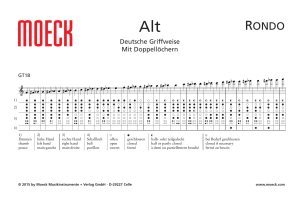
Contents - International Federation of Societies for Surgery of the
Anuncio

Contents Index § Sumario PREFACE History. Languages. Contents. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTIVE BONES JOINTS MUSCLES TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. VESSELS SKIN and ACCESSORIES. GENERAL JOINTS. MUSCLE and TENDON. NERVES. EXAMINATION: Symptoms, signs and tests. GENERAL. BONES JOINTS MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESSORIES. VESSELS. PATHOLOGY CONGENITAL BONES. JOINTS. MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESORIES. VESSELS. GENERAL. BONES. JOINTS. MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESORIES. VESSELS. SKIN CREASES THE HAND JOINT MOTION General rules THE ELBOW THE FOREARM THE WRIST THE FINGERS THE THUMB Top Sumario TERMINOLOGY FOR HAND SURGERY PREFACE ANATOMY GENERAL DESCRIPTIVE BONES JOINTS MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. VESSELS. SKIN and ACCESSORIES. FUNCTION GENERAL JOINTS. MUSCLE and TENDON. NERVES. CLINICAL EXAMINATION: Symptoms, signs and tests. PATHOLOGY TREATMENT. GENERAL. BONES. JOINTS. MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESORIES. VESSELS. SUPPLEMENT SKIN CREASES THE HAND JOINT MOTION Top PREFACE INTERNATIONAL FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Committee on Standardization of Nomenclature 1970 • • Chairman:Mr. H.G. Stack, England Members:Dr. D. Buck-Gramcko, W. Germany Dr. I. Isaksson, Sweden Dr. E. B. Kaplan, U.S.A. Dr. F. Paredes, Portugal Dr. P. Rabischong, France Prof. T. Tajima, Japan Dr. E. Zancolli, Argentina 1985 • • Chairman: Mr. N.J. Barton, England Members: Dr.D. Buck-Gramcko, W. Germany Dr. R. I. Burton, U.S.A. Dr. F. Iselin, France Dr. A. de Negri, Italy Dr. A. Pernet, Brazil Dr. F. Enriquez de Salamanca,Spain Mr. H. G. Stack, England Prof. T. Tajima, Japan 1998 • • Chairman: Alberto Lluch, MD PhD. (Spain) Members: Geoffrey Hooper, FRCS (United Kingdom) Dr. Adalbert Kapandji (France) Prof. Dr. Ulrich Lanz (Germany) Prof. Dr. Hans - Martin Schmidt (Germany) The present booklet on Terminology for Hand Surgery is an updating of the previous publications by the Committee on Standardisation of Nomenclature of the International Federation of Societies for Surgery of the Hand. The aim of the Nomenclature Committee is to select the most appropiate vocabulary to define the different anatomical structures and conditions used by those interested in the study, prevention and treatment of alterations affecting the hand. Not only will this help communication between workers who use different languages, but also we hope to achieve a uniform vocabulary, with the added benefit of precision, for professionals using the same language Related Topics: History. Languages. Contents. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Top History. The first booklet on Terminology for Hand Surgery was published in June 1970, and it was restricted to anatomical terms and a short description of motor and sensory functions. There were 422 terms, with their equivalent translation in five languages, in adtion to an atlas of joint motion, in English, following the guidelines of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. In 1983 a Clinical Section on Hand Terminology was published in the International Supplement of the Journal of Hand Surgery (Guide to terminologY* for hand surgery.~ Report of the Nomenclature Committee: Barton N. J Hand Surg 19 8 3; vol 8, No 5, Part 2:814-828). Both publications were later compiled and updated in a third publications printed by The Pilgrims Press for the IFSSH on November of 1985. Twelve years later, in 1997, Dr. Giorgio Brunelly (Italy) President of the IFSSH had asked to produce a new booklet on Terminology for Hand Surgery. We reviewed all the data compiled in the previous publications, as otherwise thig would have been a monumental task if we had to start from the beginning. Top Languages. The first problem that we were faced with was the selection of languages. The first booklet was published in 1970, with Mr. Guy Pulvertaft (England) being the President of the IFSSH, representing only 10 National and Regional Societies around the world. At present there are 48 National and Regional Societies represented by the IFSSH, communicating with a wide spectrum of languages. Although only 11 official languages have been recognised by the UNESCO, in Europe alone, 54 languages are currently in used. Although the number of languages is considerably larger around the world, it was decided to continue using the languages employed in the previous Terminology for Hand Surgery. Latin is used for the description of all anatomical terms, as this is recommended language by the Anatomists (Nomina Anatomica). The four living languages are English, German, French and Spanish. Dr. Schmidt was responsible for the Latin terms, Dr. Hooper for the English, Dr. Lanz for the German, Dr. Kapandji for the French and Dr. Lluch for the Spanish. We would like to apologize for not including other languages, as Japanese, Russian, Italian, etc, used by a large number of highly qualified Hand Surgeons around the world. This is something that we should take into consideration in the very near future. The costs and time needed to print the Terminology in as many languages as possible is a non viable project, and perkaps the solution would be to place the Terminology on Internet. By doing so, National Societies using other languages can incorporate their terms next to the ones in the present publication. Another advantage would be to keep the Nomenclature updated in almost on a dayto-day basis. All the Members of the present Committee were selected from Europe, solely for logistic reasons and to get the project finished on time. Top Contents. The booklet has been divided into four parts: I.Anatomy, 2.Function, 3. Clinical and 4. Treatment. Chapter 3 (Clinical) has been subdivided in two: 3. 1. Examination, that includes all terms related to symptoms, signs and tests, and 3.2. Pathology. The terms listed in each of the four chapters have been classified into the eight major anatomic structures composing the hand: 1.8ones, 2.Joints, 3.Muscles, 4.Tendons, 5.Fascia and aponeurosis, 6.Nerves, 7.Vessels and 8.Skin and accessories. The reader can easily find the appropiate term for any structure in relation to its anatomy, function, pathology or treatment. The search is further facilitated by the inclusion of an index of contents on the first page. The exception being congenital deformities, which are described in separate heading within the chapter on pathology, as they relate to many anatomical structures simultaneously. Following the guidelines of previous publications, the chapter on congenital anomalies avoids the use of eponims as well as of animal comparisons used -for the description of certain hand anomalies. Latin and Greek terms used for most of the anomalies have also been obviated as they are the same for all languages. However, the chapter on congenital anomalies is more of a classification than a list of words. We transcribed the classification recommended by the American Society for Surgery of the Hand (Classification for congenital limb malformations. Swanson AB. J Hand Surg 1976; 1:8-22). We are of the opinion that this chapter will need an updating in the near future, accepting the fact that it will never be a perfect classification, as many congenital hand deformities are combined. We have to regret that Chapter 3.2.3. Pathology of Joints does not include a section on carpal instabilities. The reason is that this subject is still under discussion in two different Forums: the International Wrist Investigators Workshop and the Anatomy and Biomechanics Committee of the IFSSH. There seems to be slightly different opinions about the proper definition and use of the term "instability", and even more when referring to "static instability", two apparently condradictory words. To compensate for this, the Chapter 1.3. Anatomy of Joints includes a very comprehensive and updated listing of wrist ligaments. At the end of the booklet there is an Atlas of Surface Anatomy and Joint Motion. New schematic drawings were made to show the guidelines for measuring joint mobility. The neutral position or zero starting position (00) for each joint is defined, and the range of flexion is described as positive degrees, while extension is described as negative degrees. This is a divergence from the previous Nomenclatures that followed the guidelines proposed by the AAOS for the measurement of joint motion. Top ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to thank the Chairman and Members of the preceeding Nomenclature Committees, who deserve our recognition for the tremendous task that represents the publication of the previous Nomenclatures for Hand Surgery. We have just deleted or added some terms in line with the natural evolution and better understanding of hand anatomy, physiology and pathology. • • Chairman: Alberto Lluch, MD PhD. (Spain) Members: Geoffrey Hooper, FRCS (United Kingdom) Dr. Adalbert Kapandji (France) Prof. Dr. Ulrich Lanz (Germany) Prof. Dr. Hans-Martin Schmidt (Germany) May 1998. Top GENERAL DESCRIPTIVE • • • • • Brachium Arm Arm Bras Brazo • • • • • Cubitus Elbow Ellenbogen Coude Codo • • • • • Antebrachium Forearm Unterarm Avant-bras Antebrazo • Manus • Hand • Hand • Main • Mano • • • • • • • • • • Carpus Wrist Handwurzel Poignet Muñeca • • • • • Metacarpus Metacarpal region Mittelhand Métacarpe Región metacarpiana Digiti manus Fingers (Digits) Finger Doigts de la main Dedos • • • • • Pollex Thumb Daumen Pouce Pulgar • • • • • Index Index finger Zeigefinger Index Indice • • • • • Digitus medius Middle finger Mittelfinger Medius Dedo medio • • • • • Digitus anularis Ring finger Ringfinger Anulaire Dedo anular • • • • • Digitus minimus Little finger Kleinfinger Auriculaire Dedo meñique • Ray (Metacarpal and finger) • Strahlen (Finger und Mittelhandknochen) • Rayons (metacarpien et doigt) • Rayos (metacarpiano y dedo) • • • • • Plica interdigitalis Interdigital web Zwischenfingerfalten Commissure des doigts Pliegue interdigital • • • • • Facies dorsales Dorsal surface Streckseite (Dorsalseite) Face dorsal Cara dorsal • • • • • Facies palmares Palmar surface (anterior surface) Beugeseite (Palmarseite) Face Palmaire Cara palmar (cara anterior) • • • • • Facies laterales (facies radiales) Lateral surgace (radial surface) Speichenseite (Radialseite) Face radiale Cara lateral (cara radial) • • • • • Facies mediales (facies ulnares) Medial surface (ulnar surface) Ellenseite (ulnarseite) Face cubitale Cara medial (cara cubital) • • • • • Dorsum manus Back of the hand Handrücken Dors de la main Dorso de la mano • • • • • Palma manus Palm of the hand Hohlhand (Handfläche) Paume de la main Palma de la mano • • • • • Thenar Thenar region (Thenar eminence) Daumenballen Eminence thénar Región tenar (Eminencia tenar) • Hypothenar • • • • Hypothenar region (Hypotenar eminence) Kleinfingerballen Eminence hypothénar Región hipotenar (Eminencia hipotenar) • • • • • Fovea radialis Anatomical snuff box Tabatière Tabatière Tabaquera anatómica • • • • Knuckle Knöchel Jointure IPP Nudillo • • • • • .................. Fingertip Fingerspitze (Fingerkuppe) Extremité du doigt Punta del dedo • • • • • ................... Finger pulp Fingerbeere Pulpe du doigt Pulpejo digital • • • • • Canalis carpi (sulcus carpi) Carpal canal (carpal tunnel) Karpalkanal (karpaltunnel) Canal carpien Canal carpiano • • • • • .................. Carpal tunnel (CT) Karpaltunnel Tunnel carpien Túnel carpiano • • • • • ...................... Guyon's compartment Guyon'scher Kanal (Loge) Loge de Guyon Compartimiento de Guyon Top BONES • • • • • Ossa Bones Knochen Os Huesos • • • • • Radius Radius Speiche Radius Radio Caput Head Köpfchen Tête Cabeza Collum Neck Hals Col Cuello Tuberositas radii Bicipital tuberosity Tuberositas radii Tuberosité bicipitale Tuberosidad bicipital Processus styloideus Styloid process Griffelfortsatz (der Speiche) Apophyse styloide du radis Apófisis estiloides Tuberculum dorsale Tubercle of the radius (Lister's tubercle) Listers Tuberculum Tubercule de Lister Tubérculo de Lister Incisura ulnaris Sigmoid notch Incisura ulnaris Cavité sigmoïde du radius Cavidad sigmoidea del radio Facies articularis carpea o carpalis (Fovea scaphoidea et fovea lunata) Carpal joint surface (of the radius) Speichengelenkfläche (distale) Facette articulaire carpienne Carilla articular carpiana (carilla escafoidea y carilla semilunar) • • • • • Ulna Ulna Elle Cubitus Cúbito Olecranon Olecranon Ellenhaken (Olekranon) Olécrane Olécranon Processus coronoideus Coronoid process Krokenfortsatz Apophyse coronoide Apófisis coronoides Caput ulnae Head of the ulna Ellenkopf Tête du cubitus Cabeza del cúbito Processus styloideus Styloid process Griffelfortsatz (der Elle) Apophyse styloide cubitale Apófisis estiloides • • • • • Ossa carpi (Carpalis) Carpal bones Handwurzelknochen Os du carpe Huesos del carpo Os scaphoideum Scaphoid bone Kahnbein (Skaphoid) Scaphoïde Escafoides • • • • • Tuberculum ossis scaphoidea Tubercle of the scaphoid Tuberculum ossis scaphoidei Tubercule du scaphoïde Tubérculo del escafoides Os lunatum Lunate bone Mondbein (Lunatum) Semi-lunaire Semilunar Os triquetrum Triquetrum Dreieckbein (Triquetrum) Pyramidal Piramidal Os pisiforme Pisiform bone Erbsenbein (Pisiforme) Pisiforme Pisiforme Os trapezium (os multangulum majus) Trapezium Grosses Vieleckbein (Trapezium) Trapèze Trapecio • • • • • Tuberculum ossis trapezii Tubercle of the trapezium Tuberculum des Trapezium Tubercule du Trapèze Tubérculo del trapecio Os trapezoideum Trapezoid kleines Vieleckbein (Trapezoid) Trapézoïde Trapezoide Os capitatum Capitate Kopfbein (Kapitatum) Grand os Hueso grande Os hamatum Hamate Hakenbein (Hamatum) Os crochu Hueso ganchoso • • • • • • • • Hamulus ossis hamati Hook of the Hamate Haken des Hakenbeines Apophyse unciforme de l'os crochu Gancho del ganchoso Ossa metacarpi (Metacarpalia) Metacarpal bones Mittelhandknochen • • Métacarpiens Huesos metacarpianos Os metacarpale pollicis, indicis, medius, anularis et digitus minimus) Thumb, index, middle, ring and small finger metacarpal bone Erster, zweiter,dritte, vierter, fünfter Mittelhandknochen Metacarpien du puce, de l'index, du medius, de l'anulaire et du auriculare Metacarpiano del pulgar, del índice, del medio, del anular y del meñique • • • • • • • • • • Basis Base Basis Base Base • • • • • Corpus Body Schaft Diaphyse Diáfisis • • • • • Collum Neck Hals Col Cuello • • • • • Caput Head Köpfchen Tête Cabeza Ossa digitorum manus (Phalanges) Bones of the fingers Fingerknochen Os de doigts de la main Huesos de los dedos Phalanx proximalis Proximal phalanx Grundgliedknochen (Grundphalanx) Phalange proximale (Phalange, P1) Falange proximal Phalanx media Middle phalanx Mittelgliedknochen (Mittelphalanx) Phalange moyenne (Phalange, P2) Falange media Phalanx distalis Distal phalanx Endgliedknochen (Endphalanx) Phalange distale (Phalange, P3) Falange distal • • • • • Basis phalangis Base of the phalanx Basis des...gliedknochens Base de la phalange Base de la falange • • • • • Corpus phalangis Shaft of the phalanx Schaft des...gliedknochens Corps de la phalange Diáfisis de la falange • • • • • Caput phalangis Head of the phalanx Köpfchen des...gliednochens Tête de la phalange Cabeza de la falange • • • • • Condylus Condyles Gelenkknorren Condyles Cóndilos • • • • • Tuberositas phalangis distalis Tuberosity of the distal phalanx Nagelkranz des Endgliedknochens Tubercule de la phalange distale Tuberosidad de la falange distal Ossa sesamoidea Sesamoid bones Sesambeine Os sésamoïde Huesos sesamoideos Top JOINTS • • • • • Articulationes Joints Gelenke Articulations Articulaciones • • • • • Capsula articularis Articular capsule Gelenkkapsel Capsule articulaire Cápsula articular • • • • • Ligamenta Ligaments Bänder Ligaments Ligamentos • • • • • Membrana synovialis Synovial membrane Synovialmembran (Gelenkinnenhaut) Membrane synoviale Membrana sinovial • • • • • Artticulatio humero-ulnaris Humero-ulnar joint Humeroulnar-Gelenk Articulation Humero-ulnaire ou Humero-cubitale Articulación húmero-cubital • • • • • Articulatio humero-radialis Humero-radial joint Humeroradial-Gelenk Articulation Humero-radiale Articulación húmero-radial • • • • • Articulatio radio-ulnaris proximalis Proximal radio-ulnar joint Proximales Radioulnar-Gelenk Articulation radio-cubitale proximale Articulación radio-cubital proximal • • • • • Articulatio radio-ulnaris distalis Distal radio-ulnar joint Distales Radioulnar-Gelenk Articulation radio-ulnaire distale Articulación radio-cubital distal Ligamentum radio-ulnare (dorsale et palmare) Dorsal and palmar radio-ulnar ligaments Lig. radioulnare (dorsale und palmare) Ligaments radiolunaires (dorsal et palmaire) Ligamentos radio-cubitales (dorsal y palmar) Discus articularis Triangular fibrocartilage complex Discus articularis (Zwischengelenkscheibe) Ligament triangulaire Fibrocartílago triangular Ligamentum ulno-carpale Meniscus homologue Lig. ulnocarpale Ligaments ulno-carpiens Ligamentos cúbito-carpianos • • • • • Articulatio radiocarpalis Radiocarpal joint Proximales Handwurzelgelenk Articulation radio-carpienne Articulación radio-carpiana Ligamenta radio-carpalia dorsalia Dorsal radiocarpal ligaments Dorsale radiokarpale Bänder Ligaments radio-carpiens dorsales Ligamentos radio-carpianos dorsales • • • • • Ligamentum radio-lunatum Dorsal radiolunate ligament Lig. radiolunatum Ligament radio-lunaire Ligamento radio-semilunar dorsal • • • • • Ligamentum radio-triquetrum Radiotriquetral ligament Lig. radiotriquetrum Ligament radio-pyramidal Ligamento radio-piramidal Ligamenta. radiocarpalia palmaria Palmar radiocarpal ligaments Palmare Radiokarpal-Bänder Ligaments radio-carpiens palmaires Ligamentos radio-carpianos palmares • • • • • Ligamentum radio-scapho-capitatum Radio-capitate ligament Lig. radio-scapho-capitatum Ligament radio-capital Ligamento radio-capitate (-hueso grande) • Ligamentum radio-lunatum longum • Long radio-lunate ligament • Lig. radiolunatum longum • Ligament radiolunaire long • Ligamento radio-semilunar largo • • • • • Ligamentum radio-lunatum breve Short radio-lunate ligament Lig. radiolunatum breve Ligament radiolunaire court Ligamento radio-semilunar corto Ligamentum ulno-carpale palmare Palmar ulno-carpal ligaments Lig. ulnocarpale palmare Ligaments cubito-carpiens antérieurs (palmaires) Ligamentos cúbito-carpianos anteriores (palmares) • • • • • • • • • • Ligamentum ulno-triquetrum Ulnotriquetral ligament Lig. ulnotriquetrum Ligament cubito-triquetral ou cubito-pyramidal Ligamento cúbito-piramidal • • • • • Ligamentum ulno-lunatum Ulnolunate ligament Lig. ulnolunatum Ligament ulno-lunaire Ligamento cúbito-semilunar • • • • • Ligamentum ulno-capitate Ulnocapitate ligament Lig. ulnocapitatum Ligament cubito-capital Ligamento cúbito-capitate (-hueso grande) Articulatio mediocarpalis Midcarpal joint Distales Handwurzergelenk Articulation médiocarpienne Articulación mediocarpiana Ligamenta intercarpalia dorsalia Posterior midcarpal joint ligament Ligamenta intercarpalia dorsalia Ligament intercarpien dorsal Ligamento mediocarpiano dorsal • • • • Ligamentum intercarpale dorsale Triquetrum-scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid ligament (dorsal intercarpal) Lig. intercarpale dorsale Ligament trapezo-trapezoide-triquetral (intercarpien dorsal) • Ligamento piramido-escafo-trapecio-trapezoide (transversal dorsal del carpo) Ligamenta intercarpalia palmaria Anterior midcarpal joint ligaments Ligamenta intercarpalia palmaria Ligaments mediocarpiens anterieurs (palmaires) Ligamentos mediocarpianos anteriores (palmares) Ligamentum triquetro-hamatum Triquetrohamate ligament Lig. triquetrohamatum Ligament pyramido-unciformien Ligamento piramidal-hueso ganchoso Ligamentum triquetro-capitatum Triquetrum-capitate ligament Lig. triquetrocapitatum Ligament pyramido-caìtal Ligamento piramidal-capitate (-hueso grande) Ligamentum scapho-capitatum Scaphocapitate ligament Lig. scaphocapitatum Ligament scapho-capital Ligamento escafo-capitate (-hueso grande) Ligamentum scapho-trapezio-trapezoideum Scapho-trapezio-trapezoid ligament Lig. scaphotrapeziotrapezoideum Ligament scapho-trapezo-trapezien Ligamento escafo-trapecio-trapezoide • • • • • Articulationes intercarpales Intercarpal joint Interkarpal-Gelenke Articulationes intercarpiennes Articulaciones intercarpianas Ligamenta intercarpalia interossea (dorsale et palmare) Interosseous intercarpal ligaments (dorsal and palmar) Dorsale interkarpale Bänder (dorsale und palmare) Ligaments interosseux intercarpiens (dorsales et palmares) Ligamentos interóseos intercarpianos (dorsales y palmares) • • • • • Ligamentum scapho-lunatum (dorsale et palmare) Scapho-lunate ligaments (dorsal and palmar) Lig. Scapholunatum (dorsale und palmare) Ligament escapholunaire Ligamentos escafo-semilunares (dorsal y palmar) • • • • • • • • • • Ligamentum luno-triquetrum (dorsale et palmare) Luno-triquetral ligaments (dorsal and palmar) Lig. Lunotriquetrum (dorsale und palmare) Ligament lunotriquetral Ligamentos luno-piramidales (dorsal y palmar) • • • • • Ligamentum trapeziotrapezoideum Trapeziotrapezoid ligament Lig. Trapezio-trapezoideum Ligament trapezo-trapezoidal Ligamento trapecio-trapezoide • • • • • Ligamentum trapezoido-capitatum Capitotrapezoideum ligament Lig trapezoidocapitatum Ligament capitato-trapezoide Ligamento trapezoide-capitate (-hueso grande) • • • • • Ligamentum hamato-capitatum Capitohamate ligament Lig. hamatocapitatum Ligament capitohamatal Ligamento ganchoso-capitate (-hueso grande) Articulatio ossis pisiformis Pisotriquetral joint Articulatio ossis piriformis Articulation piso-`yramidale Articulación piso-piramidal Ligamentum pisohamatum Pisohamate ligament Lig. pisohamatum Ligament pisounciforien Ligamento pisiforme-ganchoso Ligamentum pisometacarpale Pisometacarpal ligament Lig. pisometacarpale Ligament pisi-métacarpien Ligamento pisiforme-metacarpiano • • • • • Articulationes carpometacarpales Carpometacarpal joints (CMCJ) Karpometakarpal-Gelenke Articulation carpometacarpie Articulaciones carpometacarpianas Ligamenta carpometacarpalia dorsalia Dorsal carpometacarpal ligaments Ligg. carpometacarpalia dorsalia Ligament carpométacarpien dorsal Ligamentos carpometacarpianos dorsales Ligamenta carpometacarpalia palmaria Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments Ligg. Carpometacarpalia palmaria Ligaments carpométacarpiens palmaires Ligamentos carpometacarpianos palmares • • • • • Articulatio carpometacarpale pollicis Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb (trapezio-metacarpal) Karpometakarpal-Gelenk des Daumens (Daumen-Sattelgelenk) Articulation carpométacarpienne du pouce (trapezo-metacarpienne) Articulación carpometacarpiana del pulgar (trapecio-metacarpiana) Ligamentum trapeziometacarpale (volar ligament) Anterior ligament Lig. trapeziometacarpale Ligament trapezo-métacarpien palmaire Ligamento trapecio-metacarpiano palmar Ligamentum carpometacarpale obliquum anterius Anterior oblique liga,ent Lig carpometacarpale obliquum anterius Ligament trapezo-métacarpien oblique palmaire Ligamento trapezio-metacarpiano oblicuo anterior Ligamentum carpometacarpale obliquum posterius Posterior oblique ligament Lig. carpometacarpale obliquum posterius Ligament trapezo-métacarpien oblique dorsal Ligamento trapezio-metacarpiano oblicuo posterior Ligamentum carpometacarpale dorsoradiale Dorsoradial ligament Lig. carpometacarpale dorsoradiale Ligament trapezo-métacarpien oblique dorsoradial Ligamento trapezio-metacarpiano dorso-radial • • • • • Articulationes intermetacarpales Intermetacarpal joints Intermetakarpal-Gelenke Articulations intermétacarpennes Articulaciones intermetacarpianas Ligamenta metacarpalia dorsalia Dorsal metacarpal ligaments Ligg. metacarpalia dorsalia Ligaments métacarpiens dorsaux Ligamentos metacarpianos dorsales Ligg. metacarpalia palmaria Palmar metacarpal ligaments Lig. metacarpalia palmaria Ligament métacarpien palmaire Ligamentos metacarpianos palmares Ligamenta metacarpalia interossea Interosseous metacarpal ligaments Ligg. metacarpalia interossea Ligament métacarpien inter-osseux Ligamentos metacarpianos interóseos • • • • • Articulationes metacarpophalangeales Metacarpophalangeal joints (MCPJ or MPJ) Metakarpophalangeal-Gelenke (Grundgelenke) Articulations métacarpophalangiennes Articulaciones metacarpofalángicas Ligg. collateralia Collateral ligaments Seitenbänder (Kollateral-Bänder) Ligaments latéraux Ligamentos colaterales Lig. palmare Palmar ligament (palmar plate) Palmares Band (Palmare Platte) Ligament palmaire Ligamento palmar (placa palmar) Lig. metacarpale transversum profundum Deep transverse ligament of the palm (Interpalmar plate ligament) Tiefes queres Mittelhandband Ligament intermétacarpien transverse profond Ligamento transverso profundo de la palma (Ligamento interplaca palmar) • • • • • Articulatio interphalangealis (proximalis et distalis) Proximal interphalangeal joint (proximal and distal) Interphalangeal-Gelenk (proximales und distales) Articulation interphalangienne (proximale et distale) Articulación interfalángica (proximal y distal) Ligg. collateralia Collateral ligaments Seitenbänder Ligaments latéraux Ligamentos colaterales Ligamentum collaterale accesorium Accessory collateral ligament Lig. collaterale accesorium Ligament lateral accesoire Ligamento colateral accesorio Ligg. palmaria Palmar ligament Palmare Bänder (Palmare Platten) Ligament palmaire Ligamento palmar • • • • • Fibrocartilago palmaris Fibrocartilaginous portion (palmar plate) Palmare platte (Knorpeliger Anteil) Fibrocartilage glénoïdien Porción cartilaginosa (placa palmar) • • • • • ............................. Membranous portion (check-rein ligaments) Membranöser Anteil (Zügelbänder) Freins d'extension Porción membranosa Top MUSCLES. • • • • • Musculi Muscles Muskeln Muscles Músculos • • • • • Musculus brachioradialis Brachioradialis (BR) Brachioradialis Long supinateur (Muscle húmero-stylo-radial) Supinador largo • • • • • Musculus extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) Extensor carpi radialis longus Premier radial Primer radial • • • • • Musculus extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) Extensor carpi radialis brevis Deuxième radial Segundo radial • • • • • Musculus extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) Extensor carpi ulnaris Cubital postérieur Cubital posterior • • • • • Musculus extensor digitorum Extensor digitorum (ED) Extensor digitorum Extenseur commun des doigts Extensor común de los dedos • • • • • Musculus extensor indicis propius Extensor indicis (EI) Extensor indicis Muscle extenseur prope de l'index Extensor propio del índice • • • • • Musculus extensor digiti minimi Extensor digiti minimi (EDM) Extensor digiti minimi (quinti) Muscle extenseur prope du petit doigt Extensor propio del meñique • • • • • Musculus extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis longus (EPL) Extensor pollicis longus Long extenseur du pouce Extensor largo del pulgar • • • • • Musculus extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) Extensor pollicis brevis Court extenseur du pouce Extensor corto del pulgar • • • • • Musculus abductor pollicis longus Abductor pollicis longus (EPL) Abductor pollicis longus Long abducteur du pouce Abductor largo del pulgar • • • • • Musculus pronator teres Pronator teres (PT) Pronator teres Rond pronateur Pronador redondo • • • • • Musculus flexor carpi radialis Flexor carpi radialis (FCR) Flexor carpi radialis Grand palmaire Palmar mayor • • • • • Musculus palmaris longus Palmaris longus (PL) Palmaris longus Petit palmaire Palmar menor • • • • • Musculus flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) Flexor carpi ulnaris Cubital antérieur Cubital anterior • • • • • Musculus flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) Flexor digitorum superficialis (Oberflächlicher Fingerbeuger) Fléchisseur supeficiel des doigts Flexor superficial de los dedos • • • • • Musculus flexor digitorum profunds Flexor digitorum profunds (FDP) Flexor digitorum profundus (Tiefer Fingerbeuger) Fléchisseur commun profond des doigts Flexor profundo de los dedos • • • • • Musculus flexor pollicis longus Flexor pollicis longus (FPL) Flexor pollicis longus (Langer Daumenbeuger) Long fléchisseur propre du pouce Flexor largo del pulgar • • • • • Musculus pronator quadratus Pronator quadratus (PQ) Pronator quadratus Carré pronateur Pronador cuadrado • • • • • ........... Intrinsic muscles Handbinnenmuskeln Muscules intrinseques Músculos intrínsecos • • • • • Musculi lumbricales Lumbrical Muscles Lumbricales Muscles lombricaux Músculos lumbricales • • • • • Musculi interossei dorsales Dorsal interossei muscles Interossei dorsales Muscles interosseux dorsaux Músculos interóseos dorsales • • • • Musculi interossei palmares Palmar interossei muscles Interossei palmares Muscles interosseux palmaires • Músculos interóseos palmares • • • • • Musculi thenares Thenar muscles Thenarmuskeln (Daumenballenmuskeln) Muscles thénariens Músculos tenares Musculus abductor pollicis brevis Abductor pollicis brevis (APB) Abductor pollicis brevis Court abducteur du pouce Abductor corto del pulgar Musculus flexor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) Flexor pollicis brevis Court fléchisseur du pouce Flexor corto del pulgar Musculus opponens pollicis Opponens pollicis (OP) Opponens pollicis Opposant du pouce Oponente del pulgar Adductor pollicis Adductor pollicis (AP) Adductor pollicis Adducteur du pouce Aductor del pulgar • • • • • Musculi hypothenaris Hypothenar muscles Hypothenarmuskeln (Kleinfingerballenmuskeln) Muscles hypothenariens Músculos hipotenares Musculus abductor digiti minimi Abductor digiti minimi (ADM) Abductor digiti minimi Abducteur du petit doigt Abductor del meñique Musculus flexor digiti minimi brevis Flexor digiti minimi brevis (FDM) Flexor digiti minimi brevis Court fléchisseur du petit doigt Flexor corto del meñique Musculus opponens digiti minimi Opponens digiti minimi (ODM) Opponens digiti minimi Opposant du petit doigt Oponente del meñique Musculus palmaris brevis Palmaris brevis (PB) Palmaris brevis Palmaire cutané Palmar cutáneo Top TENDONS. • • • • • Tendines Tendons Sehnen Tendons Tendones • • • • • Connexus intertendineus Intertendinous connection Connexus intertendineum Bandelettes intertendineuses Conexiones intertendinosas • • • • • Aponeurosis dorsalis Extensor apparatus of the finger Streckapparat Aponevrose dorsale du doigt ou digitale dorsale Aparato extensor del dedo Lamina intertendinea superficialis Extensor hood Strecksehnenhaube Dossière des extenseurs Cofia (capuchón) de los extensores Pars transversa laminae intertendinae et ligamentum sagittale Sagittal bands Pars transversa der Lamina intertendinea (und Lig. sagittale) Cloisons sagitales Bandeletas sagitales Tractus intermedius Central slip Mittelzügel Bandelette mediane Bandeleta central Tractus laterales Lateral bands Seitenzügel Bandelettes laterales Bandeletas laterales Lamina triangularis Triangular ligament Lamina triangularis Ligament triangulaire Ligamento triangular Pars terminalis tractus lateralis Distal extensor tendon Pars terminalis tractus lateralis Tendon extenseur dustal Tendón extensor distal Ligamentum retinaculare transversum Transverse retinacular ligament Queres retinakulum (Landsmeer) Ligament retinaculaire transverse (Lig. de Landsmeer) Ligamento retinacular transverso Ligamentum retinaculare obliquum Oblique retinacular ligament Schräges Retinakulum (Landsmeer) Ligament.. retinaculaire oblique (Ligament de Landsmeer) Ligamento retinacular oblicuo • • • • • Vaginae fibrosa digitorum manus Flexor tendon sheath Fibröse Sehnenscheiden der Finger Gaines fibreuses des tendons fléchisseurs Vaina de los tendones flexores Pars anularis vaginae fibrosae (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5) Annular pulleys Ringband der Sehnenscheide Poulies annulaires Poleas anulares Pars cruciforme vaginae fibrosae (C1, C2, C3) Cruciform pulleys Kreuzförmiges Band der Sehnenscheide Poulies cruciformes Poleas cruciforme Vaginae synoviales digitorum manus Synovial sheaths of the fingers (Synovial sheaths of the finger flexors) Synoviale Sehnenscheiden der Finger Gaines séreuses des tendons des doigts Vainas sinoviales de los tendones flexores de los dedos • • • • Vincula tendinea Vincula of the tendons Vincula tendinum Mesotendons (vincula tendinum) • Vínculas tendinosas Vinculum longum Long vinculum Langes Vinculum Mesotendon long Víncula larga Vinculum brevis Short vinculum Kurzes Vinculum Mesotendon court Víncula breve • • • • • Chiasma tendinum Chiasma of the tendom Chiasma tendinum Chiasma tendineux Quiasma tendinoso Top FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. • • • • • Fascia Fascia Faszie Aponévrose Fascia • • • • • Fascia antebrachili Antebrachial fascia (forearm fascia) Fascia anterbrachii (Unterarmfaszie) Aponévrose de l'avant bras Fascia del antebrazo (fascia antebraquial) • • • • • Fascia dorsalis manus Dorsal fascia of the hand Fascia dorsalis manus (Handrückenfaszie) Aponévrose dorsale de la main Fascia dorsal de la mano • • • • • Retinaculum extensorum Extensor retinaculum Retinaculum extensorum (Dorsales Handgelenksband) Ligament annulaire dorsal du carpe Retináculo extensor • Retinaculum flexorum • • • • Flexor retinaculum Retinaculum flexorum (Queres Handgelenksband) Ligament annulaire antérieur du carpe Retináculo flexor • • • • • Aponeurosis palmaris Palmar aponeurosis (fascia) Palmaraponeurose Aprnévrose palmaire Aponeurosis (fascia) palmar Fasciculi transversi Transverse fibres Querzüge der Palmaraponeurose Ligament transverse superficiel Fibras transversas Fasciculi longitudinalis Longitudinal fibers (pretendinous bands) Längszüge der Palmaraponeurose Bandelettes prétendineuses Fibras longitudinales Lig. metacarpale transversum superficiale Natatory ligament Schwimmband Ligament métacarpien transverse superficiel Ligamento natatorio • • • • • Fascia digitorum Digital aponeurosis Fingerfaszie Aponevrose des doigts Fascia digital ...................... Skin retaining ligament Hautbänder Ligament suspenseurs de la peau Ligamentos de retención cutánea ................................ Clelenad's ligament Clelandsche Bänder Ligament de Cleland Ligamento de Cleland ............................. Grayson's ligament Graysonsche Bänder Ligament de Grayson Ligamento de Grayson ..................... Lateral digital bans of small finger Abduktorstrang Bandelette laterale de l'auriculaire Bandeleta lateral del dedo meñique Top NERVES. • • • • • Nervi Nerves Nerven Nerfs Nervios • • • • • Epineurium Epineurium Epineurium Epinèvre Epineuro • • • • • Perineurium Perineurium Perineurium Périnèvre Perineuro • • • • • Endoneurium Endoneurium Endoneurium Endonèvre Endoneuro • • • • • Neuron (Axon, Dendritum, Glyocitus perophericus) Nerve fiber (axon, dendrite, Schwann cells and connective tissue) Nervenfaser (Axon, Dendrit, Schwannzellen und Bindegewebe) Fibre nerveuse (axone, dendrite, celules de Schwann et tissue connective) Fibra nerviosa (axón, dendrita, células de Schwann y tejido conectivo)) • • • • • Funiculus (fasciculus) Bundle Faszikel (Nervenfaserbündel) Fascicule Funiculo (fascículo) • • • • • Plexus brachialis Brachial plexus Plexus brachialis (Armnervengeflecht) Plexus brachial Plexo braquial Radices Roots Wuerzeln Racines Raices Truncus superior Upper trunk Oberer Stamm (Primärstrang) Tronc primaire supérieur Tronco superior Truncus medius Middle trunk Mittlerer Stamm (Primärstrang) Trone primaire moyen Tronco medio Truncus inferior Lower trunk Unterer Stamm (Primärstrang) Tronc primaire inférieur Tronco inferior Divisio anterioris Anterior divisions Vordere Aufteilung Branche antérieure Ramas anteriores Divisio posterioris Posterior division Hintere Aufteilung Branche postérieure Ramas posteriores Fasciculus lateralis Lateral cord Lateraler Strang Tronc secondaire antero-externe Cordón lateral Fasciculus medialis Medial cord Medialer Strang Tronc secondaire antero-interne Cordón medial Fasciculus posterior Posterior cord Posteriorer (Hinterer) Strang Tronc secondaire postérieur Cordón posterior • Nervus radialis • • • • Radial nerve Speichennerv Nerf radial Nervio radial N. interosseus antebrachii posterior Posterior interosseous nerve of the forearm N. interosseus antebrachii posterior Nerf interosseux postérieur Nervio interóseo posterior Ramus superficialis nervus radialis Superficial sensory branch of the radial nerve Ramus superficialis (Oberflächlicher Ast) Branche sensitive du nerf radial Rama sensitiva del nervio radial • • • • • Nervus medianus Median nerve Medianus (Mittelnerv) Nerf médian Nervio mediano N. interosseus antebrachii anterior Anterior intereosseous nerve N. interosseus antebrachii anterior Nerf interosseux anterieur Nervio interóseo anterior Ramus palmaris n. mediani Palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve Ramus palmaris n. mediani Rameau thénarien (Branche thénarienne) Rama palmar cutanea del nervio mediano Ramus muscularis tenaris Motor branch of median nerve Thenarast Branche musculaire thénarienne Rama tenar del nervio mediano Ramus communicans cum n. ulnaris (Riche-Cannieu) Beanch Communicating with the ulnar nerve Ramus communicans cum n. ulnaris Rameau anastomotique avec le nerf cubital Ramo comunicante con el nervio cubital Nervio digitales communes Common palmar digital nerves Nn. digitales palmares communes (gemeinsame Fingernerven) Nerf digital commun du 1er, 2ème, 3ème espace Nervios digitales comunes Nervio digitales (palmares) propii Proper digital nerves Nn. digitales (palmares) proprii (Fingernerven) Nerf collateraux palmaires (interne et externe) Nervios digitales propios (radial y cubital) Nervi digitales dorsales Dorsal branche of the digital nerve Dorsale Fingernerven Rameau nerveux dorsal Rama dorsal del nervio digital • • • • • Nervus ulnaris Ulnar nerve Ulnaris Nerf cubital Nervio cubital Ramus communicans cum nervo mediano (Martin-Gruber) Communicating branch with the median nerve Ramus communicans cum n. mediano Rameau anastomotique avex le nerf médian Ramo comunicante con el nervio cubital Ramus dorsalis nervi ulnaris Dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve Ramus dorsalis n. ulnaris Branche cutanée dorsale du rerf cubital Rama dorsal de nervio cubital Ramus palmaris nervi ulnaris Palmar branch of the ulnar nerve Ramus palmaris n. ulnaris Branches palmaires du cubital Rama palmar del nervio cubital Ramus profundus Deep motor branch Ramus profundus Branche profonde du nerf cubital Rama motora profunda del nervio cubital Top VESSELS. • • • • • Arteria Arteries Arterien Arteres Arterias • Arteria radialis • • • • Radial artery Arteria radialis (Speichenschlagader) Artère radiale Arteria radial • • • • • Arteria ulnaris Ulnaris Artery A. ulnaris (Ellenschlagader) Artère cubitale Arteria cubital • • • • • Arteria interossea posterior Posterior interosseous artery A. interossea posterior Artère interosseuse postérieure Arteria interósea posterior • • • • • Arteria interossea anterior Anterior interosseous artery A. interossea communis Artère interosseuse antérieure Arteria interósea anterior • • • • • Arteria mediana Median artery A. mediana Artère du nerf médian Arteria del nervio mediano • • • • • Arcus palmaris superficialis Superficial palmar arch Oberflächlicher Hohlhandbogen Artère radiopalmaire Arco palmar superficial • • • • • Arcus palmaris profundu Deep palmar arch Tiefer Hohlhandbogen Arcade palmaire profonde Arco palmar profundo • • • • • Arteria metacarpales dorsales Dorsal metacarpal arteries Aa. metacarpales dorsales Artères interosseuses dorsales de la main Arterias intermetacarpianas dorsales • • • • • Arteriae metacarpales palmares Palmar metacarpal arteries Aa. metacarpales palmares Artères interosseuses palmares Arterias intermetacarpianas palmares • • • • • • • • • • Rami perforantes Perforating branches Rami perforantes Artères perforantes de la main Ramas perforantes • • • • • Arteriae digitales palmares communes Common palmar digital arteries Aa. digitales palmares communes Artères interosseuses palmaires Arterias digitales palmares comunes • • • • • Arteriae digitales propriae Proper digital arteries (radial and ulnar) Aa. digitales propriae Artères collatérales des doigts (interne et externe) Arterias digitales propias (radial y cubital) • • • • • Arteria princeps pollicis Princeps pollicis artery A. princeps pollicis Artère dorsale du pouce Arteria principal del pulgar Venae Veins Venen Veines Venas • • • • • Rete venosum dorsale manus Dorsal venous network of the hand Rete venosum dorsale manus (Venöses Handrückengeflecht) Arcade veineuse dorsale de la main Red venosa dorsal de la mano Top SKIN and ACCESSORIES. • • • • • Cutis Skin Haut Peau Piel • • • Epidermis Epidermis Epidermis • • Epiderme Epidermis • • • • • Corium (Dermis) Dermis Korium (Dermis) Lederhaut Derme Dermis • • • • • Cristae cutis Rugae Cristae cutis (Papillarlinien) Crêtes papilaires Crestas papilares • • • • • ............................. Finger prints Fingerabdruck Empreintes digitales. Emoreintes digito-palmaires. (Dermatoglyphes) Huellas dactilares (Dermatoglifos) • • • • • Tela subcutanea Subcutaneous tissue Unterhautfettgewebe (Subkutangewebe) Tissu cellulaire sous cutanee Tejido graso subcutáneo • • • • • Sulci cutis Skin creases Furchen Plis de flexion Pliegues de flexión cutáneos Linea carpi palmaris (proximalis et distalis) Wrist creases (proximal and distal) Handgelenksbeugefurche (proximale:Restricta; distale:Raszetta) Sillons du poignet Pliegues de flexión de la muñeca (proximal y distal) Sulcus longitudinalis thenaris (lateralis) Longitudinal thenar crease Daumenballenfurche Pli palmaire superieur ou thenarien Pliegue longitudinal tenar Sulcus longitudinalis medianus (intermedius) Longitudinal median crease Mittlere Furche Pli longitudinal interne Pliegue longitudinal medio Sulcus longitudinalis hypothenaris Longitudinal hypothenar crease Ulnare Furche Pli longitudinal hypothenarien Pliegue longitudinal hipotenar Sulcus tranversalis radialis Proximal palmar crease Proximale Hohlhandbeugefurche Pli palmaire moyen Pliegue palmar proximal Sulcus transversalis ulnaris Distal palmar crease Distale Hohlhandbeugefurche Pli palmaire inferieur Pliegue palmar distal ......................... Palmar-digital crease Grundgliedbeugefurche Pli digito-palmaire Pliegue digito-palmar ........................ Proximal interphalangeal joint crease Mittelgelenksbeugefurche Pli de l'interphalangienne proximale Pliegue de flexión de la articulación interfalángica proximal ............................. Distal interphalangeal joint crease Endgelenksbeugefurche Pli de l'interphalangienne distale Pliegue de la articulación interfalángica distal • • • • • Unguis Nail Nagel Ongle Uña Matrix unguis Nail matrix Nagelmatrix Matrice Matriz ungueal Lectulus (Solum unguis) Nail bed Nagelbett Lit de l'ongle (Sole unguéale) Lecho ungueal Lunula Lunula Lunula Région lunulaire Lúnula Margo liber Free margin Freier Rand Extremité libre Extremo libre (borde libre) Perionychium Naid bed plus nail wall Nagelhaut (Perionychium) Perionychium Perioniquio Eponychium Cuticle Eponychium Eponychium Eponiquio Hyponychium Hyponychium Hyponychium Hyponuchium Hiponiquio Paronychium Paronychium Paronychium Paronychium Paroniquio Top GENERAL • • • • • • • • Non prehensile functions Nichtgreiffunktionen Functions non prehensives Funciones no prensiles Prehensile functions Greiffunktion Fonctions de préhension Funciones de prensión • • • • Power handling Krattentwicklung Prise de force Prensión de fuerza Power grip and hook grip Kraftgriff (Grobgriff) und Hakengriff Poigne Prensión de puño y prensión de gancho Lateral pinch (Key pinch) Fingerseitgriff, Schlüsselgriff Prise lateral Prensión lateral (Prensión de llave) • • • • Precision handling Präzisionsgriff Prise de precision Funciones de precisión Pulp to pulp pinch Feingriff Pince pulpaire Presión de pulpejo con pulpejo Nail to pulp pinch Nagel-Kuppengriff Pince unguéo-pulpaire Prensión de uña a pulpejo Nail to nail pinch Nagel-Nagel griff Pince unguéo-ungueal Prensión de uña a uña Top JOINTS. • • • • Positions Positionen (Stellungen) Positions Posiciones • • • • Rest position (Neutral position) Ruhestellung (Neutralstellung) Position de repos Posición de reposo • • • • Functional position (position of arthrodesis) Funktionsstellung Position de fonction Posición funcional (posición de artrodesis) • • Protective position or safe position (intrinsic plus) Schutzstellung (Plateaustellung) • • Position de protection Posición protectiva (intrínsico plus) • • • • Motion Beweglichkeit Mouvement Movimiento • • • • Range of motion Bewegungsumfang Amplitude de movement Grado de movilidad • • • • • • • • • • • • Active motion Aktive Beweglichkeit Mobilisation active Movilidad activa • • • • Passive motion Passive Beweglichkeit Mobilisation passive Movilidad pasiva Elbow Ellleubogen Coude Codo • • • • Flexion Beugung Flexion Flexión • • • • Extension Streckung Extension Extensión • • • • Hyperextension Überstreckung Hyperextension Hiperextensión Forearm Unterarm Avant Bras Antebrazo • • • • Pronation (Internal rotation) Pronation (Innendrehung) Pronation Pronación • • • • • • • • • • • • Supination (External rotation) Supination (Aussendrehung) Supination Supinación Wrist Handgelenk Poignet Muñeca • • • • Flexion Beugung Flexion Flexión • • • • Extension Streckung Extension Extensión • • • • Radial inclination Radialduktion Inclinaison radiale Inclinación radial • • • • Ulnar inclination Ulnarduktion Inclinaison cubitale Inclinación cubital Metacarpophalangeal Grundgelenk Métacarpophalangiennes Metacarpofalángicas • • • • Flexion Beugung Flexion Flexión • • • • Extension Streckung Extension Extensión • • • • Hyperextension Überstreckung Hyperextension Hiperextensión • • • Radial inclination (Spreading abduction or divergence) Abduktion (Abspreizung) Inclinaison radiale • • • • • • • • • Inclinación radial • • • • Adduction (Closing) Adduktion (Anspreizung) Inclinaison cubitale Inclinación cubital • • • • Pronation (Internal rotation) Pronation (Innendrehung) Pronation Pronación • • • • Supination (External rotation) Supination (Aussendrehung) Supination Supinación Interphalangeal Mittlse-und Endgelenk Interphalangiennes Interfalángicas • • • • Flexion Beugung Flexion Flexión • • • • Extension Streckung Extension Extensión • • • • Hyperextension Uberstreckung Hyperextension Hiperextensión Trapezio-metacarpal Sattelgelenk Trapezo-metacarpienne Trapecio-metacarpiana • • • • Radial abduction Radiale Abduktion Inclinaison radiale Abducción radial • • • • Palmar abduction Palmare Abduktion Abduction palmaire (antepulsion) Antepulsión (Abducción palmar) • Adduction • • • Adducktion (Flexion-Adduktion) Adduction Aduccion • • • • Dorsal adduction to zero position Retroposition, Retropulsion Adduction dorsal (Retropulsion) Retropulsión • • • • Opposition Opposition (Gegenüberstellung) Opposition Oposición Top MUSCLE and TENDON. • • • • Motor function Motorische Funktion Fonction motrice Función motora • • • • Muscle strength Muskelkraft Force musculaire Fuerza de contracción muscular • • • • Agonistic muscles Synergist Muscles synergiques Músculos agonistas • • • • Synergistic contraction Synergistische Kontraktion Contraction synergique Contracción sinergística • • • • Antagonistic muscles Gegenspieler (Antagonist) Muscles antagonistes Músculos antagonistas • • • • Trick movement Trick-Bewegung Mouvement simulé Movimientos trucados • Functional adaptation • Funktionelle Anpassung (Funktionelle Adaptation) • Adaptation fonctionnelle • Adaptación funcional • • • • Tendon gliding Sehnengleiten Glissement (Jeu) tendineux Deslizamiento tendinoso Top NERVES. • • • • Sensory function Sensible Funktion Fonction sensorielle Función sensorial • • • • Tactile sensibility Taktile Sensibilität (Berührungsgefühl) Sensibilité tactile Sensibilidad tactil • • • • Epicritic sensation Epikritische Sensibilität Sensibilité épicritique Sensibilidad epicrítica • • • • Stereognosis (Position sense) Stereognosis (Lagesinn) Stéréognosie (Sens de position) Estereognosia (Sentido de posición) • • • • Proprioception Propriozeptive Sensibilität (Muskelsinn) Sensibilité proprioceptive Sensibilidad proprioceptiva • • • • Protophatic sensation Protopathische Sensibilität Sensibilité protopathique Sensibilidad protopática • • • • Protective sensibility Schutzsensibilität Sensibilité de protection Sensibilidad protectiva • • • • Deep sensibility Tiefensensibilität Sensibiité profonde Sensibilidad profunda • • • • Pain Schmerz Douleur Dolor Top EXAMINATION: Symptoms, signs and tests. GENERAL. BONES JOINTS. MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESSORIES. VESSELS. Top GENERAL. • • • • Injury Verletzung Blessure Lesión • • • • Bruising Prellung Eraflure Magullamiento • • • • Crushing Quetschung Ecrasement Aplastamiento • • • • Wound Wunde Plaie Herida • • • • Contamination Contamination (Verschmutzung) Contamination Contaminación • • • • Swelling Schwellung Enflure, gonflement Hinchazón • • • • Oedema or oedema Ödem Oedème Edema • • • • Inflammation Entzündung Inflammation Inflamación • • • • Pain (tenderness) Schmerz Douleur Dolor • • • • Loss of function Funktionsverlust Perte de fonction Impotencia funcional • • • • Impairement Beeinträchtigung Deficience Deficiencia • • • • Handicap Behinderung Gêne (Limitation, Infirmité) Minusvalía • • • • Dissability Funktionverlust, Beeinträchtigung der Gebrauchsfähigkeit Inaptitude Discapacidad • Lump • Beule, Schwellung, Knoten, Verdickung, Tumor • Tumeur, masse, excroissance • Tumor, bulto • • • • Size Grösse Taille Tamaño • • • • Shape Form Forme Forma • • • • Consistency Konsistenz Consistance Consistencia • • • • Fluctuation Fluktuation Fluctuation Fluctuación • • • • Colo(u)r Farbe Coloeur Color Top BONES • • • • Crepitus Krepitieren Craquement, crépitation Crepitación • • • • Exostosis Exostose Exostose Exostosis • • • • Deformity Deformität, Fehlstellung Déformation Deformidad • • Shortening Verkurzung • • Raccourcissement Acortamiento • • • • Rotational deformity (pronation and supination) Drehfehlstellung (Torsionsfehlstellung) Deformation en rotation axiale Deformidad rotacional (pronación y supinación) • • • • Angular deformity (sagittal and coronal planes) Knickelfstellung Deformation angulaire, angulation Deformidad angular (planos sagital y coronal) • • • • Plain Radiograph Standard- Röntgenaufnahme Radiographie simple Radiografía simple • • • • Tomography Schichtaufnahme Tomographie Tomografía • • • • Computed Axial Tomography (CAT Scan) Computertomographie (CT) Scanner Tomografía Axial Computarizada (TAC) • • • • Magnetic Resonance Imaging (RMI) Kernspintomographie (MRT) Image en resonance magnetique (IRM, RMN) Resonancia Magnética (RM) • • • • Bone scan Knochen-Szintigraphie Scanner Gammagrafía ósea Top JOINTS. • • • • Crepitus Krepitieren (Reiben) Craquement, crépitation Crepitación • Swelling • Schwellung • Tuméfaction • Hinchazón • • • • Effusion Erguss Epanchement Efusión • • • • Synovitis Synovialitis Synovite Sinovitis • • • • Locking Blockierung Blocage Bloqueo • • • • Extension lag Streckdefizit Déficit d'extension Déficit de extensión activa • • • • Stiffness Steife, Versteifung Raideur Rigidez • • • • Flexion contracture Beugekontraktur Blocage en flexion Contractura en flexión • • • • Ankylosis Versteifung (Ankylose) Ankylose Anquilosis • • • • Deformity Deformität Déformité Deformidad • • • • Recurvatum Úberstreckung Courbure Recurvatum • • • • Ulnar drift Ulnare Deviation Coup de vent cubital Ráfaga cubital • • • • Zig-zag deformities Zickzack Zig-zag Deformidades en zig-zag • • • • Claw deformity Krallenstellung, Krauenstellung Griffe Deformidad en garra • • • • Mallet finger Strecksehnenausriss am Fingerendglied, Hammerfinger Doigt en maillet Dedo en martillo • • • • Buttonhole deformity Knopflochdeformität Deformation en boutonnière Deformidad en ojal • • • • Swan-neck deformity Schwanenhalsdeformität Deformation en col de cygne Deformidad en cuello de cisne • • • • Opera-glass deformity Opernglas-Deformität Deformation "en lorgnette" Deformidad en gemelos de teatro • • • • Ligamentous hyperlaxity Bänderschlaffheit Laxité ligamentaire Hiperlaxitud ligamentosa • • • • Instability Instabilität Instabilité Inestabilidad • • • • Bouchard's nodes Bouchard-Knoten Nodules de Bouchard Nódulos de Bouchard • • • • Heberden's nodes Heberden-Knoten Nodules de Heberden Nódulos de Heberden • Plain radiograph • Standard-Aufnahme • Radiographie simple • Radiografía simple • • • • Stress radiograph Gehaltene Aufnahme Radiographie sous contrainte Radiografía forzada (en estrés) • • • • Arthrography Arthrographie Arthrographie Artrografía • • • • Bone scan Knochen-Szintigraphie Scanner Gammagrafía ósea • • • • Arthroscopy Arthroskopie Arthroscopie Artroscopía Top MUSCLES. • • • • Muscle force (Power) Kraft Puissance, force musculaire Fuerza muscular • • • • Weakness Schwäche Faiblesse Debilidad • • • • Paresia Lähmung, Schwäche (Parese) Parésie Paresia • • • • Paralysis Schlaffe Lähmung (Paralyse) Paralysie Parálisis • Wrist-drop • Fallhand • Chute du poignet • Caida de la muñeca • • • • Atrophy (wasting) Atrophie (Muskelminderung) Atrophie Atrofia • • • • Spastidity Spastizität, Spasmus Spasticité, contracture Espasticidad • • • • Thumb-in-palm Beugekontraktur des Daumens Pouce "adductus" Pulgar en palma • • • • Contracture Kontraktur Retraction Contractura • • • • Twitch Zucken Clonus Fibrilación • • • • Trick movements Trickbewegungen Mobilité trichée Movimientos compensatorios • • • • Intrinsic-plus Intrinsic-plus Intrinsèque plus Intrínseco plus • • • • Lumbrical-plus Lumbrikalis-plus Lombrical plus Lumbrical plus • • • • Intrinsic minus Intrinsic-minus Intrinsèque moins Intrínseco minus • • • • Claw hand Krallenhand Griffe Mano en garra • Strength-duration curves (endurance) • Muskelkraftkurve • Courbe d'endurance • Pruebas de resistencia muscular • • • • Electromyography Elektromyographie Electromyographie Electromiografía • • • • Fibrilation potentials Fibrillationspotentialle Fibrilation Potenciales de fibrilación Top TENDONS. • • • • Tenosynovitis Tenosynovialitis Tenosynovite Tenosinovitis • • • • Crepitus Krepitation, Knistern, Knarren, Reiben Crépitation Crepitación • • • • Triggering Shnellen, Schnappen, Schnellender Finger Ressaut Resorte (Engatillamiento) • • • • Locking Blockierung Blocage Bloqueo • • • • Adhesions Adhäsionen, Verklebungen, Verwachsungen Adhérences Adheréncias • • • • Tenodesis Tenodese Tenodèse (Adhérence tendineuse) Tenodesis • Bow-stringing • Bogensehneneffekt • Trajet en corde de l'arc • Deformidad en cuerda de arco • • • • Tenography Tenographie Ténographie Tenografía Top FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. • • • • Nodule Knoten Nodule Nódulo • • • • Cord Strang Bride Cordón (Brida) Top NERVES. • • • • Numbness Taubheit Engourdissement Acorchamiento • • • • Par(a)esthesia Parästhesie (Fehlemfindung) Paresthésie Parestesia • • • • Hyp(a)esthesia Hypästhesie (Gefühlsverminderung) Hypoesthésie Hipoestesia • Anaesthesia (Anesthesia) • Anästhesie (Gefühlosigkeit) • Anesthésie • Anestesia • • • • Thermoan(a)esthesia Warm-Kaltempfindungslosigkeit Anesthesie thermique Termoanastesia • • • • Analgesia Analgesie Analgesie Analgesia • • • • Hyperalgesia Hyperalgesie Hyperalgesie Hiperalgesia • • • • Dys(a)esthesia Dysästhesie (Missempfundung) Dysesthésie Disestesia • • • • Phantom limb Phantom Membre fantome Miembro fantasma • • • • Causalgia Kausalgie Causalgie Causalgia • • • • Astereognosis Astereognose Astéréognosie Anestereognosis • • • • Light touch Leichte Berührung Effleurement Tacto superficial • • • • Two-point discrimination (Weber test) (moving and static) (2 PD) Zweipunke-Unterscheidungsvermögen, Zweipunkte - Diskrimination, ( 2- PD) Reconnaissance de deux points Discriminación de dos puntos (en movimiento y estáticos) • • • • Pressure filaments (von Frey and Semmes- Weinstein test) Semmes-Weinstein-Haartest Presion de filaments Test de los filamentos de Semmes-Weinstein • Vibrometers (tunning fork) (30 and 256 cps) • Simmgabel-Test • Diapason • Vibrómetro (diapasón) • • • • Pain sensation Schmerzempfindung Sensibilité douloureuse Sensación dolorosa • • • • Temperature sensation Temperaturempfindung Sensibilité thermique Sensación térmica • • • • Stereognosis Stereognose Stéréognosie Estereognosis • • • • Tinel's sign Hoffmann-Tinel-Zeichen Signe de Tinel Test de Tinel • • • • Neurography Neurographie Neurographie Neurografía • • • • Conduction studies (NCS) Nervenleitungsuntersuchungen Etude des conductions Estudio de la conducción nerviosa • • • • Nerve conduction velocity (sensory and motor) (NCV) Nervenleitgeschwindigkeit Vitesse de conduction nerveuse Velocidad de conducción nerviosa (sensitiva y motora) • • • • Latency Latenz Latence Latencia Top SKIN and ACCESSORIES. • Itching • • • Jucken Démangeaison, Prurit Prurito • • • • Sweating Schwitzen Sudation Sudoración • • • • Anhidrosis Anhidrose, Hautttrockenheit Anhidrose Anhidrosis • • • • Hyperhidrosis Hyperhidrose, starkes Schwitzen Hyperhidrose Hiperhidrosis • • • • Fragility Brüchigkeit Fragilité Fragilidad • • • • Puncture Stich Piqure Pinchazo • • • • Blister Blase Ampoule, phlyctène Flictena • • • • Laceration or cut Zerreissung oder Schnitt Plaie franche, coupure Herida (corte) • • • • Sinus Sinus, Fistel Fistule Fístula • • • • Ulcer Geschwür, Ulkus Ulcère Ulcera • • • • Eschar Schorf, Borke Escarre Escara • • • • Scar Narbe Cicatrice Cicatriz Contracture Kontraktur Cicatrice rétractile Contractura Hypertrophic Überschiessend, hypertroph Hipertrophique, Chéloïde Hipertrófica Hyperpigmentation Hyperpigmentation Hyperpigmentation Hiperigmentación Depigmentation Pigmentlosigkeit Dépigmentation Despigmentación Adherence Verwachsung, Verklebung Adhérence Adherencia • • • • Nail and nail bed Nagel und Nagelbett Ongle et lit unguéal Uña y lecho ungueal • • • • Pitting Krypte, Einziehung, Delle Tomentueux Picoteado • • • • Splitting Gespalten Friable Partida • • • • Groving or guttering Rille, Furche, Rinne En tuile (cannelure) Estrías ungueales • • • Non-adherent Nicht verwachsen Décollé • Despegada • • • • Remmant Rest Résidu Residual Top VESSELS. • • • • Pallor Blässe Paleur Palidez • • • • Cyanosis Zyanose Cyanose Cianosis • • • • Raynaud's phenomenon Raynaud-Phänomen Phénomène de Raynaud Fenómeno de Raynaud • • • • Hyper(a)emia Hyperämie Hyperémie Hiperemia • • • • Pulse Puls Pouls (Pulsation) Pulso • • • • Pulselessness Pulslosigkeit Sans pouls, ansphygmie Ausencia de pulso • • • • Capillary refilling Kapillar-Reflux, -Füllung Retour capillaire Relleno capilar • Petechiase • Petechien, Blutfleck • Pétéchies • Petequia • • • • Ecchimosis Ekchimose Echymose Equimosis • • • • H(a)emorrhage Blutung Hemorragie Hemorragia • • • • H(a)ematoma Bluterguss Hématome Hematoma • • • • Splinter h(a)emorrhages Blutung unter dem Fingernagel Suffusion hémorragique sous-unguéale, Hematome sous unguéal Hematoma subungueal • • • • Arteriography Arteriographie Artériographie Arteriografía • • • • Doppler ultrasonic scanner Doppler Examen Doppler (Velocimetrie par Doppler) Doppler • • • • Venography Venographie (Phlebographie) Phlébographie Venografía (Flebografía) • • • • Lymphangiography Lymphographie Lymphangiographie Linfografía Top PATHOLOGY CONGENITAL BONES. JOINTS. MUSCLES. TENDONS. FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. NERVES. SKIN and ACCESORIES. VESSELS. Top CONGENITAL Congenital abnormalities: Note: The Greek names formely used to describe congenital abnormalities of the hand anf arm are not included here because they are the same in any modern language and because their use is discouraged by the International Federation of Societies for Surgery of the Hand. Syndromes known by the name of a person are also omitted here, as they are the same in any language. A full list with definitions of greek terms and eponymic syndromes is given at the end of A.E. Flatt's book The Care of Congenital Hand Abnormalities (St. Louis,1977, The C.V. Mosby Co), and in Dieter Buck-Gramcko's chapter on "Congenital Malformation" in Handchirurgie, vol. I, edited by H. Nigst, D. Buck-Gramko, and H. Millesi (Stuttgart, 1981, Thieme). The recommended system is that evolved by American Society for Surgeryu of the hand and described in Swanson AB: Classification for congenital limb malformations. J Hand Surg 1:8-22, 1976. This is not so much a vocabulary as a method of description, but we list below the words that are most commonly used in descriptions and some examples of vernacular names of the parts affected to describe the abnormality in each individual. Angeborene Fehlbildungen: Anmerkung: Die früher gebräuchlichen griechischen Bezeichnungen für angeboreme Fehlbildungen der Hand und des Armes sind hier nicht eingeschlosen, da sie in jeder modernen Sprache in fast gleicher Weise gebraucht werden un ihre weitere Verwendung dunch die Vrschläge der International Federation of Societes for Surgery of the Hand nicht mehr empfohlen wurden. Ebenso sind syndrome, die durch den Namen einer Person gekennzeichnet sind, ausgelassen worden, da sieebenfalls in jeder Sprache gleichartig lauten Eine vollständige Liste und Definition der griechischen und lateinischen Bezeinchnungen und mit Namen vervundenden Sydromen findet sich am Ende des Buhes von A.E. Flatt, The Care of Congenital Hand Abnormalities (St. Louis, 1977, The C.V. Mosby Co.) Und in Dieter Buck-Gramcko's Kapitel über angeborene Fehlbikdungen der Hand im I. Band des Buches Hand-chirurgie, herausgegeben von H. Nigst, D. Buck-Gramcko und H. Millesi, (Stuttgart, 1981, Thieme). Das zur Benutzung empfohlene System ist von der Amerikanischen Gesellschaft für Habdcgirurgie ebtwickelt und beschrieben in Swanson AB: Classification for congenital limb malformations. J. HAND SURG 1:8-22, 1976. Es handelt sich dabei nicht so sehr um eir Wörterverzeichnis, als mehr eine Beschreibung. Nachfolgend haben wir eine Reihe von Wörten und Begriffen aufgelistet, die am häufigsten benutzt werden, und einige Beispiele von fachlichen Bezeichnungen hinzugefügt. Diese Bezeichnungen werden meist gemeinsam mit den gewöhnlichen anatomischen Bamen der beteiligten Körperteile benutzt, um die Fehlbildungen der einzelnen Person zu beschreiben Anomalies congénitales: Note: Les termes grecs autrefois utilisés pour décrire les malformations congénitales du membre supérieur n'ont pas été retenus ici car ils sont les mêmes dans toutes les langues et surtout leur emploi n'est pas approuvé par la Fédération Internationale des Sociétés de Chirurgie de la Main. De même les syndrômes portant un nom prope n'ont pas été retenus car ils sont également les mêmes dans chaque langue. Une liste complète avec la définition des termes grecs et des syndrômes à noms propes existe à la fin du livre d' A. E. Flatt, The Care of Congenital Hand Abnormalities (St. Louis, 1977, The C. V. Mosby Co.) et dans le chapitre écrit par Dieter BuckGramvko sur les maldormations congénitales dans Hand Chirurgie, vol. I, de H. Nigst, D.Buck Gramcko, and H. Millesi (Stuttgart, 1981, Thieme). Le système proposé est celui qui a été retenu par la Société Américaine de Chirurgie de la Main et publié dans Swanson AB: Classifications. J Hand Surg 1:8-22, 1976. Il ne s'agit pas tant d'un vocabulaire que d'une méthode de description, mais nous avons donné ci-dessous les mots qui sont le plus souvent utilisés dans les descriptions et quelques exemples de termes propes à chaque langage pour désigner les éléments atteints afin de pouvoir décrire des anormalies propes à chaque cas particulier. Anomalías Congénitas: Nota: No se incluyen los nombres griegos comunmente utilizados para describir las anomalías congénitas de la mano y el brazo porque son los mismo utilizados en todos los idiomas modernos, y porque la Federación Internacional de Sociedades de Cirugía de la Mano desaconseja su uso. También se omiten los síndromes conocidos con el nombre de un autor, ya que son los mismos en cualquier idioma. En el final del libro de Flatt "The Care of Congenital Hand abnormalities," C:V: Mosby, St. Louis, 1977, y en el capítulo 1, editado por H. Nigst, escrito por D. Buck-Gramcko, y H. Millesi (Stuttgart, 1981, Thieme) se dá una lista completa de los términos griegos con su definición y de los síndromes eponímicos. El sistema recomendado es el desarrollo por la Sociedad Americana de Cirugía de la Mano y fue descrita Swanson AB: Clasification for Congenital limb malformations. J Hand Surg 1:8-22, 1976. No es tanto un vocabulario como un método de descripción. Más abajo se dan las palabras que son más usadas en las descripciones, y algunos ejemplos de nombres vernáculos de las partes afectas para describir la anomalía en cada individuo. • Failure of formation of parts, arrest of development: • Ausbleiben der Bildung einzelner Anteile, Hemmung der Entwicklung: • Arrèts de developpement: • Fallo de formación de partes, paro del desarrollo: • • • • Transverse terminal Querverlaufend Transverse Terminal transversa Absence (congenital amputation) Fehlen, Mangel Absence Ausencia (amputación congénita) Finger nubbins Fingerstummel Résidus digitaux Muñones digitales • • • • Transverse intercalated Quere interkalierte Phocomelie Transversa intercalada • • • • Longitudinal Längsverlaufend Longitudinal Longitudinal Radial Radial, speichenseitig Radial Radial • • • • Radial club-hand Klumphand Main bote radiale Mano zamba radial • • • • Absence of thumb Dammenaplasie Agenesie/absence de pouce Agenesia del pulgar • • • • Floating thumb Flottierender Daumen, Wackeldaumen Pouce flottant Pulgar flotante • • • • Hypoplastic thumb Daumenhypoplasie Hypotrophie du pouce Pulgar hipoplásico Central (cleft hand, ectrodactily) Zentral (Spalthand) Central Central (mano hendida, ectrodactilia) Ulnar Ulnar, ellenseitig Cubital Cubital • • • • Fauliure of separation or différentiation of parts: Ausbleiben der Differenzierung oder Trennung von einzelnen Anteilen: Absense de séparation, de différentiation: Fallo de separación o diferenciación de partes: • • • • Undescended shoulder Schulterblatthochstand Scapula alta Hombro no descendido • • • • Congenital fusions Angeborene Synostosen Fusion Congénitale Fusiones congénitas • • • • Radio-ulnar synostosis Radioulnare synostosis Synostose radio-cubitale Sinostosis radio-cubital • • • • Poland's syndrome Polands Syndrom Syndrome de Poland Síndrome de Poland • • • • Congenital contractures Angeborene Kontrakturen Brides congénitales Contracturas congénitas • • • • Congenital trigger digits Angeborene schnellende Finger Doigts à ressort Dedos en resorte congénitos • • • • Clasped thumb Daumen-Beugekontraktur Pouce adductus Pulgar flexo-adducto • • • • Camptodactyly Kamptodaktilie Camptodactylie Camptodactilia • • • • Clinodactyly Klinodactylie Clinodactilie Clinodactilia • Delta phalanx • Deltaphalanx • Phalange "delta" • Falanfe delta • • • • Duplication: Verdoppelung: Duplication: Duplicación: • • • • Radial polydactily Radiale Polydaktylie Polydactylie radiale Polidactilia radial Bifid thumb Pollex bifidus Pouce bifide Pulgar bífido • • • • Central polydactily Zentrale Polydaktylie Polydactylie centrale Polidactilia central • • • • Ulnar polydactily Ulnare Polydaktylie Polydactylie ulnaire (cubitale) Polidactilia cubital Mirror hand Spiegelhand Main en miroir Mano en espejo • • • • Overgrowth, gigantism Überenentwicklung, Hypertrophie oder Makrodaktylie Gigantisme, hyperplaste Hipertrofia o giganstismo • • • • Undergrowth Unterentwicklung oder Hypoplasie Hypoplasie, sous-développement Hipotrofia • • • • Hypoplastic hand Handhypoplasie Main hypoplasique Mano hipoplásica • • • • Brachymetacarpia Brachymetakarpie Brachymetacarpie Braquimetacarpiano • • Braquidactily Kurzfingrigkeit • • Brachydactylie Braquidactilia • • • • Constriction band syndrome Schnürfurchen- oder Schnürring- Syndrom Brides congénitales Síndrome de las bridas de constricción • • • • Generalized skeletal abnormalities Generalisierte Skelettfehbildungen Malformations généralisées du squelette Anomalías esqueléticas generalizadas Top BONES. • • • • Fracture Fraktur, Bruch Fracture Fractura • • • • Delayed union Verzögerte Knochenheilung Retard de consolidation Retardo de consolidación • • • • Nonunion Pseudarthose Pseudarthrose Pseudoartrosis • • • • Malunion Fehlstellung Cal vicieux Consolidación en mala posición • • • • Epihyseal separation (epiphysiolysis) Epiphysiolyse, (Epiphysenlósung) Epiphysiolyse (séparation épiphysaire) Lesión epifisaria (epifisiólisis) • • • • Osteopenia Osteopenie Ostéopénie Osteopenia • Osteoporosis • Osteoporose • Ostéoporose • Osteoporosis • • • • Osteomalacia Osteomalazie Ostémalacie Osteomalacia • • • • Hyperparathyroidism Hyperparathyreoidismus Hyperparathyroidisme Hiperparatiroidismo • • • • Osteitis Osteitis Ostéite Osteitis • • • • Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis Ostéomyélite Osteomielitis • • • • pyogenic pyogene, eitrige à pyogènes piogena • • • • nonpyogenic nicht-pyogene, nicht-eitrige à germes banals no piogena • • • • tuberculous tuberkulöse tuberculeuse tuberculosa • • • • Periostitis Periostitis Périostite Periostitis • • • • Aseptic (avascular) necrosis Aseptische, avaskuläre Nekrose Nécrose aseptique Necrosis aséptica • • • • Kienböck's disease Lunatum-Malazie, Mondbeinnekrose,Kienböck'sche Krankheit Maladie de Kienböck Enfermedad de Kienböck • • • • Preiser's disease Preiser'sche Krankheit Maladie de Preiser Enfermedad de Preiser • • • • Cyst Zyste Géode, Kyste Quiste • • • • Unicameral bone cyst Einkammerige Knochenzyste Kyste essentiel des os Quiste óseo esencial • • • • Enchondroma Enchondrom Enchondrome Encondroma • • • • Osteochondroma Osteochondrom Ostéochondrome Osteocondroma • • • • Subungeal exostosis Exostose -subunguale Exostose sous-unguéale Exóstosis subungueal • • • • Condromyxoid fibroma Chondromyxoides Fibrom Fibrome chondromyxoïde Fibroma condromixoide • • • • Osteoid osteoma Osteoid-osteom Ostéome oséoïde Osteoma osteoide • • • • Aneurysmal bone cyst Aneurysmatische Knocehnzyste Kyste anévrismal Quiste oseo aneurismático • • • • Chondrosarcoma Chondrosarkom Chondrosarcome Condrosarcoma • Osteoclastoma (giant cell tumo(u)r of bone) • Osteoklastom oder Riesenzellgeschwulst • Tumeur à cellules géantes • Osteoclasroma (tumor de células gigantes óseo) • • • • Osteogenic sarcoma Osteosarkom Ostéosarcome Sarcoma osteogénico • • • • Ewing's sarcoma Ewing-Sarkom Sarcome d'Ewing Sarcoma de Ewing • • • • Metastasis Metastase Métastase Metástasis Top JOINTS. • • • • Sprain Verstauchung, Distorsion Entorse Esguince • • • • Torn or ruptured ligament Ligament -oder Bänderzerrung, -ruptur Ligament étiré ou rompu Ruptura ligamentosa • • • • Dissociation Dissoziation Dissociatia Dissociation • • • • Subluxation Subluxation, Teilverrenkung Subluxation Subluxación • • • • Dislocation Luxation, Verrenkung Luxation Luxación • • • acute akute aiguë • • • • • • • • • • • • • aguda • • • • chronic chronische chronique crónica • • • • recurrent wiederholte récidivante recidivante • • • • voluntary willkürliche volontaire voluntaria Infective arthritis Infektiöse Arthritis Arthrite Artritis infecciosa • • • • pyogenic (septic) pyogene, eitrige à pyogènes, septique piógena (séptica) • • • • non-pyogenic nicht-pyogene, nicht-eitrige à germes-banals no piógena Cristal arthropathy Kristallarthropathie Arthropatie cristalline Artropatía por microcristales • • • • Gout (uric acid) Gicht Goutte Gota (ácido úrico) • • • • Pseudogout (calcium pyrophospate) Pseudogicht Pseudo-goute Pseudogota (pirofosfato cálcico) Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Rheumatische Arthritis Arthrite rhumatoïde Artritis reumatoide • Psoriatic arthritis • Psoriatische, Psoriasis-Arthritis • Arthrite psoriasique • Artritis reumatoide • • • • Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Lupus erythematodes Lupus érithémateux Lupus eritematoso sistémico • • • • Polyarteritis nodosa Periarteriitis nodosa Périartérite nouese Poliarteritis nodosa • • • • Ankylosing spondylitis Ankylosierende Spondylitis, Bechterew'sche Krankheit Spondylite ankylosante Espondilitis anquilosante • • • • Osteoarthrosis (degenerative osteoarthritis ) (OA) Arthrose, Osteoarthrose Arthrose déformante, ostéarthrite Artrosis • • • • Acute calcification Akute Verkalkung, Kalkablagerung Calcification aiguë Calcificación aguda • • • • Ganglion Ganglion Kyste synovial Ganglión • • • • Carpo-metacarpal boss Handrückenexostose Exostose carpo –métacarpienne Giba carpo-metacarpiana (carpo giboso) • • • • Pigmented villonodular synovitis (giant cell tumo(u)r of tendon sheath) (PVNS) Villonoduläre Synovitis, gitartiger Riesenzelltumor, gutartiges Synovite villonodulaire (tumeur bénigne à cellules géantes) Sinovitis villonodular pigmentada (tumor de células gigantes de vainas tendinosas) • • • • Synovial sarcoma Synovialsarkom Synoviosarcome, synoviome malin Sarcoma sinovial Top MUSCLES. • • • • Absent Fehlend Absent Ausente • • • • Accesory Hinzutretend, zusätzlich Accessoire Accesorio • • • • Supernumerary Anomal, abnormal oder abweiichend, abirrend Surnuméraire Supernumerario • • • • Compartment syndrome Kompartment-Syndrom Syndrome compartimental Síndrome compartimental • • • • Volkmann's isch(a)emic contracture Kontraktur -Volkmannsche ischämische Kontraktur Rétraction -ischémique de Volkmann Contractura isquémica de Volkmann • • • • Myositis Myositis Myosite Miositis • • • • Myositis ossificans Myositis ossificans Myosite ossifiante Miositis osificante Top TENDONS. • • • • Absent Fehlend Absente Ausente • Accesory • Hinzutretend, zusätzlich, akzessorisch • Accesoire • Accesorio • • • • Supernumerary Überzählig Surnumaraire Supernumerario • • • • Laceration (division, cut) Durchtrennung Section Sección • • • • complete Komprett, vollständig complète completa • • • • partial or incomplete teilweise oder inKomplett, unvollständig partielle ou incomplète parcial o imcompleta • • • • Avulsion Ausriss Avulsion Avulsión • • • • Attrition Abnutzung, Abreibung Attrition Atrición • • • • Rupture Ruptur Rupture Rotura, ruptura • • • • Retraction Retraktion Rétraction Retracción • • • • Adhesions Verwachsung, Adhäsion Adhérence Adherencias • • • • Dislocation Dislokation, Verrenkung, Verlagerung, Luxation Luxación (dislocación) • • • • Tendonitis (enthesopathy) Tendinitis Tendinite Tendinitis (entesopatía) • • • • Tenosynovitis Tenosynovialitis Ténosynovite Tenosinovitis • • • • • • • • • • • • septic septische infectieuse séptica • • • • tuberculous tuberkulöse tuberculeuse tuberculosa • • • • rheumatoid rheumatoide rhumatoïde reumatoide Stenosing tenovaginitis Stenosierende Tendovaginose, Sehnenscheidenentzündung Ténosynovite sténosante Tenovaginitis estenosante • • • • trigger finger schnellender Finger doigt à ressaut dedo en resorte (gatillo) • • • • trigger thumb schnellender Daumen pouce à ressaut pulgar en resorte (gatillo) • • • • De Quervain's disease Stenosierende Tendovaginose des ersten Streckesehnenfaches (De Quervain) maladie de De Quervain enfermedad de De Quervain Acute calcification Akute Verkalkung Calcification aiguë Calcificación aguda • Ganglion • Überbein, Ganglion • Kyste synovial • Ganglión • • • • Pigmented villonodular synovitis (giant cell tumo(u)r of tendon sheath) (PVNS) Villonoduläre Synovialitis, gutartiger Riesenzelltumor Synovite villonodulaire (tumeur bénigne à cellules géantes) Sinovitis villonodular pigmentada (tumor de células gigantes de vainas tendinosas) • • • • Synovial sarcoma Synovialsarkom Synovio-sarcome, synoviome malin Sarcoma sinovial Top FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. • • • • Dupuytren's disease Palmare fibromatose, Dupuytren'sche Erkrankung Maladie de Dupuytren Enfermendad de Dupuytren • • • • Knuckle pads Knöchelpolster Coussinets dorsaux (Nodules de Garrod) Almohadillas en los nudillos (Nódulos de Garrod) • • • • Dupuytren's contracture Rétraction de l'aponévrose palmaire Dupuytren'sche Kontraktur Contractura de Dupuytren • • • • Nodule Knoten, Knötchen Nodule Nódulo • • • • Palmar cord or band (Pretendinous) Palmar Strang, Fasciculi longitudinalis Bride palmaire (Pretendineuse) Brida o banda palmar (Pretendinosa) • • • • Digital cords Digitale Stränge Brides digitales Bridas o bandas digitales central Zentral centrale central oblique Schräg oblique oblícua lateral Seitlich latérale lateral "spiral" (central + oblique + lateral + Grayson's ligament spiral band, spiralig "spirale" (ídem) "espiral" ídem retrovascular retrovaskulär rétro-vasculaire retrovascular • • • • Fibroma Fibrom Fibrome Fibroma Top NERVES. • • • • Neurapraxia Neurapraxie Neurapraxie Neuroapraxia • • • • Axonotmesis Axonotmesis Axonotmésis Axonotmesis • • • • Neurotmesis Neurotmese Neurotmésis Neurotmesis • Wallerian degeneration • Degeneration -Waller'sche • Dégénérescence wallérienne • Degeneración walleriana • • • • Regeneration Regeneration Regenescense Regeneración • • • • Neuropathy Neuropathie Neuropathie Neuropatía • • • • Neuritis Neuritis Névrite Neuritis • • • • Leprosy Lepra Lèpre Lepra • • • • Laceration (cut, division) Zerreissung oder Schnittverletzung Section franche Sección (corte) • • • • Traction Dehnungs -(Traktions) schaden Traction Tracción • • • • Avulsion Ausrissverletzung, Avulsion Avulsion Avulsión • • • • Compression (entrapment) Kompression, Druckschädigung Compression dans un défilé Compresión • • • • Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) Karpaltunnelsyndrom Syndrôme du canal carpien Síndrome del tunel carpiano (STC) • • • • Ulnar tunnel syndrome (arcade of Osborne) Ulnariskompressionssyndrom in der ellenbogen (Osborne arkade) Syndrome du cubital au coude Síndrome del túnel cubital en en colo (arcada de Osborne) • Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome • • • Interosseus anterior-Syndrom (Kiloh-Nevin-Syndrom) Syndrome du nerve interosseux anterior Síndrome del nervio interóseo anterior (Kiloh-Nevin) • • • • Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome (arcade of Frohse) Interosseus posterior-Syndrom Syndrome du nerf interosseux posterieur Síndrome del nervio interóseo posterior • • • • Hemiplegia Hemiplegie, Halbseitenlähmung Hémiplégie Hemiplegía • • • • Tetraplegia Tetraplegie Tétraplégie Tetraplegía • • • • Poliomyelitis Poliomyelitis, Kinderlähmung Poliomyélite Poliomielitis • • • • Cerebral palsy Spastische Lähmung Paralysie cérébrale Parálisis cerebral • • • • Neuroma Neurom Névrome Neuroma • • • • • • • • Amputation neuroma Amputationsneurom Nevrome d'amputation Neuroma de amputación • • • • Pseudoneuroma in continuity Pseudoneurom Nevrome en continuité Pseudoneuroma en continuidad • • • • Bowler's thumb Kegler-Daumen Pouce des joueurs de boules Pulgar del jugador de bolos Neurilemmoma (benibn schwannoma) Neurilemmom, Neurinom oder Schwannom Schwannome, neurilemmome Neurilemoma (schwannoma benigno) • • • • Neurofibroma Neurofibrom Neurofibrome Neurofibroma • • • • Lipofibromatous hamartoma (median nerve) Lipofibromätoses Hamartom Lipofibrome Lipofibroma (nervio mediano) • • • • Neurofibromatosis Neurofibromatose Neurofibromatose Neurofibromatosis • • • • Malignant nerve sheath tumor (malignant schwannoma, neurofibrosarcoma) Neurofibrosarkom Neurofibrosarcome Neurofibrosarcoma (schwannoma maligno, tumor maligno de la la vaina nerviosa) Top SKIN and ACCESORIES. • • • • Crush Quetschung, Quetschwunde Plaie contuse Aplastamiento • • • • Abrasion Abschürfung Abrasion Abrasión • • • • Wound Wunde Blessure Herida • • • • Laceration or cut Zerreissung oder Schittverlctzung Coupure Laceración o corte • • • • Bite Biss Morsure Mordedura (mordisco) • • • • Degloving Ablederung Dégantement Desguantamiento • • • • Burn Verbrennung, Brandverletzung Brûlure Quemadura Thermal Thermische Thermique Térmica Scald Verbrühung Brûlure par échaudage Escaldadura Chemical Chemische Chimique Química Electrical Elektrische Électrique Eléctrica from friction Reibung par friction por fricción from radiation Strahlenschädigung, Strahlenfolge, Strahlenverbrennung par radiation por irradiación • • • • Pyogenic granuloma Pyogenes Granulom Granulome -à pyogènes Granuloma piógeno • • • • Boil Furunkel Furoncle Forunculo • • • • Intertrigo Intertrigo Intertrigo Intertrigo • • • • Scar Narbe Cicatrice Cicatriz Hypertrophic Hypertrophisch Hypertrophique Hipertrófica Keloid Keloid Chéloïde Queloide • • • • Scleroderma Skleroderma Sclérodermic Escleriodemia • • • • Dermatomyositis Dermatomyositis Dermatomyosite Dermatomiositis • • • • Epidermal inclusion cyst Epidermoid-Zyste Kyste epidermoïde Quiste de inclusión epidérmico • • • • N(a)evus -junctional Naevus - junktions Naevus plan Nevus • • • • Basal-cell carcinoma Basalzellkarzinom, Basaliom Carcinome basocellulaire Carcinoma de células basales • • • • Squamous cell carcioma Plattenepithelkarzinom, Spinaleom Carcinome spinocellulaire Carcinoma espinocelular • • • • Carcinoma, epithelioma Karzinom, Ca, Epitheliom Carciome, apithélioma Carcinoma, epitelioma • Nail and nail-bed: • Nagel und Nagelbett: • Ongle et Lit unguéal: • Uña y lecho ungueal: • • • • • • • • Onychogryposis Onychogryphose Onychogrypose, hypertrphie unguéale Onicogriposis • • • • Paronychial fungal infection Paronychie durch Pilzinfektion, Mykose Mycose périunguéale Paroniquia por micosis • • • • Infectious paronychia (whitlow) Infektionen -Paronychie oder Umlauf Panaris peri-unguéal, tourniole Paroniquia (uñero) • • • • Subungual h(a)ematoma Subunguales Hämatom Hématome sous-unguéal Hematoma subungueal • • • • Glomus tumo(u)r Glomustumor Tumeur glomique Tumor glómico • • • • Subungual melanoma Subunguales Melanom Mélanome sous-unguéal Melanoma subungueal • • • • Subungual carcinoma Subunguales Karzinom Epithélioma sous-unguéal Carcinoma subungueal Subcutaneous tissue: Subkutangewebe, Unterhautfettgewebe: Tissu sous- cutané: Tejido graso subcutáneo: • • • • Cellulitis Phlegmone Cellulite Celulitis • • • • Erysipeloid Erysipeloid Erysipéloïde Erisipeloide • Carbuncle • • • Karbunkel Anthrax Forunculo • • • • Abscess Abszess Phlegmon Abceso • • • • Pulp infection Fingerkuppenabszess Panaris pulpaire Infección pulpar, panadizo • • • • Pilonidal sinus Pilonidal-Sinus, -Zyste Sinus pilonidal Fístula pilonidal • • • • Rheumatoid nodule Rheuma-Knoten Nodule rhumatoïde Nódulo reumatoideo • • • • Tophus Tophus, Gichtknoten Tophus Tofo gotoso • • • • Calcinosis circumscripta Calcinosis circumscripta Calcinosis circumscripta Calcinosis circunscrita • • • • Dermoid cyst Dermoid-Zyste Kyste dermoïde Quiste dermoide • • • • Mucoid cyst Mucoidzyste Kyste mucoïde Quiste mucoide • • • • Ganglion Ganglion, überbein Kyste synovial Ganglión • • • • Dermatofibroma Molluscum, dermato-fibrome Dermatofibrom Dermatofibroma • • • • Xanthoma Xanthom Xanthome Xantoma • • • • Lipoma Lipom Lipome Lipoma • • • • Liposarcoma Lipsarkom Liposarcome Liposarcoma Top VESSELS. • • • • Spasm Spasmus Spasme Espasmo • • • • Isch(a)emia Ischämie Ischémie Isquemia • • • • Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD) Algodystrophie, SympatischeReflexdystrophie, Morbus Sudeck Neuro-algodystrophie, Dystrophie sympathique Distrofia Neurovascular Refleja (DNVR), Distrofia simpática refleja • • • • Raynaud's phenomenon Raynaud'sches Phänomen Phénomène de Raynaud Fenómeno de Raynaud • • • • Raynaud's disease Raynaud'sche Erkrankung Maladie de Raynaud Enfermedad de Raynaud • • • • Arteritis Arteriitis Artérite Arteritis • • • • Thrombosis Thrombose Thombose Trombosis • • • • Gangrene Gangrän Gangrène Gangrena • • • • Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) Arteriovenöse Fistel Fistule artérioveineuse Fístula arteriovenosa • • • • Aneurysm Aneurysma Anévrisme Aneurisma • • • • H(a)emangioma Hämangiom Hémangiome Hemangioma Top GENERAL. • • • • Traction Traktion oder Dehnung Traction Tracción • • • • Manipulation Manipulation Manipulation Manipulación • • • • Reduction (realignment) Reposition Réduction Reducción • • • • Immobilization Immobilisation, Ruhigstellung Immobilisation Inmovilización • • • • Plaster cast Gipsverband Plàtre Escayola • • • • Fiberglass polyuretane resin casting tape ..................... Appareill de contention en resine Vendaje de resina y fibra de vidrio • • • • Orthosis Orthosen Orthèse Ortesis • • • • Splint, brace Schienen Attelle Férula • • • • • • • • • • • • static statische statique estática • • • • dynamic dynamische dynamique dinámica Prothesis Prothesen Prothèse Prótesis • • • • cosmetic kosmetische esthéstique estética • • • • active aktive fonctionnelle activa Mobilization Mobilisation Mobilisation Movilización • Rehabilitation • Rehabilitation • Rééducation fonctionnelle • Rehabilitación • • • • Physiotherapy, physical, therapy (PT) Physiotherapie, physikalische Therapie, Krankengymnastik Physiothérapie Fisioterapia (FT) • • • • Hand therapy Handtherapy Rééduction de la main Fisioterapia de la mano • • • • Occupational therapy (OT) Beschäftigungstherapie, Ergotherapie Ergothérapie Terapia ocupacional (TO) • • • • Exercices Übungen Exercices de mobilisation Ejercicios • • • • active aktive active activos • • • • passive passive passive pasivos • • • • Stretching Streckung oder Dehnung Traction, elongation Estiramiento • • • • Aspiration Aspiration Aspiration Aspiración • • • • Injection Injektion Injection Inyección • • • • Esmarch bandage Esmarchsche Binde Bande d'Esmarch Venda de Esmarch • • • • Exsanguination Auswickeln des Armes Exsanguination Exanguinación, expresión sanguínea • • • • Pneumatic tourniquet Blutleere -pneumatische Garrot –pneumatique Torniquete neumático • • • • Optical magnification Vergrösserung Grossissement Magnificación óptica • • • • Microsurgical technique Mikrochirurgische Technik Techniques micro-chirurgicales Técnica microquirúrgica • • • • Exposure (approach) Freilegung oder Zugang Voie d'abord Via de abordaje • • • • Incision Inzision, Schnittführung Incision Incisión • • • • transverse querverlaufend transversale transversa • • • • longitudinal längsgerichtet longitudinale longitudinal • • • • midaxial (in the finger) in der Mittellinie médiane ou axiale axial-media (en el dedo) • • • • midlateral (on the finger) mediolateral -oder MittSeiten-Schnitt, Kantenschnitt médio-latérale mediolateral (en el dedo) • • • s-shaped bogenförmig sinueuse • sinuosa (en S) • • • • zig-zag zickzack-förmig en zig-zag en zig-zag • • • • Surgical exploration Revision, Exploration Chirurgische Exploration chirurgicale Exploración quirúrgica • • • • Drainage Drainage Drainage Drenaje • • • • Excision Exzision Excision Excisión • • • • Reconstruction Reconstruktion Rekonstruction Reconstrucción • • • • Revascularization Revaskularisation Revascularisation Revascularización • • • • Replantation Replantation Replantation Reimplante • • • • Autografting Autogreffe Autotransplantation Autoinjerto • • • • Allografting Allotransplantation Allogreffe, hétérogreffe Aloinjerto • • • • Tension Spannung Tension Tensión • Rod • Stab • Cordon, tige • Varilla • • • • Sheet Schicht, Blatt, Folie Feuille Lámina • • • • Pull-out wire Ausziehdraht Fil d'extraction Alambre extraible • • • • Primary repair Primärversorgung Suture primaire Reparación primaria • • • • Delayed primary repair Verzögert-primäre Versorgung Suture secondaire précore Reparación primaria diferida • • • • Secondary repair Sekundärversorgung Suture secondaire Reparación secundaria • • • • Amputation Amputation Amputation Amputación • • • • Ray excision (resection) Fingerstrahleresektion Résection d'un rayon Resección de un radio digital • • • • Digital transfer Fingertransposition Translocation digitale Transposición digital • • • • • • • • Pollicization Pollizisation, Daumenbildung Pollicisation Pulgarización Toe transfer Zehenübertragung, Zehentransplantation Transfert d'orteil Transferencia de un dedo del pie Top BONES. • • • • • • • • • • • • Reduction of fracture Reposition einer Fraktur oder eines Bruches Réduction de fracture Reducción de fractura • • • • closed geschlossene fermée cerrada • • • • open offene ouverte ou sanglante abierta Internal fixation (osteosynthesis) Innere Fixation (osteosynthese) Fixation interne (osteosynthèse) Fijación interna (osteosíntesis) • • • • Plate and screws Platte und chrauben Plaque et vis Placa y tornillos • • • • Intramedullary nail Intramedulläre Negelung Clou centro-medullaire Clavo endomedular • • • • Staples Klammer Agrafe Grapa • • • • Kirschner wire (K-wire) Kirschnerdraht Broche de Kirschner Aguja de Kirschner Percutaneous fixation Osteosynthese perkutane Fixation percutanée Fijación percutánea • • • • External fixation Äussere Fixation (Fixateur externe) Fixateur externe Fijación externa • • • • Bone graft Knochentransplantation, Knochenspanübertragung Greffe osseuse Injerto óseo • • • • Osteotomy Osteotomie Ostéotomie Osteotomía • • • • • • • • wedge Keil coin en cuña • • • • shortening verkürzung accourcissement de acortamiento • • • • lengthening Verlängerung allongement de alargamiento Excision Exzision Excision Excisión Top JOINTS. • • • • Arthrotomy Arthrotomie Arthrotomie Artrotomía • • • • Capsulotomy Kapsulotomie Capsulotomie Capsulotomía • • • • Capsulectomy Kapsulektomie Capsulectomie Capsulectomía • • • • Arthrolysis Arthrolyse Arthrolyse Artrolisis • • • • Capsulodesis Kapsulodese Capsulodèse Capsulodesis • • • • Capsulorrhaphy Kapselnaht Capsulorraphie Capsulorrafía • • • • Arthroplasty Arthroplastik Arthroplastie Artroplastia • • • • • • • • resection (excision) rexzisionsarthroplastik résection de resección • • • • interpositio Interpositionsarthroplastik Interposition de interposición • • • • implant (replacement) Implantationsarthroplastik, Alloarthroplastik par substitution (implant, prothèse) de implante Arthrodesis Arthrodese Arthrodèse Artrodesis Top MUSCLES. • • • • Exercises Übungen Exercices Ejercicios • • • • Decompression Dekompression Décompression Decompresión • • • • Muscle Slide Desinsertion oder Muskelursprungsverschiebung Désinsertion pour allongement Desinserción • • • • Epimysiotomy Spaltung der Muskelfaszie Myotomie Epimisiotomía • • • • Excision, myectomy Exzision, Myektomie Excision, myectomy Excisión, miectomía • • • • Transposition Transposition, Tranfer Tranfert, transposition Transposición Top TENDONS. • • • • Tenotomy Tenotomie Ténotomie Tenotomía • • • • Tendon lengthening Sehnenverlängerung Plastie tendineuse d'allongement Alargamiento tendinoso • • • • Tendon shortening Sehnenverkürzung Raccourcissement tendineux Acortamiento tendinoso • • • • Tendon suture (tenorrhaphy) Sehnennaht Suture tendineuse (ténorraphie) Sutura tendinosa (tenorrafia) • • • • Tendon advancement Sehnenverschiebung, Reinsertion Réinsertion Avance tendinoso • • • • Two stage tendon repair Zweizeitige Sehnenverschiebung Reparation tendineuse en deux temps Reparación tendinosa en dos tiempos • • • • Silicone rubber rod Silikon-Stab Tige de silicone Varilla de silicona • • • • Tendon graft Sehnentransplantation Greffe tendineuse Injerto tendinoso • • • • Tenolysis Tenolyse Ténolyse Tenolisis • • • • Tenodesis Tenodese Ténodèse Tenodesis • • • • Tenosynovectomy Tenosynovialektomie Ténosynovectomie Tenosinovectomía • • • • Tendon transfer Sehnentransposition, Sehnenverlagerung Transposition tendineuse Transferencia tendinosa • • • • Opponensplasty Opponens-Plastik Transfert d'opposition Plastia de oponente • Incision (excision) of fibrous tendon sheath • Inzision (Exzixion) der fibrösen Sehnenscheide • Incision (excision) de la gaine fibreuse • Incisión (excisión) de la vaina tendinosa • • • • Pulley advancement "Pulley advancement" Avancement de poulie Avanzamiento de polea • • • • Pulley reconstruction Ringband-Rekonstruktion, Wiederherstellung Reconstruction de poulie Reconstrucción de polea • • • • Enlarging pulley-plasty Ringbanderweiterungs-plastik Plastie d'agrandissement de la poulie Plastia de elongación de la polea Top FASCIA. • • • • Fasciotomy Fasziotomie Aponévrotomie Fasciotomía • • • • Fasciectomy Aponeurektomie Aponévrectomy Fasciectomía • • • • partial partielle, teilweise partielle parcial • • • • radical radikale, vollständige radicale radical Top NERVES. • • • • Suture (repair) Naht oder Wiederherstellung Suture Sutura (raparación, neurorrafia) • • • • epineural epineural épineurale epineural • • • • perineural perineural périneurale perineural • • • • fascicular faszikulär fasciculaire fascicular • • • • Nerve grafting Nerventransplantation Greffe nerveuse Injerto nervioso • • • • Pedicle graft Gestielte Nerventransplantation Greffe pédiculée Injerto pediculado • • • • Decompression Dekompression Décompression Descompresión • • • • Neurolysis Neurolyse Neurolyse Neurolisis • • • • Epineurotomy Spaltung des äusseren Epineuriums Epineurotomie Epineurotomía • • • • Internal neurolysis Innere Neurolyse Endoneurolyse Endoneurolisis • Transposition • Transposition • Transposition • Transposición • • • • Excision of neuroma Neuromexzision Excision de névrome Exéresis de neuroma • • • • Denervation Denervation Dénervation Denervación • • • • Neurotomy Neurotomie Neurotomie Neurotomía • • • • Neurectomy Nervenresektion Résecton nerveuse Neurectomía Top SKIN and ACCESORIES. • • • • Suture Naht Suture Sutura • • • • Z-plastie Z-Plastik Plastie en Z Plastia en "Z" (zetaplastia) • • • • Open-palm "Open palm"- Technik Paume ouverte Palma abierta • • • • Excision Exzision Excision Excisión • Escharotomy • Nekrosenabtragung • Mise à plat, escharotomie, excision d'eschare • Escarectomía, seciestrectomía • • • • Cover Hautdeckung Couverture Cobertura • • • • Graft Transplantat Greffe Injerto • • • • • • • • partial thickness (split thickness) Spalthaut grefe mince grosor parcial • • • • full thickness Vollhaut de peau totale grosor total Local flap Lokale Verschiebelappen Lambeau local Colgjao local • • • • advancement Dehnungslappen d'avancement de avanzamiento • • • • V-Y plasty V-Y- Plastik Plastie en VY plastia en V-Y • • • • rotation Rotationslappen de rotation de rotación • • • • transposition, transposed Transpositionslappen de glissement de translación • • • • cross-finger gekreuzter Fingerlappen hétérodactyle heterodigital • flag • • • • • • • Fähnchenlappen en drapeau en bandera • • • • thenar Thenarlappen thénarien tenar • • • • neurovascular island Neurovaskulärer Insellappen Lambeau pédiculé Neurovascular en isla Distant flap Fernlappen Lambeau à distance Colgajo a distancia • • • • pedicled Gestielt pédiculé pediculado • • • • tubed Rundstiellappen tubulé tubulado • • • • cross-arm Gekreuzter Armlappen hétéro-brachial brazo cruzado • • • • pectoral Brusthautlappen pectoral pectoral • • • • abdominal abdominal Bauchhautlappen abdominal • • • • groin Leistenlappen inguinal inguinal • • • • cutaneous Hautlappen cutanée cutáneo • • • • Composite: Cusammengesetztier Lappen: Composité: Compuestos: skin and fascia (dermofascial) Fasziokutan fascio-cutané fascio-cutáneo skin and bone osteokutan osteo-cutané osteo-cutáneo myocutaneous myokutaner Lappen myocutané miocutáneo • • • • Avulsion of nail Nagelausriss Avulsion unguéale Avulsión ungueal • • • • Excision of nail-bed or matrix Exzision des Nagelbettes Excision du lit unguéal ou de la matrice Excisión del lecho ungueal o de la matriz • • • • Nail bed graft Nagelbett - Transplantat Greffe du lit unguéal Injerto de lecho ungueal Top VESSELS. • • • • Arteriotomy Arteriotomie Artériotomie Arteriotomía • • • • Revascularization Revaskularisation Revascularisation Revascularización • • • • Microvascular anastomosis Mikrovaskuläre Anastomose Anastomose microvasculaire Anastomosis microvascular • • • • Arterial suture or anastomosis Arteriennaht oder -anastomose Suture ou anastomose artérielle Sutura o anastomosis arterial • • • • Venous suture or anastomosis Venennaht oder -anastomose Suture ou anastomose veineuse Sutura o anastomosis venosa • • • • Vein graft Venentransplantat oder -interponat Greffe veineuse Injerto venoso Top SKIN CREASES The skin creases ("joints" of the digital and palmar skin) are listed in the different languages on FASCIA and APONEUROSIS. Palmar creases. In the palm there are three longitudinal and two transverse creases. The longitudinal creases are the thenar, the central and the hypothenar. The most constant and easily differenciated is the thenar crease, due to the wide mobility of the carpo-metacarpal joint ofthe thumb. The central and hypothenar creases are the reflection of the mobility at the carpometacarpal joints of the ring and small fingers. The two transverse creases are the proximal and the distal. The distal crease starts at the u1nar side of the hand and finishes in between the middle and index fingers, as most of the hand functionsare done with the uInar fingers in flexion for power grasp, while the index and the thumb remain inextension for precision manipulation. The middle finger can either help the thumb and index formanipulation, or the ring and small fingers if more power grasp is needed. The proximal creasestarts at the radial side of the hand along with the longitudinal thenar crease. Flexion of themetacarpo-phalangeal joints takes place in a transverse line between the origin of the distal palwarcrease on the uInar side and the proximal palmar crease on the radial side. Individuals with Down'ssyndrome just have one transverse palmar crease. Digital creases. Usually there are two creases at the level of each joint, being most prory,,inent theproximal one. The palmar digital crease of the triphalangeal fingers is usually located at theproximal third of the proximal phalanx. The palmar digital crease of the thumb is longitudinallyoriented and slightly proximal to the metacarpo-phalangeal joint. Top THE HAND In order to avoid mistaken identity, the fingers are referred to by name, rather than the number. Following the same rule, the bones of each finger are named by the name given to that finger. For example: the metacarpal of the index finger or the middle phalanx of the ring finger The joints are named after the name of the bones that they unite. The triphalangeal or long fingers have two interphalangeal joints, wich will be named proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. The carpo-metacarpal joints of the thumb is also commonly referred as trapeziometacarpal joint. Top JOINT MOTION General rules THE ELBOW THE FOREARM THE WRIST THE FINGERS THE THUMB Top General rules The anatomical or zero starting position is considered with the,upper extremity aligned next to the trunk with the palm of the hand facing anteriorly. Any joint movement in the anterior direction is considered as flexion and should be recorded as positive degrees. On the contrary, any movement in a posterior direction is called extension, and should be recorded as negative degrees. The extension motion in joints that usually do not extend is called hyperextension. The terms dorsal flexion or dorsiflexion should be avoided. Dorsal extension is redundant and should not be used. Active and passive range of motion should always be recorded when examining a joint. Passive joint motion can be of greater magnitude in the presence of nerve, muscle or tendon pathology. In the following pages the most frequenty observed arcs of joint movility will be given as an orientation, although they may very up to 20" in many individuals. It is for this reason that all joint movements should be compared with the normal joint on the opposite extremity. Top THE ELBOW The main joint at the elbow is the humero-ulnar, which is a hinge joint, meaning that only moves in one plane. The neutral position is in full extension, whith the humerus axially aligned with the ulna, and this is considered as the zero starting position. The elbow flexes to an average of 145". The only restrains are the soft tissues in the anterior surface of the upper extremity and the bone contact between the coronoid fossa of the humerus and the coronoid process of the ulna. The motion in the direction of flexion is measured as positive degrees from the zero starting position. Some individuals can slightly hyperextend the elbow. This joint motion is measured as negative degrees. Top THE FOREARM The movements of pronation and supination take place in the forearm. The radius rotates around the ulna along an slightly oblique axis crossing the proximal and distal radio-ulnar joints. The hand is attached to the radius, and follows it during the movements of rotation. The amount of hand supination and pronation at the wrist level is negligible, although a slight degree of passive rotation can be noted. The scapulo-humeral joint can also internally and externally rotate, transmitting this movement to the hand. This movement of rotation at the shoulder will be blocked if the arm is kept next to the torax and the elbow is flexed 90". External rotation is known as supination (the palm of the hand faces the anterior aspect of the arm), and internal rotation is known as pronation (the palm of the hand faces the posterior aspect of the arm), and Although the zero starting position, or anatomical position of the forearm, is ir,. full supination, it has been agreed that the neutral position should be considered at the mid point of the full arch of rotation. The neutral position or zero starting position is with the "thumb up", with the palm of the hand in the sagital plane. The rotation of the forearm with the palm facing up is known as supination and usually measures 85". The rotation of the forearm with the palm of the hand facing down is known as pronation, and usually measures 75", a little less than supination. Top THE WRIST The wrist can move in the sagital plane (flexion and extension) and in the coronal plane (radial and u1nar deviation). As mentioned before, the wrist allows for some degree of rotation, which can be observed by passive manipulation of the joint. However, this type of movement is almost negligible and cannot be clinically measured. The neutral or zero starting position is with the longitudinal axis of the middle finger metacarpal aligned with that of the radius. The wrist usually extends 70º and flexes 80º. The arc of extension is generally smaller than the one of flexion. Flexion and extension varie among different individuals. Some individuals cannot flex further than 65º, while others with joint hyperlaxity can flex the wrist more than 90º. Radial deviation usually measures 20º, while u1nar deviation is 40º. Wrist movements are usually measured with the forearm in pronation as this is the position with which the patient presents the hand to the examiner, however, it would be more accurate to perform all wrist measurements with the forearm in neutral positio, as there can be minor differences in total range of movement when the forearm is fully pronated. Top THE FINGERS The METACARPO-PHALANGEAL JOINTS can move in the sagittal plane (flexion and extension) and in the coronal plane (radial and u1nar deviation). Some degree of rotation is also possible, from selective contraction of the intrinsic muscles. This freedom of movement in pronation and supination is very usefull when performing tasks of precision handling. From the practical point of view it is very difficult to measure, and for this reason it is not usually recorded in clinical practice. The zero starting position is when the proximal phalanx is axially aligned with the metacarpal. The metacarpo-phalangeal joints flex an average of 90º. The index finger usually flexes less than 90º, but flexion progressively increases in the most u1nar fingers, being more than 90º in the small finger. The MID joints can hyperextend up to 30º, and even more in individuals with joint hyperlaxity. Full MP joint hyperextension is generally accomplished with moderate interphalangeal joint flexion in order to relax the palmar skin. The motion of the MP joints in the coronal plane is defined as radial and u1nar deviation. The terms abduction and adduction could also be used, but confusion may arise when defining the longitudinal axis of reference. When using this terminology, the axis of the middle finger ray should be used, rather than the longitudinal axis of the body used for the rest of the joints. This method has the disadvantage of not differentiating the abduction of the middle finger in two opposite directions. The INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS are hinge joints and can only move in the sagittal plane. The zero starting position is with the finger in extension, with the three phalanges aligned with each other. Full flexion is accomplished when both proximal and distal phalanx are parallel to each other, which means a combined flexion of 180". The PIP joint however flexes a little more than the DIP joint, averaging 105" and 75" respectively. Some hyperextension of the DIP joint is not unusual; however, hyperextension of the PIP joint is only seen in people with joint laxity. Motion at the DIP joint should not be measured by holding the PIP joint in extension, as in this position DIP joint flexion will be restricted from preventing the lateral bands to glide to the sides of the PIP joint. Active DIP joint motion should be recorded with all the fingers flexed simultaneously, as the flexor digitorum profundus is a single muscletendon unit, with the occasional exceptions to the index finger. A quick method of mesuring the composite finger motion is by measuring the distance from the fingertip to the palmar-digital crease (this measures flexion of both interphalangeal joints) or to the proximal palmar crease (this also measures the flexion of the MP joint). This method is not fully accurate as different examiners can use different parts of the finger tip as a reference: the free edge of the nail, the end o'l the fingertip or that part of the finger pulp closer to the skin crease. Top THE THUMB The mtions of the thumb, mainly at the carpometacarpal joint, are complex, and all definitions aresomewhat arbitrary. Motion of the interphalangealand metacarpo-phalangeal joints take place in aplane perpendicular to the one of the rest of thefingers. Motion at the INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT is limitedto flexion and extension, in a plane perpendicular tothe nail of the thumb. The zero starting position iswith the proximal and distal phalanges aligned toeach other. Flexion averages 80", and manyindividuals can hyperextend the joint up to 45* ormore. Motion at the METACARPO-PHALANGEAL JOINTis mainly in the plane of flexion and extension. Somelateral motion (radial and u1nar deviation) and rotation(supination and pronation) are also present. Whenthe pulp of the thumb is opposed to the pulp ofanother finger, with the fingernails parallel to each other, some radial deviation and pronation takesplace at the MP joint of the thumb. The triphalangealfinger also rotates slightly into supination. There is awide variation in the range of motion of the MP jointin the different individuals. More than in any otherjoint of the hand, motion of the MP joint shouldalways be compared to the one in the oppositethumb. Some individuals can only flex the joint about200, while others can flex it up to 90", and evenhyperextend it. . The CARPO-METACARPAL JOINT (TRAPEZIO-METACARPAL) is a universal joint, in the sense that it can move in two planes and can also rotate along its longitudinal axis. The zero starting position is with the thumb metacarpal as parallel as possible to the index finger metacarpal. The thumb lies next to the antero-radial border of the palm. Anteposition or Palmar abduction is the movement in wich the thumb metacarpal moves away from the index metacarpal at right angle to the plane of the palm. It is measured by the angle formed between the thumb and the index metacarpals, averaging about 40º. Retroposition is the opposite to palmar abduction (anteposition). The thumb moves towards the back of the hand. Retropulsion is measured by the angle formed by the thumb metacarpal passing to the palm, averaging about 15º. Abduction or Radial abduction (to differentiate it from palmar abduction) is the movement in which the thumb metacarpal moves away from the index finger metacarpal in the plane of the palm. It is measured by the angle formed between the thumb and index metacarpals, averaging about 40º. Adduction is the opposite of radial abduction. The thumb metacarpal moves towards the center of the palm. The thumb al the T-MC joint is limited to about 15º Opposition is a composite motion of the entire thumb ray by placing its pulp paralle to that of the rest of the fingers. Measuring the thumb's opposition is very difficult, because it combines movement a the trapeziometacarpal, metacarpophalalgeal and interphalangeal joints. It is the resul of different degrees of palmar abduction, pronation (internal rotation), adduction an flexion at the three joint levels. One way to evaluate this composite motion is by the Total Opposition Test (TOT). It i divided into 10 stages, according to the place where the pulp of the thumb reaches th differents parts of the fingers. Stages 7 to 10 do not measure true opposition, but rathe adduction of the T-MC joint, and flexion of MID and IP joints. The examiner should be aware that an apparent loss of thumb opposition to the smal finger can also be secondary to a loss of opposition of the latter, from hypothena muscle weakness or C-MC joint stiffness. Top