GRAMMAR TENSES IN ENGLISH
Anuncio
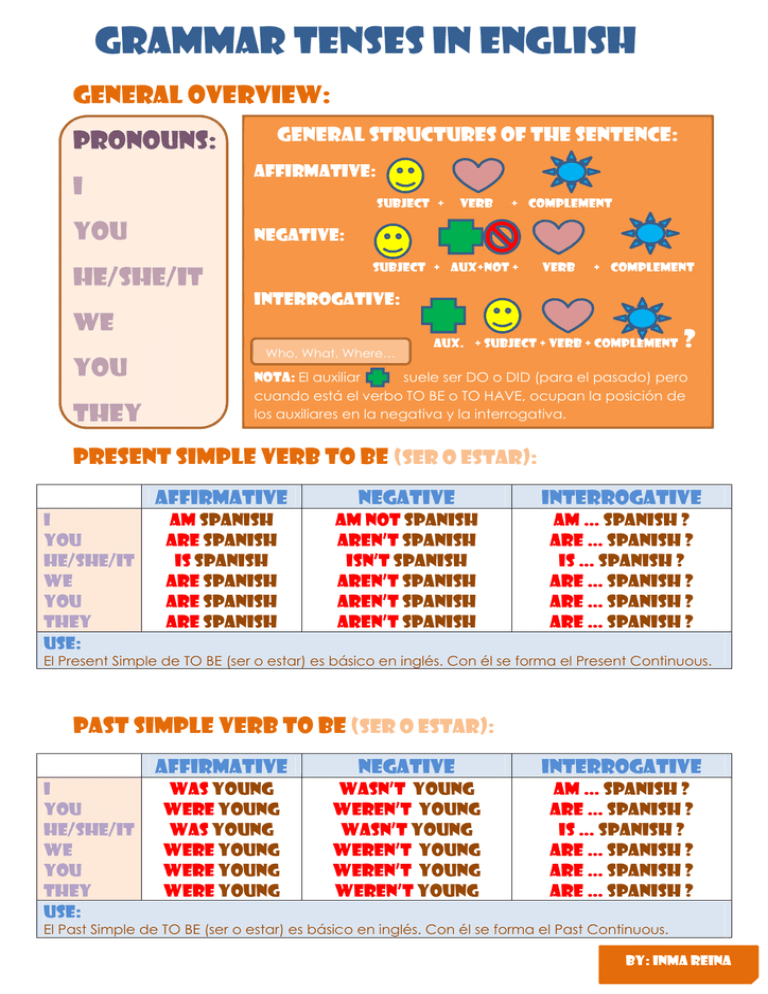
GRAMMAR TENSES IN ENGLISH GENERAL OVERVIEW: GENERAL STRUCTURES OF THE SENTENCE: PRONOUNS: AFFIRMATIVE: I SUBJECT + YOU VERB + COMPLEMENT NEGATIVE: SUBJECT + AUX+NOT + HE/SHE/IT VERB + COMPLEMENT INTERROGATIVE: WE YOU THEY Who, What, Where… AUX. + SUBJECT + VERB + COMPLEMENT ? NOTA: El auxiliar suele ser DO o DID (para el pasado) pero cuando está el verbo TO BE o TO HAVE, ocupan la posición de los auxiliares en la negativa y la interrogativa. Present simple verb to be (ser o estar): I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY USE: AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE Am spanish Are spanish is spanish Are spanish Are spanish Are spanish Am not spanish Aren’t spanish Isn’t spanish Aren’t spanish Aren’t spanish Aren’t spanish Am … Spanish ? Are … spanish ? is … spanish ? Are … spanish ? Are … spanish ? Are … Spanish ? El Present Simple de TO BE (ser o estar) es básico en inglés. Con él se forma el Present Continuous. Past simple verb to be (ser o estar): I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY USE: AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE was young were young was young were young were young were young Wasn’t young Weren’t young Wasn’t young Weren’t young weren’t young weren’t young Am … Spanish ? Are … spanish ? is … spanish ? Are … spanish ? Are … spanish ? Are … Spanish ? El Past Simple de TO BE (ser o estar) es básico en inglés. Con él se forma el Past Continuous. BY: INMA REINA Present simple: I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE READ A BOOK READ A BOOK READs A BOOK READ A BOOK READ A BOOK READ A BOOK DON’T READ A BOOK DON’T READ A BOOK DO… READ A BOOK? DO… READ A BOOK? DOESN’T READ A BOOK DOES… READ A BOOK? DON’T READ A BOOK DON’T READ A BOOK DON’T READ A BOOK DO… READ A BOOK? DO… READ A BOOK? DO… READ A BOOK? USE: El Present Simple se utiliza para hablar de las cosas que hacemos habitualmente. TIME EXPRESSIONS: Frequency adverbs other expressions (antes del verbo) (al final o al principio –seguido por coma-) Always usually Often Sometimes Rarely Never on Mondays/Tuesdays/Fridays… every day/week/month/year/summer once a week/ twice a week Past simple: I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE Helped my mum Helped my mum Helped my mum Helped my mum Helped my mum Helped my mum didN’T help my mum didN’T help my mum didN’T help my mum didN’T help my mum didN’T help my mum didN’T help my mum INTERROGATIVE Did… help my mum? Did… help my mum Did… help my mum Did… help my mum Did… help my mum Did… help my mum USE: El Present Simple se utiliza para hablar de las cosas que hicimos es el pasado. TIME EXPRESSIONS: (al final o al principio, seguido de coma) Yesterday Last week/month/year/course… A week/month/year … ago When… BY: INMA REINA Present continuous: I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE Am helping my mum Are helping my mum is helping my mum Are helping my mum Are helping my mum Are helping my mum Am not helping my mum Aren’t helping my mum Isn’t helping my mum Aren’t helping my mum Aren’t helping my mum Aren’t helping my mum Am … helping my mum? Are … helping my mum? is … helping my mum? Are … helping my mum? Are … helping my mum? Are …helping my mum? USE: El Present Continuous se utiliza para hablar de lo que está pasando cuando se habla. También se utiliza para hablar de los planes que tienes a corto plazo (p.ej. El fin de semana) TIME EXPRESSIONS: (al final o al principio, seguido de coma) now right now at the moment (planes) tonight today this Saturday… Past continuous: AFFIRMATIVE I YOU HE/SHE/IT WE YOU THEY was helping my mum were helping my mum was helping my mum were helping my mum were helping my mum were helping my mum NEGATIVE Wasn’t helping my mum Weren’t helping my mum Wasn’t helping my mum Weren’t helping my mum weren’t helping my mum Weren’t helping my mum INTERROGATIVE was … helping my mum? were … helping my mum? was … helping my mum? were … helping my mum? were … helping my mum? were …helping my mum? USE: El Past Continuous se utiliza para hablar de lo que estaba ocurriendo en un momento concreto en el pasado. Se suele utilizar combinado con el Past Simple, para expresar lo que ocurría “de fondo”: I was listening to music when a bomb exploded. El hecho de que “yo estaba escuchando música” ocurría cuando la “bomba explotó”. TIME EXPRESSIONS: (al final o al principio, seguido de coma) While… At 9.00 o clock (a horas concretas) BY: INMA REINA