SODIUM Mg-Uranylacetate Method
Anuncio

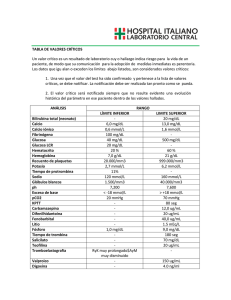
Presentation: 1 x 60 mL. Ref.: 30335 Store: 2 - 8 ºC. Sodium-p Quantitative determination of Sodium. 4. 5. 6. 7. Only for in vitro use in clinical laboratory (IVD) TEST SUMMARY Sodium is precipitated with Mg-uranyl acetate; the uranyl ions remaining in suspension form a yellow-brown complex with thioglycolic acid. The difference between reagent blank (without precipitation of sodium) and analysis is proportional to the sodium concentration. REAGENTS COMPOSITION Uranyl acetate PREC 19 mmol/L Magnesium acetate 140 mmol/L R Ammonium thioglycolate Ammonia 550 mmol/L 550 mmol/L NA-p CAL Sodium aqueous primary standard 150 mmol/L PRECAUTIONS PREC: Xn; F; R: 11-20/22-33; S: 1/2-7-16-20/21-45: R: T; R: 25-36/37/38-43; S: 1/2-9-16-25-26-27-28-36/37/38/39-45-61 Signs of reagent deterioration: - Precipitating solution becomes discoloured when exposed to the light. Store protected from light. A slight turbidity does not affect the determination. All the reagents of the kit are stable up to the end of the indicated month and year of expiry. Store tightly closed at 2-8ºC. Do not use reagents over the expiration date. SPECIMEN Serum. MATERIAL REQUIRED BUT NOT PROVIDED - Spectrophotometer or colorimeter measuring at 410 nm. - Matched cuvettes 1.0 cm light path. General laboratory equipment(Note 1, 2, 3). TEST PROCEDURE 2. 3. Assay conditions: Wavelength: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410 nm Cuvette: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 cm. light path Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37ºC /15-25ºC Adjust the instrument to zero with distilled water. Pipette into a cuvette: Blank Standard Standard (µL) Sample (µL) Precipitating sol. (mL) ---- 20 -1.0 Precipitating sol. (µL) 20 --Supernatant (µL) -20 20 Reagent (mL) 1.0 1.0 1.0 8. Mix and incubate for 5-30 at room temperature. 9. Read the absorbance (A) of the blank, standard and samples. The color is stable for at least 30 minutes. CALCULATIONS(Note 2) A Blank - A Sample x 150 (Standard conc.) = mmol/L sodium in the sample A Blank - A STD Sample -20 1.0 REAGENT PERFORMANCE 1. Measuring range: From detection limit of 40 mmol/L to linearity limit of 400 mmol/L. If the results obtained were greater than linearity limit, dilute the sample 1/2 with NaCl 9 g/L and multiply the result by 2. 2. Precision: Intra-assay (n=20) Inter-assay (n=20) Mean (mmol/L) 144.25 161.75 133.75 157.75 SD 1.89 2.87 3.20 6.70 CV (%) 1.31 1.78 2.39 4.25 3. Sensitivity: 1 mmol/L = 0.0006 A 4. Accuracy: Results obtained using LABKIT reagents did not show systematic differences when compared with other commercial reagents. The results of the performance characteristics depend on the analyzer used. Conversion factor: mmol/L = mEq/L. INTERFERING SUBSTANCES QUALITY CONTROL A list of drugs and other interfering substances with sodium determination has been reported by Young et. al5,6. Control sera are recommended to monitor the performance of the procedure, LABTROL H Normal Ref. 30950 and LABTROL H Pathological Ref. 30955. If control values are found outside the defined range, check the instrument, reagents and calibrator for problems. REAGENT PREPARATION AND STABILITY All the reagents are ready to use. 1. Close tubes and mix well. Allow stand for 5 minutes Shake intensively for at least 30 sec. Allow standing for 30 min. Centrifuge at high speed for 5-10 min. Separate the clear supernatant and pipette on another cuvettte: Blank Standard Sample SODIUM Mg-Uranylacetate Method Serum controls are recommended for internal quality control. Each laboratory should establish its own Quality Control scheme and corrective actions. 1. 2. 3. REFERENCE VALUES1 Serum: NOTES 135 - 155 mmol/L 4. 5. It is suggested that each laboratory establish its own reference range. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE This test is performed when symptoms of a sodium imbalance are present, or when disorders associated with abnormal sodium levels develop. Sodium (Na+) is the major positive ion in the fluids outside of cells. The concentration of sodium inside cells is only about 5 mEq/L compared with 140 mEq/L outside. The sodium content of the blood is a result of a balance between the amount in the food and beverages you consume, and the amount your kidneys excrete. (In addition, a small percent is lost through the stool and sweat.) Many factors affect sodium levels, including the steroid hormone aldosterone, which decreases loss of sodium in the urine. ANP (atrial natriuretic protein) is a hormone secreted from the heart that increases sodium loss from the body. Despite the integral relationship between sodium and water, the body regulates them independent of each other if necessary. CHEMELEX, S.A. Pol. Ind. Can Castells. C / Industria 113, Nau J 08420 Canovelles –BARCELONA- Tel- 34 93 849 17 35 Fax- 34 93 846 78 75 6. NA-p CAL: Proceed carefully with this product because due its nature it can get contamined easily. Detergents usually contain high sodium concentrations. The equipment (test tubes, pipettes, stoppers, cuvettes) must therefore be rinsed carefully with distilled water. Avoid contamination by traces of sodium. Disposable plastic tubes are recommended for the determination to avoid contaminations. Avoid the contact with metal materials. Calibration with the aqueous standard may cause a systematic error in automatic procedures. In these cases, it is recommended to use a serum Calibrator. CHEMELEX has instruction sheets for several automatic analyzers. Instructions for many of them are available on request. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Trinder P., Analyst 76, 596 (1951) Henry R.J. et al., Clin. Chem., Harper & Row New York, Sec. Edit. 643 (1974) ISO 15223 Medical devices – Symbols to be used with medical device labels, labelling and information to be supplied. Young DS. Effects of drugs on Clinical Lab. Tests, 4th ed AACC Press, 1995. Young DS. Effects of disease on Clinical Lab. Tests, 4th ed AACC 2001. LKBSIS54 Ed. 02/2007 Determinación cuantitativa de Sodio. 4. Solo para uso in vitro en laboratorio clínico (IVD). 5. 6. 7. PRINCIPIO El sodio se precipita con Mg acetato de Uranilo; los iones de uranilo en suspensión forman un complejo de color marrón-amarillento con ácido tioglicólico. La diferencia entre el blanco del reactivo (sin precipitación de sodio) y la muestra es proporcional a la concentración de sodio. COMPOSICIÓN DE LOS REACTIVOS Acetato de uranilo PREC 19 mmol/L Acetato de magnesio 140 mmol/L R Tioglicolato de amonio Amonio 550 mmol/L 550 mmol/L NA-p CAL Patrón primario acuoso de Sodio 150 mmol/L PRECAUCIONES - PREC: Xn; F; R: 11-20/22-33; S: 1/2-7-16-20/21-45: - R: T; R: 25-36/37/38-43; - S: 1/2-9-16-25-26-27-28-36/37/38/39-45-61 PREPARACIÓN DEL REACTIVO Y ESTABILIDAD Ambos reactivos se encuentran listos para su uso. Indicadores de deterioro de los reactivos: - El reactivo precipitante puede presentar decoloración al contacto con la luz. Conservar al resguardo de la luz directa. Una ligera turbidez en el reactivo no afecta la determinación. Todos los reactivos del kit son estables hasta el final del mes del año de caducidad indicado en la etiqueta. Con los frascos bien cerrados y conservado entre 2-8ºC. No usar el reactivo pasada su fecha de caducidad. SODIO Método Mg-Uranilacetato Presentación: 1 x 60 mL. Ref.: 30335 Conservar entre: 2 - 8 ºC. Sodium-p 8. 9. Tapar los tubos y mezclar cuidadosamente. Dejar reposar durante 5 minutos. Agitar vigorosamente durante 30 segundos. Dejar reposar 30 min. Centrifugar a alta velocidad de 5 a 10 minutos. Separar el sobrenadante y pipetear en una cubeta: Blanco Patrón Muestra 20 --Sol. Precipitante (µL) -20 20 Sobrenadante (µL) Reactivo (mL) 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mezclar e incubar entre 5 y 30 minutos a 15-25ºC. Leer la absorbancia (A) del blanco, del standard y de las muestras, frente a agua destilada. El color es estable 30 minutos. CÁLCULOS(Nota 2) A Blanco - A Muestra x 150 (Conc. Patrón) = mmol/L de iones sodio A Blanco - A STD Factor de conversión: mmol/L= mEq/L. Si la concentración de la muestra es superior al límite de linealidad, diluir 1/2 con agua destilada y multiplicar el resultado final por 2. 2. Precisión: Intraserie (n=20) Interserie (n=20) Media (mmol/L) 144.25 161.75 133.75 157.75 SD 1.89 2.87 3.20 6.70 CV (%) 1.31 1.78 2.39 4.25 3. Sensibilidad analítica: 1 mmol/L = 0,0006 A. 4. Exactitud: Los reactivos LABKIT no muestran diferencias sistemáticas significativas cuando se comparan con otros reactivos comerciales. Las características del método pueden variar dependiendo del instrumento utilizado. SUSTANCIAS QUE INTERFIEREN Se han descrito varias drogas y otras substancias que interfieren con la determinación del sodio 5,6. NOTAS CONTROL DE CALIDAD 1. Es recomendable utilizar sueros de control, LABTROL H Normal Ref. 30950 y LABTROL H Patológico Ref. 30955. Si los valores obtenidos están fuera de rango, se deben revisar los reactivos, calibrador e instrumento utilizados. 2. Los sueros de control son recomendables para los controles de calidad internos. Cada laboratorio debería establecer su propio esquema de calidad y acciones correctivas si los controles no cumplen con las tolerancias. VALORES DE Suero: REFERENCIA1 135 - 155 mmol/L Es recomendable que cada laboratorio establezca sus propios valores de referencia. MUESTRAS 3. 4. 5. 6. Suero. MATERIAL NECESARIO NO INCLUIDO - Espectrofotómetro o analizador con cubeta para lecturas a 410 nm. - Cubetas de 1,0 cm. de paso de luz. Equipo general de laboratorio. (Nota 1, 2, 3). PROCEDIMIENTO 1. 2. 3. Condiciones del ensayo: Longitud de onda: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410 nm Cubeta:. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 cm paso de luz Temperatura . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37ºC /15-25ºC Ajustar el espectrofotómetro a cero frente a agua destilada. Pipetear en una cubeta: Patrón Muestra 20 -Standard (µL) -20 Muestra (µL) Sol. Precipitante (mL) 1.0 1.0 SIGNIFICADO CLÍNICO Este test se realiza cuando hay síntomas de la presencia de un desequilibrio en los niveles de sodio, o cuando se aprecian desórdenes provocados por valores anormales de sodio. El sodio (Na+) es uno de los iones mayoritarios en los fluidos externos de las células. La concentración en el interior de dichas células es aproximadamente 5 mmol/L mientras que en el exterior es aprox. 140 mmol/L. El contenido de sodio es el resultado entre la cantidad consumida y la que es capaz de excretar el hígado (además, una parte se elimina a través del sudor). Diferentes factores pueden afectar a los niveles de sodio, incluyendo la hormona esteroide aldosterona, que disminuye el nivel de este ión en la orina. La ANP (proteína atrial natriuretica) es una hormona segregada por el corazón que aumenta la secreción de sodio. K NA-p CAL: Debido a la naturaleza del producto, es aconsejable tratarlo con sumo cuidado ya que se puede contaminar con facilidad. Los detergentes por lo general tienen altas concentraciones de sodio. Todo el material usado en la determinación (tubos de ensayo, cubetas, tapones, pipetas, etc.) debe lavarse cuidadosamente con agua destilada. Evite la contaminación por residuos de sodio. Se recomienda utilizar material de plástico de un solo uso para evitar contaminaciones. Evitar el contacto con partes metálicas. La calibración con el patrón acuoso puede dar lugar a errores sistemáticos en métodos automáticos. En este caso, se recomienda utilizar calibradores séricos. CHEMELEX dispone de instrucciones detalladas para la aplicación de este reactivo en distintos analizadores. BIBLIOGRAFIA 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Trinder P., Analyst 76, 596 (1951) Henry R.J. et al., Clin. Chem., Harper & Row New York, Sec. Edit. 643 (1974) ISO 15223 Medical devices – Symbols to be used with medical device labels, labelling and information to be supplied. Young DS. Effects of drugs on Clinical Lab. Tests, 4th ed AACC Press, 1995. Young DS. Effects of disease on Clinical Lab. Tests, 4th ed AACC 2001. CARACTERÍSTICAS DEL REACTIVO 1. Rango de medida: Desde el límite de detección de 40 mmol/L hasta el límite de linealidad de 400 mmol/L. CHEMELEX, S.A. Pol. Ind. Can Castells. C / Industria 113, Nau J 08420 Canovelles –BARCELONA- Tel- 34 93 849 17 35 Fax- 34 93 846 78 75 LKBSIS54 Ed. 02/2007