Speech-Language Pathology in Spanish: Podcasts for the Bilingual
Anuncio

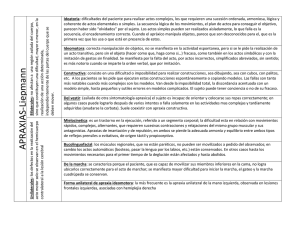
Speech-Language Pathology in Spanish: Podcasts for the Bilingual Clinician Assessment Overview of Childhood Apraxia of Speech Vocabulary: 1.Speech language pathologist 2. Childhood apraxia of speech 3. Speech disorder 4. Questionnaire 5. Syllables 6. Words 7. Intonation 8. Intensity 9. Repetitions 10. Dominant language 11. Oral mechanism exam 12. Diadochokinesis performance 13. Arrhythmic productions 14. Generalization 15. Functional communication 16. Articulation exam 17. Segmental errors 18. Evaluation 19. Consistently 20. Phonetic inventory 21. Phonemic accuracy 22. Intelligibility Terapista de habla y lenguaje Apraxia del habla infantil Desorden del habla Cuestionario Sílabas Palabras Entonación Intensidad Repeticiones Idioma dominante Examen periférico oral Ritmo diadococinético Producciones arrítmicas Generalización Habilidades comunicativas funcionales Examen de articulación Errores segmentarios Evaluación Consistentemente Inventario de fonemas Precision de fonemas Inteligibilidad Childhood Apraxia of Speech Assessment Practice Sentences: 1. I’m the speech-language pathologist. ● Soy la terapista de habla y lenguaje. 2. Children with childhood apraxia of speech have problems with motor planning and saying sounds, syllables, and words. ● Los niños con apraxia del habla infantil tienen problemas en planeando y diciendo sonidos, sílabas y palabras. 3. Childhood apraxia of speech is an uncommon speech disorder. ● La apraxia del habla infantil es un desorden del habla incomún. 4. Looking at the questionnaire that you filled out, I noticed that you have some concerns about your child’s speech. ● Viendo el cuestionario que usted llenó, notó que tiene algunas preocupaciones por el habla de su hijo. 5. One of the tasks will look at your child’s productions with words that have multiple syllables. ● Una de las pruebas verá las producciones de su hijo con las palabras de múltiples sílabas. 6. Your child has difficulty coordinating the muscle movements necessary to say those words. ● Su hijo tiene dificultad para coordinar los movimientos musculares necesarios para decir estas palabras. 7. The connected speech sample will take a look at intonation. ● La muestra de habla conectada mostrará los patrones de entonación. 8. I will observe his voluntary control of his voice intensity. ● Voy a observar el control voluntario de su intensidad de voz. 9. Another task that is used to diagnose childhood apraxia of speech is looking at syllable repetitions. ● Otra prueba que se hace para diagnosticar el apraxia del habla infantil es ver las repeticiones de sílabas. 10. Almost all of the evaluation will be done in both languages and not just in the dominant language . ● Casi toda la evaluación va hacer en los dos idiomas y no solo en el idioma dominante. 11. An important part of this evaluation is an oral mech exam to rule out organic differences. ● Una parte importante de esta evaluación incluye un examen periférico oral para asegurarnos que no haya una causa orgánica. 12. a. The diadochokinesis performance task explores happens when syllable length and complexity increase little by little. ● Cuando se hace la prueba de ritmo diadococinético vemos que sucede cuando las sílabas y la complejidad van aumentando poco a poco. b. Often this diadochokinetic task differentiates a typical speech sound disorder from childhood apraxia of speech. ● Muchas veces la prueba del ritmo diadococinético hace una diferencia al diagnosticar el apraxia del habla infantil y un desorden típico del habla. 13. Children with childhood apraxia of speech may have arrhythmic productions or inability to sustain sounds over longer periods. ● Los niños con apraxia del habla infantil pueden tener producciones arrítmicas o la inhabilidad de sostener los sonidos por un largo tiempo. 14. One of the core deficits of childhood apraxia of speech is generalizability. ● Uno de los déficit básicos del apraxia del infantil es la generalización. 15. Functional communication skills are important for children with childhood apraxia of speech and include the use of important words in both languages. ● Las habilidades comunicativas funcionales son importante para los ninos con apraxia del habla infantil e incluye el uso de palabras claves en ambos idiomas. 16. An articulation exam can be used to evaluate speech sound inconsistencies. ● Un examen de articulación se puede utilizar para evaluar inconsistencias con los sonidos y producciones de palabras. 17. Segmental errors can look like inconsistencies with vowels and consonants. ● Errores segmentarios pueden verse como inconsistencias entre vocales y consonantes. 18. A bilingual assessment for childhood apraxia of speech will also provide knowledge of whether sounds exist in both languages ● En una evaluación de apraxia del habla infantil bilingüe también se proporciona el conocimiento de todos los sonidos del habla de ambos idiomas. 19. If your child does not say the same words consistently this can be a red flag for childhood apraxia of speech. ● Si su hijo/hija no dice las mismas palabras consistentemente esto puede llamar la atención para el apraxia del habla infantil. 20. It is necessary to know how many sounds or phonemes the child produces so can see their phonetic inventory. ● Es necesario saber cuántos sonidos o fonemas produce su hijo y así podemos ver su inventario fonético. 21. Phonemic accuracy shows how accurately your child produces a sound when given multiple opportunities. ● La precisión de fonemas demuestra que tan bien el niño puede producir el sonido en ocasiones múltiples. 22. Intelligibility shows how well a child can be understood by unfamiliar listeners. ● La inteligibilidad demuestra que tan bien personas desconocidas entienden al niño. Useful Resources: Rvachew, S., Hodge, M., & Ohberg, A., (2005). Obtaining and Interpreting Maximum Performance Tasks from Children: A Tutorial. Journal of Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology - Vol. 29, No.4.