![كيمياء[1]](http://s2.studylib.es/store/data/009423600_1-a916a3fbb6869b8a5dee75dcad5184cd-768x994.png)
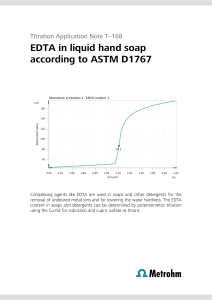
First: The best experiment to determine the concentration of an unknown acid solution is to titrate an acid with a base. This technique involves gradually adding a solution of known concentration (titrate) to the unknown solution until the reaction between the acid and base is complete. By measuring the volume of acidic solution required to reach the endpoint, we can determine the concentration of the unknown acidic solution. Second: The following is a brief description of the procedures for the acid-base titration experiment: 1. Prepare the necessary materials, including the unknown acidic solution, a standard (titrated) basic solution, an indicator (such as phenolphthalein or bromothymol blue), a burette, a beaker, and appropriate safety equipment. 2. Calibrate the buret and fill it with the basic solution. 3. Accurately measure a known volume (e.g., 25 mL) of the unknown acidic solution using a pipette and transfer it to the vial. 4. Add a few drops of the indicator to the vial. The indicator will change color at or near the end point of the titration. 5. Slowly add the basic solution from the buret to the beaker while stirring the beaker continuously. The basic solution reacts with the acid in the unknown solution. 6. We notice the color change in the beaker. When the color change corresponding to the end point is reached, we stop adding the base solution. 7. Record the volume of base solution (titanizer) used to reach the end point. Third: Discussing and calculating the experimental data. In the experiment we have the following data: 1. Total volume of the unknown acidic solution: 2 litres To determine the concentration of an unknown acidic solution, we perform an acid-base titration using a known concentration of the basic solution (titrant) and measure the volume of basic solution required to reach the endpoint. Suppose that during the titration, it took (0.05 V_base) a liter of base solution (with concentration. 0.1 mol/L C_base) to reach the end point. To calculate the concentration of the unknown acidic solution (C_acid), we can use the following formula: C_acid = (C_base * V_base) / V_acid In this formula: - C_base is the concentration of the basic solution (in mol/L) - V_base is the volume of base solution used (in litres) - V_acid is the volume of the unknown acidic solution (in litres) C_acid = (0.1 mol/L * 0.05 L) / 2 L C_acid = 0.00125 mol/L Therefore, the concentration of the unknown acidic solution would be 0.00125 mol/L. Fourth: Accurate determination of solution concentration is crucial in the field of chemical engineering for several reasons: 1. Process Control: In chemical plants and manufacturing processes, accurate knowledge of solution concentrations is essential to maintaining process control and ensuring consistent product quality. Solution concentration can greatly affect reaction rates, productivity, and overall process efficiency. 2. Safety and Environmental Considerations: Some chemicals may pose safety risks or have harmful effects on the environment at certain concentrations. Accurate determination of concentration allows engineers to implement appropriate safety measures, handle and store chemicals safely, and ensure compliance with regulations. 3. Optimization and troubleshooting: Determining the solution focus helps in process optimization and troubleshooting. By accurately measuring and controlling concentrations, engineers can identify and correct problems with reaction kinetics, product quality, and equipment performance. 4. Formulation and Product Development: In industries involving product formulation, such as pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, and cosmetics, accurate determination of concentration is critical to developing formulations with desired properties, taste, efficacy, and stability.