1 tema 10. reacciones inmunitarias mediadas por células.
Anuncio

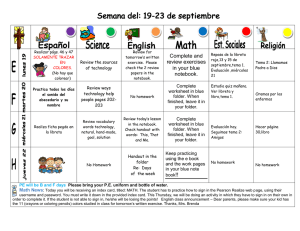
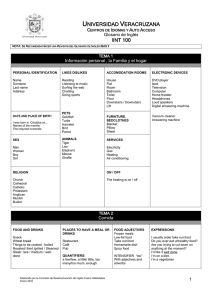
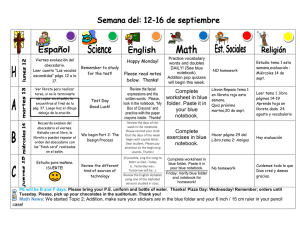
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature, and individual cytokines may belong to two groups, e.g. the chemokine interleukin-8 (IL-8). Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Most cytokines have many effects and act on several different cell types. A single example of each is selected in this table. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 1 Four families of cytokine receptors are identified. Examples are given of each type. Type I is the cytokine-receptor family, typically consisting of separate binding and signalling subunits. The binding subunits have domains containing conserved motifs (WSXWS). The type III family consists of molecules which have cysteinerich domains of the NGF-receptor type. Type IV receptors have immunoglobulin superfamily domains. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular The high-affinity IL-2 receptor is formed by three polypeptide chains, of which the α and β chains bind to the cytokine, while the γ chain is involved in signalling to the cell. The IL-4 receptor shares the γ signalling chain, but has a unique α chain which specifically recognizes IL-4. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 2 A simple model for cytokine activation of a cell is shown. Cytokine binds to its receptor on the cells and induces dimerization or polymerization of receptor polypeptides at the cell surface. This causes activation of intracellular signalling pathways (e.g. kinase cascades), resulting in the production of active transcription factors which migrate to the nucleus and bind to the promotor or enhancer regions of genes induced by that cytokine. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular The intracellular signalling pathways activated by IFNα are illustrated diagramatically. IFNα binding aggregates the two subunits of the receptor. This leads to activation and phosphorylation of two Jak kinases, Jak1 and Tyk2, which then phosphorylate Stat1 and Stat2. These two transcription factors form a complex with a DNA-binding protein called p48. The complex moves to the nucleus and induces transcription of genes bearing an interferon response element (ISRE). Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 3 TNF induces the trimerization of the TNF receptor on the cell surface, which causes adaptor molecules to be recruited to the receptor complex. One pathway leads to the activation of caspase-8 and apoptosis. Other pathways lead to the activation of the transcription factors AP-1 and NFκB, which cause gene activation and may offset the effects of the caspase pathway. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 4 Los receptores Toll-like reconocen estructuras y patrones conservados en los microorganismos. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 5 Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 6 The diagram illustrates the differentiation of murine Th cells into subsets with distinctive patterns of cytokine release. IL-12, IFNγ and TGFβ favour differentiation of Th1 cells and IL-4 favours Th2 cells. The cytokine patterns influence the effector functions that are activated. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Not only does their cytokine output drive different effector pathways, but Th1 cells tend to switch off Th2 cells, and vice versa. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 7 Cytotoxic T cells recognize processed antigen presented on the target cell by MHC molecules using their T-cell receptor (TCR). Most Tc cells are CD8+ and recognize antigen presented by MHc class I, but a minority are CD4+ and recognize antigen presented by MHC class II. By contrast, NK cells have receptors that recognize MHC class I on the target and signal inhibition of cytotoxicity. They use a number of different receptors (NK receptors) to identify their targets positively for killing, including CD2, CD69, or antibody bound to their Fc receptor (CD16). Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Some of the ligands involved in the interaction between cytotoxic T cells and their targets. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 8 The inhibitory receptors consist of the lectin-like CD94 disulphide bonded (red) to peptides from the NKG2 locus, such as NKG2A which have intracellular domains carrying ITIM motifs (immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motif). The non-inhibitory receptors, such as CD94/NKG2C, lack ITIMs, but have a charged lysine (K) in the transmembrane segment which allows them to interact with signal transducing molecules. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular These receptors consist of either two or three extracellular Ig superfamily domains. The inhibitory forms are longer and have intracellular ITIMs, while the non-inhibitory forms have the charged residue in the membrane comparable to the non-inhibitory forms of CD94/NKG2. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 9 The molecule Fas (CD95), the two TNF receptors and the lymphotoxin receptor are illustrated diagramatically. The extracellular domains are similar to those found in the NGF receptor. Both Fas and TNFR-1 have death domains which are involved in the recruitment of caspases. The ligands for these receptors are indicated at the top. Lymphotoxin-α can form homotrimers or heterotrimers with lymphotoxin-β. Up to 25 other members of these families have been identified by data-base searching. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Ligation of CD95 or TNFR-1 causes trimerization of the receptors. Death domains in the cytoplasmic portion of CD95 bind to the adaptor protein FADD (=MORT-1), which recruits caspase 8 or 10. TNFR-1 can activate either caspase 8 or 10, via TRADD and FADD, or caspase 2 via RIP and RAIDD. Caspase 8 can further activate other caspases, and these in concert lead to apoptosis of the target cell. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 10 The cytotoxic lymphoid cell degranulates, releasing perforin and various enzymes (granzymes) into the immediate vicinity of the target cell membrane. In the presence of Ca2+ there is enzymic polymerization of the perforin to form polyperforin channels on the target cell (1). Enzymes which activate the apoptosis pathways, degradative enzymes or other toxic substances released from the cytotoxic cell may pass through the channels on the target and cause cell damage or killing (2). Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 11 Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 12 Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 10. Inmunidad celular 13