (NG/INT)….ya, aún, todavía For…durante Since…desde Just…acabo de This week/ month… Recently has He / She / It eaten? PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS A: I / You / We / They have been eating He / She / It has been eating N: I / You / We / They haven't been eating He / She / It hasn't been eating Q: have I / You / We / They been eating? has He / She / It been eating? En las expresiones It's the first/ second time: It's the first time I've eaten raw fish Tiene el mismo uso que el present perfect simple pero resaltando la duración de la actividad: I've been working in this factory since 1999. Para hablar de acciones pasadas que acaban de concluir y su resultado es evidente: Have you been frying fish? Adverbios de frecuencia: ever… Already (AF)…ya Yet (NG/INT)….ya, aún, todavía For…durante Since…desde Just…acabo de This week/ month… Recently Adverbios de frecuencia: ever… TENSE PAST PERFECT SIMPLE FORM A: He had eaten N: He hadn't eaten Q: Had he eaten? PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS A: He had been eating N: He hadn't been eating Q: Had he been eating? USE SIGNAL WORDS Para hablar de una acción pasada que ocurrió antes que otra: The school had already closed when I arrived. En oraciones condicionales de 3er tipo En oraciones temporales para enfatizar que una acción pasada estaba totalmente acabada antes de comenzar otra: He didn't go to bed until the last TV programme had finished. Con I wish / If only para lamentarnos de algo que ha ocurrido en el pasado: If only they had stayed with us (ojalá) Already (AF)…ya Just Until / Till Before As soon as After En la expresión It was the first / the second… time: It was the second time I had flown. Para hablar de una acción pasada que ocurrió antes que otra pero poniendo énfasis e la duración de la misma: She was so ill because she had been eating so many chocolates. For Since The whole day / all day TENSE FUTURE SIMPLE (WILL) FUTURE SIMPLE (GOING TO) FORM USE SIGNAL WORDS A: He will eat N: He won't eat Q: Will he eat? Expresar certeza en el futuro: We will definitely phone her tonight. Predicciones: It'll be windy tomorrow. Promesas: I'll buy you a present for your birthday. Tomar una decisión en el momento de hablar: It's hot in here. I'll open the windows. Hacer un ofrecimiento: I'll carry the suitcase if you like. Pedir algo educadamente: Will you do it for me? En condicionales de 1er tipo: If it rains, we'll stay at home. Tomorrow Next day/ week…. A: I am going to eat He / She / It is going to eat We / You / They are going to eat N: I am not going to eat He / She / It isn't going to eat We / You / They aren't going to eat Q: Am I going to eat? Is He / She / It going to eat? Are We / You / They going to eat? Cuando sugerimos algo utilizamos SHALL: Shall we go to the cinema tonight? Expresar intenciones: I'm going to eat less. Para hablar de planes futuros: They're going to build a new bridge in autumn. Para hacer predicciones de futuro a través de hechos evidentes en el presente: It's very hot today. We are going to sweat . Para hablar de hechos que van a ocurrir con seguridad en el futuro: I'm going to finish Bachillerato next year. Fechas futuras Tomorrow Next day/ week…. Fechas futuras TENSE FUTURE CONTINUOUS FORM USE SIGNAL WORDS A: He will be eating N: He won't be eating Q: Will he be eating? Para hablar de acciones que estarán en marcha en un momento determinado del futuro: At this time next web we'll be flying to New York. Tomorrow Next day/ week…. FUTURE PERFECT SIMPLE A: He will have eaten. N: He won't have eaten. Q: Will he have eaten? FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS A: He will have been eating. N: He won't have been eating. Q: Will he have been eating? Para preguntar por los planes de los demás sobre todo, cuando queremos pedir un favor: Will you be driving to the supermarket tomorrow. Acciones que estarán finalizadas en un momento determinado del futuro: We'll have flown to New York by next week. Acción que tiene lugar antes de un momento exacto del futuro poniendo énfasis en la duración de la acción: By midnight I Hill have been sleeping for 2 hours. Fechas futuras By Monday… In a week… By Monday… In a week…