Funciones exponencial y logaritmo.
Anuncio

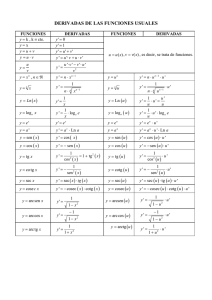
Derivada de FUNCIONES LOGARÍTMICAS F. logaritmo Neperiano f x=ln u ; F. logaritmo base a f x= log a u= lnu ln a f ' x= u' · ; 1 u' = ------ f x=ln x u u f ' x = ; f ' x = u' ln x ----- f x= log a x= u· lna ln a ; 1 x f ' x = 1 x · ln a EJEMPLOS a) f(x)= ln (2x+1) f ' ( x)= b) f(x) =ln ( sen x + cos x) 4 2 2x+1 f '(x)= c) f(x)= log3 (3x5 –2x+3) cos x−sen x sen x+cos x 15 x −2 (3x −2x+3 )· ln 3 y'= d) f(x) =log (1+arctg x); y'= 5 1 (1+x2 )· (1+arctg x) · ln 10 EJERCICIOS 1. y= ln ( x3 – 4x2 + 3) 4. y= log3 (ex) 7. y= ln (x2 + 1) – ln ( x2 – 1) 2. y= ln ( tg x) 5. y= log5 (2·arc sen x) 3. y= ln (3x – 2 sen x) 6. y= log2 (x2 – 3x) – 3· ln (1 – 2x2) 8. y= log 3 x4 y=log ( sen √ x) 9. 2 10. y= ln ( x+ √ x +1) NOTA: En ocasiones conviene aplicar las propiedades de logaritmos que ya hemos estudiado. • ln a · b=ln aln b • ln a = ln a−ln b b • p ln a = p · ln a EJEMPLOS a) f(x)= ln 3x+ 2 2 = ln (3x+ 2)−ln ( x − x) x 2−2x 3 b) f(x)= ln ( sen3x)= 3·ln (sen x) 4 3 3 1 2 4 c) f(x) = ln ( √ x · √ x)= · ln x+ · ln x= 2 2x−2 −3x −4x+4 f '(x)= 3x+2 − 2 = ( x − x) (3x+2 )( x2 − x) f '(x)= 11 · ln x 6 f '(x) = 3 cos x =3· cotg x sen x 11 6x EJERCICIOS 11. f(x)= ln 12.f(x)= ln ( 3x +1 2x −3 ) 5 √ x9 5 13. f(x) = log [(2x+1) · tg x ] 14. f(x) = log 2 √ ( ) ex e +1 16. f(x)= 2·ln (x·arcsen x) x 15. f(x)= ln 1−cos x 1+cos x 17. f(x)= log 3 2 4 √ (3x²+1 )3 18. f(x) = ln (3·sen4 x) Soluciones 2 1. y'= 2x 3 x −8 x x 3−4 x 2+3 2x −4x 7. y= x 2+1 − x 2−1 = x 4 −1 2 −4 x · ln 10 tg x+1 =tg x+cotg x 2. y'= tg x 8. y= 3−2cos x 3x−2 sen x 3. y'= 9. y'= ln 10 · 2 √ x ( 1 2 1+tg 2 x + ln 10 2x+1 tg x 13.y'= 1 1 14.y'= ln 2 · e x +1 cotg √ x 1 15.y'= sen x 1 √ x 2 +1 4. y'= 1 ln 3 10.y'= 5. y'= 2 2 ln 5· arc sen x· √ 1− x 11. y'= (3x+1)(2x −3) 17.y'= ln 3 · 2 6 x +2 12.y'= −9 18.y'=4·cotg x 2x−3 2 12x 2 16.y'= x + √ 1− x2 · arcsen x −11 6. y'= ln 2 · ( x2 −3x) + 1−2 x 2 ) 1 5x −9x Derivada de FUNCIONES EXPONENCIALES F. exponencial base e f (x )=e u ; f ' ( x)= u ' · e F. exponencial base a f (x )=a u ; f ' ( x)= u ' · a u · ln a ----- f (x )=a x Nota: las funciones tipo y= u f (x )=e ------ x ; f ' (x )= e x f ' (x )= a x · ln a ; 1 , conviene derivarlas haciendo y= a −u au EJEMPLOS a) f(x)= e 2x+1 2 f '(x)= 2·e 2x+1 2+ x 2+ x 4 · ln 3 2− x ·3 f '(x)= (2−x )2 2− x b) f(x)= 3 2 c) f(x) = e 3x +cos x d) f(x)= f '(x)= (6x−sen x )· e3x +cos x √5x+3 () 2 5 f '(x)= ln () EJERCICIOS 1. y= 10√ x+1 2. y= e e x +e−x 2 3. y= 1 2 3− x 4. y= 3 5. y= 3x+1 2 sen x 6. y= e 1. 2. 2x y'= e 3−x 2 2 (3−x ) 2x 2 3−x 9. y= 3. y'= 4. y'= 2 ln 3 · sen x · cos x ·3 sen 6. 6+2x 2 x −3 y'= − 2 ·e ( x −3)2 7. x y'= −12 5 ·e 8. y'= − sen √ x · a cos √ x · ln a 9. y'= − 1+ 2 1 5. y'= e x −e−x 2 −11 · ln2 ·2 ( 5x−2)2 3x+1 5x−2 2 x 3 4 x 2√x ( ) x · 5−( x+ √ x +1) √ x 2+1 2 4 a cos√ x 8. 2x 2 ex 1 Soluciones ln 10 10 √ x+1 y'= 2 √ x+1 3 7. y= 2 5x −2 √ 5x+3 () 2 5 2 · 5 2 · √5x+3 5 1 5 x+√ x +1 2