IFAC Normal Template
Anuncio

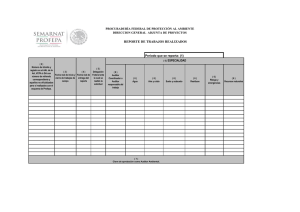
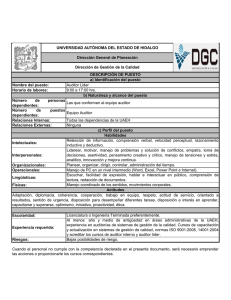
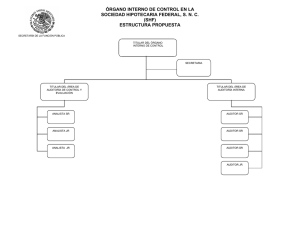
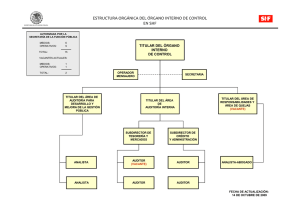
Note to Users of the 2009 Edition of the Handbook of International Standards on Auditing and Quality Control: ISREs issued by the IAASB as of January 1, 2008 are contained in Part I of the 2008 edition of the IFAC Handbook of International Standards on Auditing, Assurance, and Ethics Pronouncements. Part I of the 2008 edition of the IFAC Handbook will remain in effect during 2009. Conforming amendments to ISRE 2410, “Review of Interim Financial Information Performed by the Independent Auditor of the Entity” as a result of ISA 200, “Overall Objectives of the Independent Auditor and the Conduct of an Audit in Accordance with International Standards on Auditing” 15. The procedures performed by the auditor to update the understanding of the entity and its environment, including its internal control, ordinarily include the following: … Considering significant financial accounting and reporting matters that may be of continuing significance such as material weaknesses significant deficiencies in internal control. … 18. This understanding enables the auditor to focus the inquiries made, and the analytical and other review procedures applied in performing a review of interim financial information in accordance with this ISRE. As part of obtaining this understanding, the auditor ordinarily makes inquiries of the predecessor auditor and, where practicable, reviews the predecessor auditor’s documentation for the preceding annual audit, and for any prior interim periods in the current year that have been reviewed by the predecessor auditor. In doing so, the auditor considers the nature of any corrected misstatements, and any uncorrected misstatements aggregated by the predecessor auditor, any significant risks, including the risk of management override of controls, and significant accounting and any reporting matters that may be of continuing significance, such as material weaknesses significant deficiencies in internal control. Spanish Translation 15. Los procedimientos que lleva a cabo el auditor para actualizar el conocimiento de la entidad y su entorno, incluyendo su control interno, generalmente incluyen lo siguiente: … a. Considerar asuntos importantes de contabilidad y auditoría que puedan ser de importancia continua, tales como las debilidades materiales deficiencias significativas en el sistema de control interno. … 18. Este conocimiento permite al auditor definir las preguntas y los procedimientos analíticos y otros procedimientos de revisión que se aplican al realizar una revisión de información financiera intermedia de acuerdo con esta NITR. Como parte de la obtención de este conocimiento, el auditor generalmente hace preguntas al auditor anterior y, cuando es factible, revisa la documentación del auditor anterior relativa a la auditoría anual precedente y a cualesquiera periodos intermedios anteriores del año actual que hayan sido revisados por el auditor anterior. Al realizar estos procedimientos, el auditor considera la naturaleza de cualquier incorrección corregida o no corregida detectadas por el auditor anterior, cualquier riesgo significativo, incluyendo el riesgo de que la dirección eluda los controles establecidos, así como los asuntos importantes de contabilidad o auditoría que puedan tener una importancia continuada, tales como las debilidades significativas deficiencias significativas del sistema de control interno. Derechos de autor © 2010 de la Federación Internacional de Contadores (IFAC). Reservados todos los derechos. Utilizado con permiso de la IFAC. Para solicitar permiso para reproducir, almacenar, transmitir, o realizar otros usos similares de este documento, contactar en [email protected]