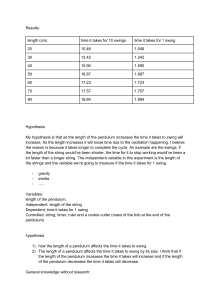
Scientific Method Objectives Describe the steps of the scientific method. Differentiate between the independent and dependent variables, and define th control variables that need to be considered in a given experiment. Use the scientific method to investigate an ecological problem related to your campus. Scientific method Scientific information is acquired by a process know as the scientific method. The scientific method involves a series of steps: Observation Problem Hypothesis Experiment Data Conclusions Observation Observation involves gathering information as well as studying previous data. Scientists use all of their senses to make observations (sight, smell, taste, touch, sound). They also use instruments like the microscope and take advantage of the past work of other scientists. Problem (asking the question) Making observations leads to questions. Scientists only consider questions that can be answered by experimentation. Moral and religious beliefs are not testable scientifically. The problem should be a question asking how one variable affects another. Hypothesis The hypothesis is a testable statement that tells how you believe one variable will affect another, based on input from various sources. The hypothesis is usually expressed as a prediction with an if…then format. State your hypothesis in a way that can be easily measured and that will help answer your original question. Variables A variable is any factor, trait or condition that can exist in different amounts or types. An experiment usually has three types of variables: the experimental or independent variable the response or dependent variable Experiments also have controlled variables. Controlled variables can affect the dependent variable and therefore must remain constant. Most experiments have more that one controlled variable. The Independent and Dependent Variables Independent variable Dependent variable Is the variable being tested. Is the variable that changes in response to the independent variable. It is the variable that can be manipulated by the scientist. It is also called the experimental variable. It is also called the response variable. Experiment Testing your hypothesis involves either conducting an experiment or making further observations. The experiment should have a control group or control which goes through all the steps of an experiment but lacks the variable being tested. Data The results of an experiment are referred to as the data. Data should be observable and objective rather that subjective or based on opinion. Mathematical data are often displayed in the form of a graph or table. The larger the sample size, the larger the effect, the less likely that the result is due to chance. Statistical tests are used to evaluate how likely the results are due to chance. Conclusion Scientists analyze the data in order to reach a conclusion. The conclusion states whether the results of the experiment support or reject the hypothesis. Experiments and observations must be repeatable (get the same results). An example of using part of the Scientific Method Question (problem) How much water flows through a faucet at different openings? Independent variable Water facet opening (closed, half open, fully open) (what I change) Dependent variable (what I observe) Amount of water flowing measured in liters per min. Controlled variables (what I keep the same) The faucet Water pressure Hypothesis If I open the faucet, then it will increase the flow of water. (If __(I do this)__, then ___(this)__will happen. Scientific Method Activity: Problem 1 Question (problem) Independent variable (what I change) Dependent variable (what I observe) Controlled variables (what I keep the same) Hypothesis (If __(I do this)__, then ___(this)__will happen. Does heating a cup of water allow it to dissolve more sugar? Scientific Theory The ultimate goal of science is to understand the natural world in terms of scientific theories. Scientific theories are concepts that join together related and well-supported hypothesis. A theory is supported by a broad range of observations, experiments and data. Basic Theories of Biology Theory concept Cell All organisms are composed of cells, and new cells only come from preexisting cells. Homeostasis The internal environment of an organism stays relatively constant, within a range that is protective of life. Gene Organisms contain coded information that dictates their form, function, and behavior. Ecosystem Organisms are members of populations, which interact with each other and with the physical environment within a particular locale. Evolution A change in the frequency of traits that affect reproductive success in a population or species across generations. Visual aid VIDEO: Animated Science. Episode 1. The Scientific Method https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tUP8rFWzVt4