TEMA 5. ANÁLISIS DE GENEALOGÍAS
Anuncio
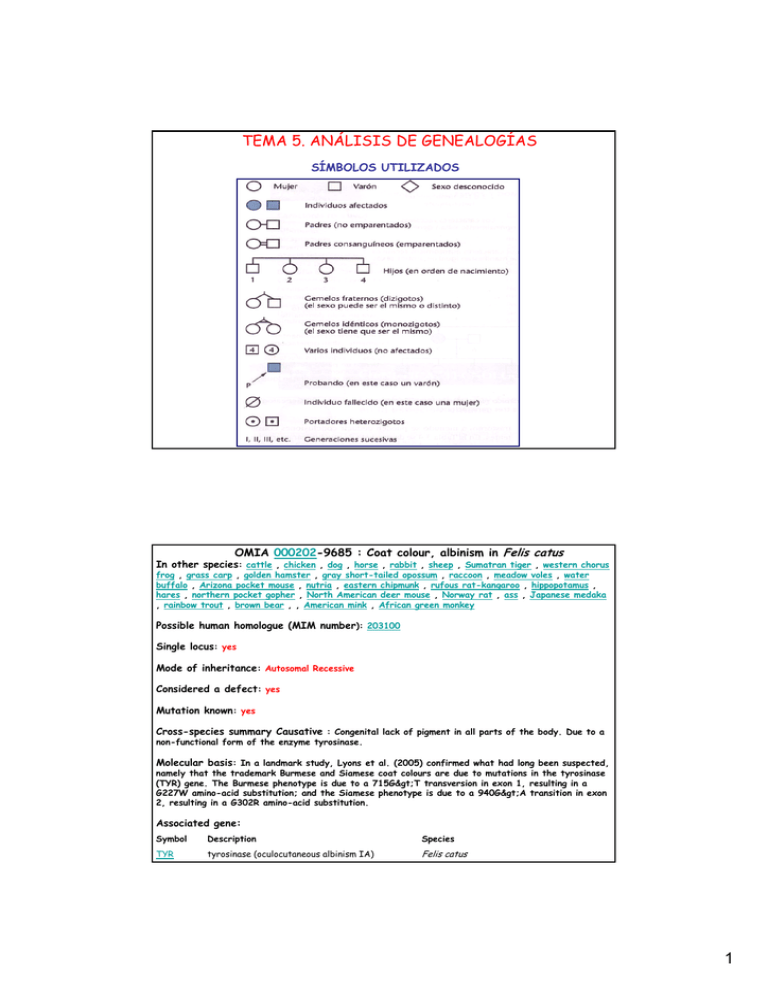
TEMA 5. ANÁLISIS DE GENEALOGÍAS SÍMBOLOS UTILIZADOS OMIA 000202-9685 : Coat colour, albinism in Felis catus In other species: cattle , chicken , dog , horse , rabbit , sheep , Sumatran tiger , western chorus frog , grass carp , golden hamster , gray short-tailed opossum , raccoon , meadow voles , water buffalo , Arizona pocket mouse , nutria , eastern chipmunk , rufous rat-kangaroo , hippopotamus , hares , northern pocket gopher , North American deer mouse , Norway rat , ass , Japanese medaka , rainbow trout , brown bear , , American mink , African green monkey Possible human homologue (MIM number): 203100 Single locus: yes Mode of inheritance: Autosomal Recessive Considered a defect: yes Mutation known: yes Cross-species summary Causative : Congenital lack of pigment in all parts of the body. Due to a non-functional form of the enzyme tyrosinase. Molecular basis: In a landmark study, Lyons et al. (2005) confirmed what had long been suspected, namely that the trademark Burmese and Siamese coat colours are due to mutations in the tyrosinase (TYR) gene. The Burmese phenotype is due to a 715G>T transversion in exon 1, resulting in a G227W amino-acid substitution; and the Siamese phenotype is due to a 940G>A transition in exon 2, resulting in a G302R amino-acid substitution. Associated gene: Symbol Description Species TYR tyrosinase (oculocutaneous albinism IA) Felis catus 1 CARÁCTER AUTOSÓMICO RECESIVO: Albinismo -Normalmente se saltan generaciones -Se manifiestan en ambos sexos -Los descendientes afectados suelen tener progenitores no afectados -Aparece mas frecuentemente en descendientes de cruzamientos consanguíneos OMIA 000187-9615 : Chondrodysplasia in Canis lupus familiaris In other species:domestic pig , cattle , sheep , domestic cat Mammalian Phenotype Ontology (MPO) number: MP:0002657 Single locus: yes Mode of inheritance: Autosomal Considered a defect: yes Causative mutation known: yes Cross-species summary: Abnormal growth of cartilage, leading to disproportionate dwarfism. Associated gene: Symbol Description Species FGF4 fibroblast growth factor 4 Canis lupus familiaris References 2 Smit, JJ., Temwitchitr, J., Brocks, BA., Nikkels, PG., Hazewinkel, HA., Leegwater, PA. : Evaluation of 0 candidate genes as a cause of chondrodysplasia in Labrador retrievers. Vet J 187:269-71, 2011. 1 Pubmed reference: 20018534. 1 2 CARÁCTER AUTOSÓMICO DOMINANTE: Acondroplasia -Raramente se saltan generaciones -Se manifiestan en ambos sexos -Todos los individuos afectados tienen un progenitor afectado -Los progenitores no afectados, no transmiten el rasgo OMIA 000437-9615 : Haemophilia A in Canis lupus familiaris In other species: domestic cat , horse , domestic pig , sheep , , cattle Possible human homologue (MIM number): 306700 Single locus: yes Mode of inheritance: X-linked recessive Considered a defect: yes Causative mutation known: yes Cross-species summary: Also called factor VIII deficiency. Impaired coagulability of the blood, with a consequential strong tendency to bleed, due to a deficiency of the clotting factor VIII. Since the gene for this factor is located on the X chromosome, the disorder is expected to be X-linked. In domesticated animals, the disorder has been reported in a large range of species, but in no case has the molecular basis yet been determined. Associated gene: Symbol F8 Description coagulation factor VIII, procoagulant component Species Chr acc Chr name Canis lupus familiaris NC_006621. 2 X 3 Hemofilia: recesivo ligado al X -Afecta con mayor frecuencia a los machos -El rasgo se suele saltar generaciones -Nunca se transmite del progenitor al descendiente macho -Todas las hembras descendientes de machos afectados son portadoras CARACTERES DOMINANTES LIGADOS AL CROMOSOMA X • Estan afectados ambos sexos, pero es mas frecuente en hembras • Los machos afectados transmiten la “condición “ a todas sus descendientes hembras, pero a ningún macho • Las hembras afectadas transmiten la condición a la mitad de sus descendientes tanto machos como hembras •No suele saltar generaciones Ej.: Ej.: Raquitismo hipofosfatemico 4 HERENCIA LIGADA AL CROMOSOMA Y ¾Los genes de la región diferencial del cromosoma Y son heredados solamente por los descendientes machos (provenientes del progenitor macho). ¾No salta generaciones ¾A excepción de los genes relacionados con la determinación del sexo, no se ha demostrado con claridad el ligamiento al Y de ningún fenotipo humano. 5