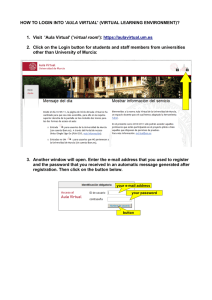
Advice Virtual learning environments (VLE) Page 16 of 19 - Technology and tools for online learning About this guide Published: 20 January 2016 Updated: 12 February 2016 Questions to consider 1 Can the institutional VLE be as exible as the online course or class curriculum needs it to be? 2 How can you integrate the VLE with external networking technologies? Virtual learning environments (VLE's) are now well established in educational institutions as a means to structure, manage and deliver learning activities and content. They are recognised as having strengths in student tracking and managing online assessments. These integrated tools may be one product (eg, Blackboard [http://uki.blackboard.com/sites/international/globalmaster/platforms/blackboard-learn.html] , Moodle [https://moodle.org/] ) or an integrated set of individual, perhaps open-source, tools with additional functions such as eportfolios. Bene ts These centrally managed systems support both campus-based and online courses and have the advantage of: Technical support Potential to present a consistent experience for students and staff Ability to deliver courses to a large number of students. They include communication mechanisms to support student dialogue with staff and peers within courses through email, and on bulletin board discussions. They can also offer shared workspaces to support collaboration. Curriculum design One advantage of using VLEs is that institutions can train all staff to make the most of their particular system. However, VLEs have been criticised for not inspiring innovative curriculum design, or offering exible ways for learners to engage with content. Staff can be tempted to simply upload all their existing content, rather than consider how they could use technology to change the design of the curriculum. Inclusivity In addition to delivering content in a range of formats, students can also submit coursework using VLEs, incorporating assessment and feedback through multiple choice questionnaires. But institutional ownership and control of these platforms can make it di cult to include participants from outside the institution, and they may not link well with social networking or other external technologies and services. Staff may not easily be able to share their practice outside the institution if it requires authentication, so VLEs can hamper open practice making publicly funded content available. Some content creation tools (for example Xerte toolkits [http://www.xerte.org.uk] ) get round this problem by sitting outside the VLE and including inbuilt export feeds and public/private sharing options. Co-created content VLEs may also limit student co-creation of content and may discourage students from taking control of their own learning. For example, students may not be allowed to create their own discussion boards. It’s likely that students and staff will work around the VLE when it fails to be exible enough for their needs, resulting in content being generated and managed outside the system. The University of Lincoln used open source content creation tools to overcome this problem by developing student-centred approaches to learning. Personal learning environments The idea of ‘personal learning environments’ (PLE) has been around since the early VLE systems (the rst recorded use of the term was at the Cetis [http://cetis.org.uk/] conference in 2004). The concept acknowledges that learners need to create their own learning environment, and allows them to control this. This idea is particularly relevant for online learning where students may choose which technologies and services are most appropriate to them; this may, of course, include an institutional VLE. Social networking software, which allows students to take control of their learning experience, offers ways to truly personalise their learning experience. Barriers What you can do Lobby to use advanced features Institutional guidelines on how to use VLEs may restrict innovative curriculum development. Try to use VLEs and external technologies in combination. External participants, such as open students or professional experts, may not be able to access Try to get external log-ins in bulk, rather than for the VLE. individuals.