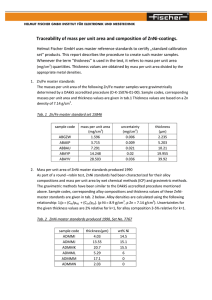
TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 Rev. : R0 Page : 1 CONTENTS Page 0.0 Cover Sheet 1 1.0 General 2 2.0 Thickness Calculation as per ASME B 31.3 2–3 3.0 General Notes 3–6 4.0 Steps to determine Pipe Wall Thickness 6 Applicable Revision: Prepared: Checked: Approved: Date: First Edition: R0 Prepared: DNL Date: Date: Checked: AKB Approved: RUD Date: File Name: C-6 Date: Server: Date: VKO: KUMUS 209 PUNE: KUMUS 207 Directory: PUNE: Refer \ Pi \ Training Manual VKO: Refer \ Training Manual TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited 1.0 DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 Rev. : R0 Page : 2 GENERAL: The following method is issued for metallic pipes to calculate the wall thickness. The following parameter are to be known: • • • • • 2.0 Internal Design pressure. Design temperature. Pipe material specification. Pipe size (O.D. or I.D.) Applicable code (ASME B 31.3/ IBR/ Other) THICKNESS CALCULATION AS PER ASME B 31.3: The required thickness of straight sections of pipe as per ASME B 31.3 is given by tm = t + c where, tm = t = c = Minimum required thickness including mechanical, corrosion and erosion allowances Pressure thickness in order to sustain internal design pressure P Sum of mechanical allowances (Thread or groove depth) plus corrosion and erosion allowances. If ‘T’ is the Nominal pipe wall thickness then, T ≥ tm + Manufacturer’s negative tolerance. As per code, T = PD 2(SE+PY) (Cl. 304.1.2) .......... (Eq.1) where, P D = = Internal design gauge pressure, psig Outside diameter of pipe, inch S = Allowable stress value for the pipe material, psi E = Quality factor (Longitudinal weld joint efficiency for pipe) Y = Coefficient as per Table - I, valid for t < D/6 and for materials shown. The value of Y (dimensionless factor varying with temperature) may be interpolated for intermediate temperatures. d = Inside diameter of pipe. DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited Rev. : R0 Page : 3 TABLE - 1 Value of coefficient Y for t < D/6 TEMPERATURE °F MATERIALS 900 & lower 950 1000 1050 1100 1150 Ferritic steels 0.4 0.5 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 Austenitic steels 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.5 0.7 Other ductile Materials 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 Cast Iron 0.0 - - - - - Following equation may also be used as per code in lieu of (Eq.1) for calculating pressure thickness ‘t’ to provide pressure integrity t = PD 2 SE = D 2 (Cl. 304.1.2) OR SE – P t (Lame’s Equation) 1SE + P OR t = 3.0 P(d+2c) 2 [(SE-P(1-Y)] (where thickness is calculated based on inside diameter) GENERAL NOTES : • Limitation on diameter to thickness Ratio: Formulae as given are applicable for t ≤ D/6, which in fact is the usual case. However, for t ≥ D/6 or for P / SE > 0.385, calculation of pressure design thickness for metallic straight pipe requires special consideration of factors such as theory of failure, effect of fatigue and thermal stress. TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited • DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 Rev. : R0 Page : 4 ‘S’ Allowable Stress Values: Allowable stress values for different ASTM pipe materials at various temperature are listed under Table A1 ASME B 31.3 (Appendix A) e.g. Allowable stress for: A53Gr.B at 200 °F A53Gr.B at 500 °F A106Gr.B at 600 °F • = = = 20,000 psi 18,900 psi 17,300 psi ‘E’ weld joint efficiency (Quality factor): Weld joint efficiency (Quality factors) for different ASTM pipe material specifications are listed under Table A1B ASME B 31.3 e.g. Quality factors for: A53 A53 A312 A312 A312 ERW Seamless Seamless pipe EFW double butt seam EFW single butt seam = = = = = 0.85 1.00 1.00 0.85 0.80 (For all seamless pipes ‘E’ value is 1.00) • ‘C’ Sum of Mechanical, corrosion and erosion allowances. Following are the usual allowances to be accounted. 1. Threads: This is applicable if the pipes are threaded for making joints as is the case with galvanized piping. The nominal thread depth has to be accounted under such situation. Refer table 314.2.1 “ Minimum Thickness of male threaded components” 2. Corrosion/erosion allowances: These allowance depend upon the type of fluid handled and are indicated by the Process licenser. These allowances vary from 1mm to 6mm, and in some cases even more. As a good engineering practice, it is advisable to consider minimum 1mm corrosion allowance for all other services where Process licenser has not specifically indicated any requirement. This also takes care of external corrosion if any. 3. Bending Allowance: If the pipes are to be used for making bends, then it may be necessary to increase the thickness ‘tm’ by a factor called bend thinning allowance. During bending the outer fibres get stretched and in order to maintain minimum wall thickness ‘tm’ at all point in a completed bend, one has to add allowance for thinning. TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 Rev. : R0 Page : 5 Flattening of a bend, the difference between maximum and minimum diameters at any cross section, shall not exceed 8% of nominal outside diameter for internal pressure. Following Bend thinning factors are recommended (refer Table th bends” – Piping Handbook 7 Edition by M. L. Nayyor). • C-4.5 “ Pipe Thickness for Radius of Pipe Bend Min. THK. recommended prior to bending 6D (nom. Dia) 5D 4D 3D 1.06 tm 1.08 tm 1.14 tm 1.25 tm Manufacturer’s Negative Tolerance: While specifying the pipe thickness for ordering, it is necessary to account for Manufacturer’s negative tolerance since we require minimum thickness ‘tm’ at all points after the pipes are manufactured. The tolerances depend upon the method of manufacturing pipes and these are given in 1 respective ASTM PIPE material specs. The negative tolerance on specified thickness is 12 /2 % for seamless pipes. Thus for seamless pipes if ‘tm’ is the minimum thickness required then the nominal thickness T should be equal or greater than tm / 0.875. Similarly, for electric fusion welded steel pipes as per ASTM A672 the manufacturer’s negative tolerance is 0.01 inch (0.3mm). Hence for pipes conforming to A 672 nominal thickness T should be equal or greater than (tm + 0.01 inch) • Schedule-Number Selection After calculating ‘T’ the nominal wall thickness which is required for design conditions, one can order the pipes provided the quantity is large enough for special rolling. Otherwise, as per ANSI B36.10 for Carbon steel and ANSI B36.19 for stainless steel, Pipes are readily available in various thickness specified by their schedule numbers It is recommended to make use of these standard pipe thickness which are available. Schedule number selected should have nominal thickness equal or greater than the calculated nominal thickness required for design condition. • Structural Rigidity: Some times we may arrive at a very low thickness which is adequate to sustain pressure temperature conditions given but such pipes if used will not have enough structural rigidity and may get deformed even during handling. These pipes if used would require careful handling and closer supports. TRAINING MANUAL- PIPING PIPE DESIGN Uhde India Limited DOC No. : 29040-PI-UFR-0006 Rev. : R0 Page : 6 Unless the material is very costly, we usually decide minimum thickness for various pipe sizes at the initial stage of the project on structural rigidity criteria. Following minimum thickness excluding corrosion allowance are recommended. Pipe Size Minimum Thickness 1/2” to 4” 5” to 12” 14” to 24” 0.06” 0.09” 0.12” For Carbon Steel piping in refinery and petrochemical plants especially for process lines, following minimum schedules are usually adopted. Pipe Size Schedule No. 1/2” to 2” 2 1/2” to 10” 12” to 24” Sch. 80 Sch. 40 STD Wall For utilities like water, air and general purpose services one can adopt lower minimum schedules indicated below: Pipe Size Schedule No. 1/2” to 1 1/2” Sch.40 Sch.80 (If 5D bends are to be made at site) Sch.40 Sch.20 2” to 6” 8” to 24” 4. STEPS TO DETERMINE PIPE WALL THICKNESS: • Using the minimum inside diameter determined from the fluid flow evaluation, select the next larger standard nominal size or outside diameter (OD) pipe from the listings provided in ASME B 36.10M for Standard Wrought Steel Pipe or B 36.19M for Stainless Steel Pipe. • Based upon the Fluid and Service select a suitable piping material and if necessary determine the corrosion, erosion, joining or mechanical strength allowances. • Using equations provided in the design Code, calculate the required minimum wall thickness to provide for pressure integrity and allowances. • Refer to ASME B 36.10M or ASME B 36.19M to select an appropriate nominal wall thickness or Schedule. • Confirm that the standard manufacturing tolerance will not reduce the minimum calculated wall thickness or selected nominal wall thickness in the steps above. • Confirm that the inside diameter of the pipe based on the selected nominal wall thickness is compatible with the required inside diameter based on the fluid flow evaluation.