Garantía y Seguridad en Sistemas y Redes. Tema 6. Denial-of
Anuncio

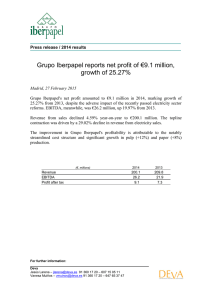
Garantía y Seguridad en Sistemas y Redes Tema 6. Denial-­‐of-­‐Service Esteban Stafford Departamento de Ingeniería Informá2ca y Electrónica Este tema se publica bajo Licencia: Crea2ve Commons BY-­‐NC-­‐SA 4.0 Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 6. Denial-of-Service G678: Garantía y Seguridad en Sistemas y Redes Esteban Stafford Santander, October 26, 2015 Contents Denial-of-Service Attacks Flooding Attacks Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks Reflector and Amplifier Attacks Application-Layer Attacks Defenses Against Denial-of-Service Attacks Responding to a Denial-of-Service Attack Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 1 Denial-of-Service Attacks Criminals might find benefit in an entity not providing its service. This can be done by infiltrating the machine with malware. But also from outside with Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. They exploit flaws in the communication/services layers. Request flood Incomplete/delayed protocol Application overload Trigger bugs (poison packet) Can be Single source or Distributed DoS (DDos) Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 2 Classic DoS Attacks Ping flood attack. Needs has higher bandwidth than victim. Attacker has to deal with backscatter traffic and is not anonymous. Source address spoofing. Ping packets have spoofed source addresses. Active machines with spoofed addresses respond with more ICMP. Unilateral source tracing impossible. Egress filtering recommended but not widely done. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC PC ISP WWW DNS WWW SMTP PC PC PC Internet ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores ISP 3 Denial-of-Service Attacks Criminals might find benefit in an entity not providing its service. This can be done by infiltrating the machine with malware. But also from outside with Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. They exploit flaws in the communication/services layers. Request flood Incomplete/delayed protocol Application overload Trigger bugs (poison packet) Can be Single source or Distributed DoS (DDos) Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 2 Classic DoS Attacks Ping flood attack. Needs has higher bandwidth than victim. Attacker has to deal with backscatter traffic and is not anonymous. Source address spoofing. Ping packets have spoofed source addresses. Active machines with spoofed addresses respond with more ICMP. Unilateral source tracing impossible. Egress filtering recommended but not widely done. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC PC ISP WWW DNS WWW SMTP PC PC PC Internet ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores ISP 3 SYN Spoofing Attack causes recipient to overflow TCP connection request table. Spoofed addresses are usually unused: Timeout and retransmission. Attacker does not need high bandwidth. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS K /APC NM SYIC ISP PC ISP WWW SMTP PC Internet PC PC SYN ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 4 Flooding Attacks ICMP Flooding ICMP Ping is sometimes disabled to prevent attacks. But ICMP unreachable or time exceeded can not. These can be larger, thus more effective for attack. UDP Flooding Any port can be used. If listening it will emit response UDP. If closed system will emit ICMP unreachable. TCP Flooding Generate congestion, not overload system (SYN). Uses data packets, with large payload. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 5 SYN Spoofing Attack causes recipient to overflow TCP connection request table. Spoofed addresses are usually unused: Timeout and retransmission. Attacker does not need high bandwidth. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS K /APC NM SYIC ISP PC ISP WWW SMTP PC Internet PC PC SYN ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 4 Flooding Attacks ICMP Flooding ICMP Ping is sometimes disabled to prevent attacks. But ICMP unreachable or time exceeded can not. These can be larger, thus more effective for attack. UDP Flooding Any port can be used. If listening it will emit response UDP. If closed system will emit ICMP unreachable. TCP Flooding Generate congestion, not overload system (SYN). Uses data packets, with large payload. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 5 Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks Botnets are used to coordinate large scale attacks. No need for spoofing, thus unaffected by egress filtering. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC PC ISP WWW DNS WWW SMTP PC Flood PC PC Attack Internet ISP ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 6 Reflection Attacks Send source spoofed traffic to intermediary systems. Service on intermediary sends larger responses to victim. ECHO, CHARGEN, DNS, SNMP, BGP, SYN. DNS: A 60-byte query can turn to a 512-byte or more response. Attacker regulates the use of each intermediary systems. Can even create loops between intermediary and victim systems. PC PC DNS PC DNS ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS DNS ISP PC ISP WWW SMTP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores PC Internet PC PC DNS ISP 7 Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks Botnets are used to coordinate large scale attacks. No need for spoofing, thus unaffected by egress filtering. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC PC ISP WWW DNS WWW SMTP PC Flood PC PC Attack Internet ISP ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 6 Reflection Attacks Send source spoofed traffic to intermediary systems. Service on intermediary sends larger responses to victim. ECHO, CHARGEN, DNS, SNMP, BGP, SYN. DNS: A 60-byte query can turn to a 512-byte or more response. Attacker regulates the use of each intermediary systems. Can even create loops between intermediary and victim systems. PC PC DNS PC DNS ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS DNS ISP PC ISP WWW SMTP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores PC Internet PC PC DNS ISP 7 Amplification Attacks Send source spoofed traffic to broadcast addresses. Attackers need to find intermediate networks that: Allow external broadcast packets. Have ICMP/UDP services open. Are well connected. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS ICMP PC ISP WWW SMTP PC Internet PC PC ICMP ISP ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 8 Application layer attacks Application level flood Target expensive server procedures or limited resources. Request to download large file. Recursively download site. Incomplete requests (Slowloris). Application level attack Hard to spot. Legitimate application traffic: HTTP, XML... Target a bug, insecure feature. Low traffic volume. Single request DoS. No source IP spoofing. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 9 Amplification Attacks Send source spoofed traffic to broadcast addresses. Attackers need to find intermediate networks that: Allow external broadcast packets. Have ICMP/UDP services open. Are well connected. PC PC PC PC PC ISP PC PC PC WWW DNS ICMP PC ISP WWW SMTP PC Internet PC PC ICMP ISP ISP Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 8 Application layer attacks Application level flood Target expensive server procedures or limited resources. Request to download large file. Recursively download site. Incomplete requests (Slowloris). Application level attack Hard to spot. Legitimate application traffic: HTTP, XML... Target a bug, insecure feature. Low traffic volume. Single request DoS. No source IP spoofing. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 9 Preventing DoS Attacks What should be done? Outlaw source spoofing: RFC-2827. Throttle diagnostic ICMP/UDP. Ignore external broadcast packets. Protection against Bots. What can we do? Modified TCP can work when table is full. Drop incomplete handshakes from table. Throttle lengthy queries when congested. Harden servers (Patching) Use Capcha on web servers. Monitoring and replication. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 10 DOS attack response Seek cooperation from ISP: Contact must be possible without network. Plan and establish protocols and responsibilities. Within an organization: Implement solidarity measures. Automated network monitoring and intrusion detection. Know your traffic pattern. Notice the trouble before the users complain. During attack: Analyse traffic and identify type of attack Implement specific filters at ISP. Bug attack must be identified and corrected in the future. Switch to alternate backup servers. Provide service on different address. Trace origin of attack? Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 11 Preventing DoS Attacks What should be done? Outlaw source spoofing: RFC-2827. Throttle diagnostic ICMP/UDP. Ignore external broadcast packets. Protection against Bots. What can we do? Modified TCP can work when table is full. Drop incomplete handshakes from table. Throttle lengthy queries when congested. Harden servers (Patching) Use Capcha on web servers. Monitoring and replication. Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 10 DOS attack response Seek cooperation from ISP: Contact must be possible without network. Plan and establish protocols and responsibilities. Within an organization: Implement solidarity measures. Automated network monitoring and intrusion detection. Know your traffic pattern. Notice the trouble before the users complain. During attack: Analyse traffic and identify type of attack Implement specific filters at ISP. Bug attack must be identified and corrected in the future. Switch to alternate backup servers. Provide service on different address. Trace origin of attack? Grupo de Ingeniería de Computadores 11