Clase 7 - Facultad de Psicología
Anuncio

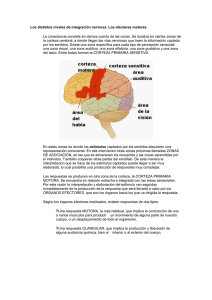
Prof. Alberto A. NEUROFISIOLOGÍA II 7ta. clase teórica FACULTAD DE PSICOLOGÍA CONTROL DEL MOVIMIENTO - INTEGRACION SENSORIO MOTORA CONTROL DEL MOVIMIENTO - INTEGRACION SENSORIO MOTORA CONTROL DEL MOVIMIENTO - INTEGRACION SENSORIO MOTORA CONTROL DEL MOVIMIENTO - INTEGRACION SENSORIO MOTORA NIVELES DE CONTROL MOTOR NIVELES DE CONTROL MOTOR NIVELES DE CONTROL MOTOR Concepto de vía final común del sistema de control motor: Las motoneuronas alfa son la vía final donde convergen las conexiones segmentarias de la médula espinal, y supra-segmentarias encefálicas. NIVELES DE CONTROL MOTOR Sistema “piramidal” o córtico-espinal, y su proyección sobre los efectores musculares somáticos. NIVELES DE CONTROL MOTOR Concepto de unidad motora: Motoneuronas alfa y fibras musculares estriadas inervadas por cada motoneurona. NIVEL ESPINAL - NEUROMUSCULAR REFLEJOS ESPINALES REFLEJO EXTENSOR REFLEJOS ESPINALES REFLEJO EXTENSOR REFLEJOS ESPINALES REFLEJO EXTENSOR REFLEJOS ESPINALES A. FIBRAS EXTRAFUSALES B. FIBRAS INTRAFUSALES HUSO NEUROMUSCULAR REFLEJO FLEXOR REFLEJOS ESPINALES REFLEJO FLEXOR REFLEJOS ESPINALES TRONCO CEREBRAL - CEREBELO HEMISFERIOS CEREBRALES – GANGLIOS BASALES NIVELES ENCEFÁLICOS CORTEZA MOTORA Representacións “somatotópica” cortical del sistema motor. CORTEZA MOTORA SISTEMA VESTIBULAR SISTEMA VESTIBULAR NIVEL TRONCO-ENCEFÁLICO Sistema “extrapiramidal” HEMISFERIOS CEREBRALES - GANGLIOS BASALES TRONCO CEREBRAL - CEREBELO CORTEZA CEREBELOSA ´TRASTORNOS MOTORES