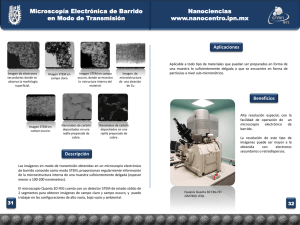
Presentación de PowerPoint - Fundacion Conchita Rabago de
Anuncio

Neurogénesis y neurodegeneración: cuando el desarrollo se encuentra con la patología Isabel Fariñas [email protected] Neural (synaptic) plasticity Yuste R. Neuron 71, September 8, 2011 Cell regeneration in the nervous system: the unforeseen plasticity “…el aprendizaje hace que las células nerviosas existentes emitan o hagan crecer nuevas prolongaciones para reforzar sus conexiones con otras células nerviosas…” “Preciso es reconocer que, en los centros adultos, las vías nerviosas son algo fijo, acabado, inmutable. Todo puede morir, nada renacer”. Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1928 Adult neurogenesis t Adult neurogenesis in humans ? Alonso-Nanclares & De Felipe BrdU BrdU Ericksson et al. (Gage), 1999 NeuN GFAP Adult neurogenesis in humans Incorporation of 14C in new born neurons Nuclear bomb testderived 14C 14C Frisen lab: 14C-based neuron birthdating Cell regeneration in the nervous system: the unforeseen plasticity “Preciso es reconocer que, en los centros adultos, las vías nerviosas son algo fijo, acabado, inmutable. Todo puede morir, nada renacer”. “…será tarea de la ciencia del futuro cambiar, si es posible, este duro decreto”. Synaptic plasticity + Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1928 Adult neurogenesis Neurogenic niches in the adult mammalian brain Subventricular zone (SVZ) Subgranular zone (SGZ) (Dentate gyrus) Olfactory bulb SVZ Corpus callosum SGZ Cerebellum Neurogenic niches in the adult mammalian brain: GFAP+ NSCs SVZ DNA GFAP S100β SGZ DNA GFAP Origin of adult neural stem cells Neural tube Neuroepithelium Origin of adult neural stem cells t Radial glial cells as NSCs Adult NSCs: B1 cells beta-catenin (membranes) γ-tubulin (cilial basal bodies) GFAP The Stem Cell Niche O2 & small ions Immune/inflammatory cells Neurons Perivascular & endothelial cells Neurotransmitters, ECM neuropeptides Adhesion & signalling receptors (integrins, cadherins, GPCRs, Notch,…) Stem cell Soluble factors (growth factors, hormones, chemokines, neurotransmitters,…) Support cells (ependyma in the CNS) Ferrón et al. Development, 131:4059-4070 (2004) Ramírez-Castillejo et al. Nature Neuroscience, 9:331-339 (2006) Ferrón et al. Nature Protocols, 2:849-859 (2007) Ferrón et al. J. Neuroscience, 29:14394-14407 (2009) Andreu-Agulló et al. Nature Neuroscience, 12:1514-1523 (2009) Mira et al. Cell Stem Cell, 7:79-89 (2010) (in collaboration) Ferrón et al. Cell Stem Cell, 7:367-379 (2010) Ferrón et al. Nature, 475:381-385 (2011) (in collaboration) Marqués-Torrejón et al. Cell Stem Cell, 12:88-100 (2013) Porlan et al. Nature Neuroscience,16:1567-75 (2013) Porlan et al. Nature Cell Biology, 16:629-38 (2014) Delgado-Fumero et al. Neuron, 83:572-85 (2014) Adult tissue-specific stem cells PHYSIOLOGICAL Neoplasic mutations CANCER Tumour formation and recurrence Self-renewal vs differentiation TISSUE HOMEOSTASIS Tissue renewal and regeneration Increased cell death or senescence AGEING Age-related deteriorations Age-related disorders Targeting deregulated selfrenewal. TUMOUR TREATMENT Stem cell source: ex vivo expansion & customized differentiation. Endogenous stem cell activation. REGENERATIVE MEDICINE NICHE INTERACTIONS MOLECULAR REGULATION OF SELF-RENEWAL PATHOLOGICAL The Study of Neurogenesis in Neurogenerative Contexts In PD, specific alterations in neurogenic areas parallel some of the early or premotor symptoms that are seen in the early stages of these diseases, such as depression or olfactory dysfunction. Reported Dopamine Effects on Proliferation/Neurogenesis Dopamine: ↑ or ↓proliferation (transient amplifying progenitor –TAP- cells) ↑ or ↓neurogenesis From: Arias-Carrión O, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6:326-35 (2007) Synaptic marker TH GFAP Neurogenic niches in the adult mammalian brain OB Striatum Frisen lab: 14C-based neuron birthdating The Stem Cell Niche as a ‘‘Druggable’’ Target for Regenerative Medicine: “Niche Therapies’’ Neurons Immune/inflammatory cells O2 & small ions Neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, synaptic regulators Adhesion & signalling receptors (integrins, cadherins, GPCRs, Notch,…) Perivascular & endothelial cells ECM Stem cell Soluble factors (growth factors, hormones, chemokines, neurotransmitters,…) Support cells (ependyma in the CNS) Synaptic plasticity Adult neurogenesis Potential Entry Points for Niche-Directed Stem Cell Therapies Stem cell expansion Expand niches High engraftment Stem cells Stem cells w/ niche Ex vivo culture Transplantation w/o niche Untreated Low engraftment Alter niches Stem cell loss Biased cell type production Transplantation Loss of stem cell niches Aging/Disease Rejuvenation Endogenous targeting Dysfunction of stem cell niches Martina Kirstein Francisco Pérez-Sánchez Sacri R. Ferrón José Manuel Morante Alex Bizy Ana Pérez-Villalba Salomé Sirerol Carmen Ovejero María Pimentel Germán Belenguer Beatriz Martí-Prado Ana Domingo Mª José Palop Fabrice Durupt BIOTECMED ERI de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Estructura de Recerca Interdisciplinar de la Universitat de València