material-voz-pasiva
Anuncio
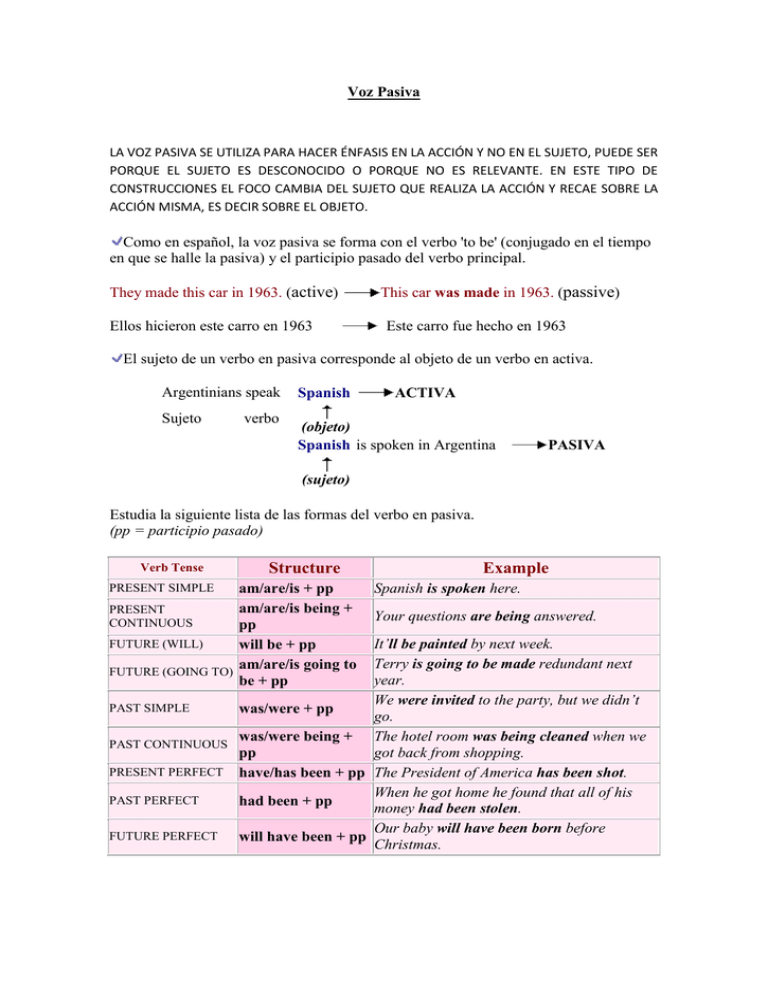
Voz Pasiva LA VOZ PASIVA SE UTILIZA PARA HACER ÉNFASIS EN LA ACCIÓN Y NO EN EL SUJETO, PUEDE SER PORQUE EL SUJETO ES DESCONOCIDO O PORQUE NO ES RELEVANTE. EN ESTE TIPO DE CONSTRUCCIONES EL FOCO CAMBIA DEL SUJETO QUE REALIZA LA ACCIÓN Y RECAE SOBRE LA ACCIÓN MISMA, ES DECIR SOBRE EL OBJETO. Como en español, la voz pasiva se forma con el verbo 'to be' (conjugado en el tiempo en que se halle la pasiva) y el participio pasado del verbo principal. They made this car in 1963. (active) Ellos hicieron este carro en 1963 This car was made in 1963. (passive) Este carro fue hecho en 1963 El sujeto de un verbo en pasiva corresponde al objeto de un verbo en activa. Argentinians speak Sujeto verbo Spanish ACTIVA (objeto) Spanish is spoken in Argentina PASIVA (sujeto) Estudia la siguiente lista de las formas del verbo en pasiva. (pp = participio pasado) Verb Tense Structure am/are/is + pp am/are/is being + PRESENT CONTINUOUS pp FUTURE (WILL) will be + pp am/are/is going to FUTURE (GOING TO) be + pp PRESENT SIMPLE Example Spanish is spoken here. Your questions are being answered. It’ll be painted by next week. Terry is going to be made redundant next year. We were invited to the party, but we didn’t PAST SIMPLE was/were + pp go. was/were being + The hotel room was being cleaned when we PAST CONTINUOUS got back from shopping. pp PRESENT PERFECT have/has been + pp The President of America has been shot. When he got home he found that all of his PAST PERFECT had been + pp money had been stolen. Our baby will have been born before FUTURE PERFECT will have been + pp Christmas. Para decir quién hacía la acción o qué la causaba, usa 'by'. This house was built by my mother. / Esta casa fue construida por mi madre. Pakistan was bombed by Washington. / Pakistán fue bombardeada por Washington. La voz pasiva se suele utilizar cuando se desconoce o no interesa mencionar quién o qué hace la acción. Es más normal encontrar en español formas con ‘se’, por ejemplo: ‘se habla’, ‘se alquila’ o verbos en plural como ‘venden’, ‘compran’. German is spoken here / Aquí se habla alemán When was this house built? / ¿Cuando se construyó ( fue construida) ésta casa? A lot of songs have been written about love / Se han escrito muchas canciones sobre el amor Si una oración activa tiene complemento directo e indirecto, cualquiera de los dos complementos puede ser sujeto paciente de la pasiva: ACTIVE: Someone gives me a dog PASSIVE 1: A dog is given to me PASSIVE 2: I am given a dog (forma pasiva idiomática) La forma pasiva de doing, seeing, etc es being done, being seen, etc. ACTIVE: I don't like people telling me what to do PASSIVE: I don't like being told what to do Las construcciones impersonales (se dice, se comenta, etc.) son muy típicas de la pasiva y difíciles de traducir para los hispanoparlantes. Este tipo de construcción pasiva -utilizada cada vez con mayor frecuencia en los medios- se forma con la estructura sujeto + to be + participle: It is reported (Se informa); It is said (Se dice); It is known (Se sabe); It is supposed (Se supone); It is considered (Se considera); It is expected (Se espera). Veamos algunos ejemplos: ACTIVE: Everybody thinks Cathy works very hard. PASSIVE 1: Cathy is thought to work very hard. (Se piensa que Cathy...) PASSIVE 2: It is thought that Cathy works very hard. (Se piensa que Cathy...) ACTIVE: They believe Tom is wearing a white pullover. PASSIVE 1: Tom is believed to be wearing a white pullover. (Se cree que...) PASSIVE 2: It is believed that Tom is wearing a white pullover. (Se cree que...)







