módulo tres
Anuncio
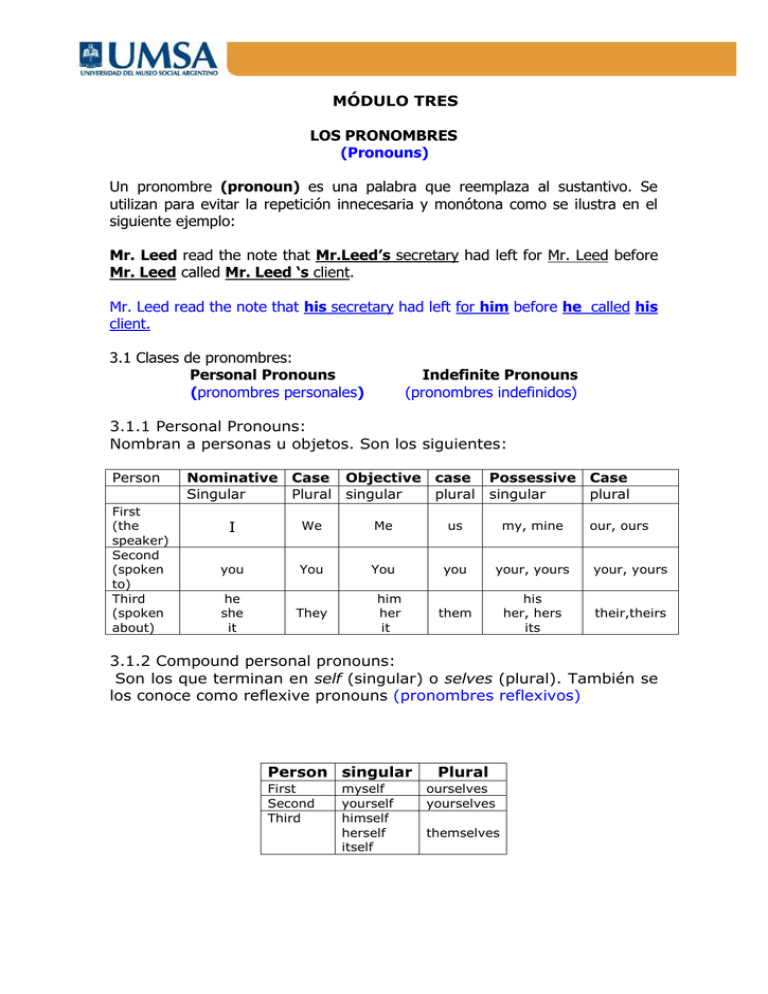
MÓDULO TRES LOS PRONOMBRES (Pronouns) Un pronombre (pronoun) es una palabra que reemplaza al sustantivo. Se utilizan para evitar la repetición innecesaria y monótona como se ilustra en el siguiente ejemplo: Mr. Leed read the note that Mr.Leed’s secretary had left for Mr. Leed before Mr. Leed called Mr. Leed ‘s client. Mr. Leed read the note that his secretary had left for him before he called his client. 3.1 Clases de pronombres: Personal Pronouns (pronombres personales) Indefinite Pronouns (pronombres indefinidos) 3.1.1 Personal Pronouns: Nombran a personas u objetos. Son los siguientes: Person First (the speaker) Second (spoken to) Third (spoken about) Nominative Case Objective case Possessive Case Singular Plural singular plural singular plural I We Me us my, mine you You You you your, yours your, yours he she it They them his her, hers its their,theirs him her it our, ours 3.1.2 Compound personal pronouns: Son los que terminan en self (singular) o selves (plural). También se los conoce como reflexive pronouns (pronombres reflexivos) Person singular First Second Third myself yourself himself herself itself Plural ourselves yourselves themselves I saw myself reflected in the mirror Me vi reflejado en el espejo The manager of the company gave himself a modest salary increase. El gerente de la empresa se otorgó un modesto aumento de salario. 3.1.3 Indefinite Pronouns: A diferencia de los pronombres personales, no cambian de forma para indicar, número o género. Estos son algunos de los pronombres indefinidos más comúnmente usados: All todo Both ambos some algunos any alguno each cada (uno) anybody alguien nobody nadie everyone cada uno someone alguien few pocos none ninguno many muchos anything algo no one nadie something algo nothing nada several varios Someone left his briefcase in my office. Alguien dejó su maletín en mi oficina. Everyone felt that something should be done to correct the situation. Todos pensaron que había que hacer algo para corregir la situación. Atención: Cuando se utilizan para modificar un sustantivo, funcionan como adjetivos All invoices must be checked very carefully. Toda factura debe controlarse cuidadosamente. We have received several inquiries from prospective customers. Hemos recibido varias consultas de posibles compradores. 3.1.4 Demonstrative pronouns (pronombres demostrativos) Los cuatro pronombres demostrativos son: Singular Plural this these Este, esta Estos, estas That those Ese, esa,eso Esos, esas This is mine and that is yours. Este es mío y ese es tuyo. These are Bill’s and those are Maria’s. Estos son de Bill y esos son de María. Atención: Cuando se utilizan como adjetivos this y that modifican sustantivos en singular; these y those modifican sustantivos en plural. This coat belongs to Mr. Klein; that umbrella belongs to Mr. Allen Este saco pertenence al Sr. Klein; ese paraguas pertenece al Sr. Allen These drapes are fire-resistant but those curtains are not. Estos cortinados son resistentes al fuego pero esas cortinas no. 3.1.5 Interrogative pronouns: (pronombres interrogativos) Se utilizan para introducir preguntas directas o indirectas. Son: Who quien Whom a/ de quien Which cual What que Whose cuyo Direct question: Who is to be the keynote speaker at the dinner meeting? ¿Quién será el orador principal en la cena? Indirect question: The interviewer asked me who founded the company. El entrevistador me preguntó quien fundó la compañía. 3.1.6 Relative pronouns (pronombres relativos) Who, whom, which y that también se utilizan como pronombres relativos. The person who wishes to be considered for the job should contact me. La persona que quiera ser considerada para el puesto debe contactarme. Miss Lee, whom you will remember, will supervise the project. La señorita Lee a quien recordarán, supervisará el proyecto. Mr. Richards said that he would leave at five o’clock. El señor Richards dijo que se retiraría a las cinco en punto. 3.2 Características de los pronombres: A continuación nos referiremos a algunas de las características de los pronombres: Person (persona), number (número), gender (género) y case (caso). 3.2.1 Person: Los pronombres personales cambian para indicar la persona que habla (first person :I), la persona a quien se habla (second person: You) y la persona u objeto del que se habla (third person: He, she, it). 3.2.2 Number: Los pronombres personales cambian su forma para indicar el número (singular or plural). I/we; you/you; he, she, it/ they. 3.2.3 Gender: Solamente la tercera persona del singular indica el género: He, him, his son masculino She, her, hers son femenino It, its son común o neutro. 3.2.4 Case: El caso está determinado por la ubicación del pronombre en la oración: Nominative case: We received a large order. (We es el sujeto) (Nosotros) recibimos una orden grande. Objective case: We saw her this morning (her es complemento directo) La vimos esta mañana Objective case: Frank gave me his address (me es complemento indirecto) Frank me dió su dirección Possessive case: Your secretary said these papers were yours (yours se refiere y significa lo mismo que papeles). Su secretaria dijo que estos documentos eran de usted. Síntesis del Módulo Tres Los pronombres Personal Pronouns (pronombres personales) Person First (the speaker) Second (spoken to) Third (spoken about) Nominative Case Objective case Possessive Case Singular plural singular plural singular plural I We Me us my, mine you You You you your, yours your, yours he she it They them his her, hers its their,theirs him her it Compound personal pronouns Person singular First Second Third myself yourself himself herself itself Plural ourselves yourselves themselves Indefinite Pronouns All Few Both None Some Many Todo Pocos Ambos Ninguno algunos muchos Any Anything Each No one Anybody Something alguno algo Cada uno nadie Alguien algo Nobody Nothing Everyone Several Someone nadie nada cada uno varios alguien Demonstrative pronouns Singular Plural this these Este, esta Estos, estas That Those Ese, esa,eso Esos, esas our, ours Interrogative pronouns Who Whom Which What Whose Relative pronouns Who, whom, which that Características de los pronombres: Person (persona), number (número), gender (género) y case (caso). Person: Los pronombres personales cambian para indicar la persona que habla (first person :I), la persona a quien se habla (second person: You) y la persona u objeto del que se habla (third person: He, she, it). Number: Los pronombres personales cambian su forma para indicar el número (singular or plural). I/we; you/you; he, she, it/ they. Gender: Solamente la tercera persona del singular indica el género: He, him, his son masculino She, her, hers son femenino It, its son común o neutro. Case: El caso está determinado por la ubicación del pronombre en la oración: Nominative case: We received a large order. (We es el sujeto) Objective case: We saw her this morning (her es complemento directo) Objective case: Frank gave me his address (me es complemento indirecto) Possessive case: Your secretary said these papers were yours (yours se refiere y significa lo mismo que papeles). MODULO TRES EJERCICIO UNO Clasificación de pronombres Indica que tipo de pronombre es el subrayado en las siguientes oraciones. 1. He read at least two newspapers every day. ………………………………………………………. 2. Sara took the folder and put it in the file . ………………………………………………………. 3 Everyone was please to hear the news. . ………………………………………………………. 4 Mr. King typed the letter himself. . ………………………………………………………. 5 This is a cheap model. ………………………………………………………. 6 Whom would you like to see? ………………………………………………………. 7 Who processed the order? ………………………………………………………. 8 where should I send them? ………………………………………………………. 9 We should do something to help him. ………………………………………………………. 10 The man who spoke tonight was Mr. Hill ………………………………………………………. Indica que pronombre puede substituir la palabra o palabras que se encuentran entre paréntesis. 1. (An unknown person) stole the money. ………………………………………………………. 2. (Vera) may need to hire an attorney. . ………………………………………………………. 3. We were very eager to settle (the dispute) . ………………………………………………………. 4 (Mr. Adams) prepares the sales estimates. ………………………………………………………. 5 President Fisher addressed (the graduates). ………………………………………………………. 6 (All citizens) were complaining. ………………………………………………………. 7 What do you think of (Mr. Richardson)? ………………………………………………………. 8 (The actress) gave a superb performance ………………………………………………………. 9 This may be (Mary’s) book ………………………………………………………. 10 (The order) was mailed yesterday ………………………………………………………. MODULO TRES RESPUESTAS EJERCICIO UNO Clasificación de pronombres Indica que tipo de pronombre es el subrayado en las siguientes oraciones. 1. He read at least two newspapers every day. PERSONAL/NOMINATIVE 2. Sara took the folder and put it in the file . PERSONAL /OBJECTIVE 3 Everyone was please to hear the news. . INDEFINITE 4 Mr. King typed the letter himself. . COMPOUND PERSONAL 5 This is a cheap model. DEMONSTRATIVE 6 Whom would you like to see? INTERROGATIVE 7 Who processed the order? INTERROGATIVE 8 where should I send them? PERSONAL/OBJECTIVE 9 We should do something to help him. INDEFINITE 10 The man who spoke tonight was Mr. Hill RELATIVE Indica que pronombre puede substituir la palabra o palabras que se encuentran entre paréntesis. 1. (An unknown person) stole the money. SOMEONE 2. (Vera) may need to hire an attorney. . SHE 3. We were very eager to settle (the dispute) . IT 4 (Mr. Adams) prepares the sales estimates. HE 5 President Fisher addressed (the graduates). THEM 6 (All citizens) were complaining. THEY 7 What do you think of (Mr. Richardson)? HIM 8 (The actress) gave a superb performance SHE 9 This may be (Mary’s) book HER 10 (The order) was mailed yesterday IT


