Técnicas de Predicción
Anuncio

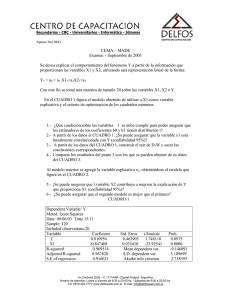
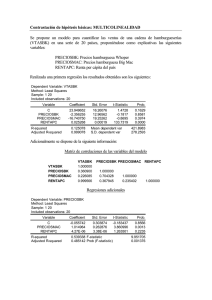
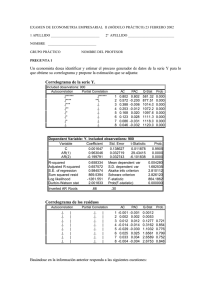
Técnicas de Predicción Curso 2005/2006 Práctica 2 Datos a emplear tomados de la base EcowinPro: a) Serie anual Gasto en Consumo de los hogares en EEUU para el periodo de 1948 a 2005. b) Serie mensual Índice de Producción industrial (IPI) español para el periodo 1975 a 2005. Pasos a dar: Abrir Excel y seleccionar TIME SERIES de EcowinPro y apretar en el según botón que está su derecha después del nombre de la series. a) Para el caso del gasto, en source elija IMF IFS y seleccione el país de interés (United States). Después seleccione NATIONAL ACCOUNTS OR POPULATION y elija HOUSEH.CONS.EXPEND.,INCL.NPISHS, SA, USD. y escoja la que dice Year que empieza en 1948. b) En el caso del IPI, en source elija EcoWin Economic y seleccione el país de interes (Spain). Después seleccione Industry, luego Production y al final By Industry y elija hasta el final la serie que dice Total industry index que empieza en 1975. esp02005 Después sólo hace falta dar a EXPORT TO EXCEL para la hoja de cálculo y automáticamente tendrá los datos listos para trabajar. Guarden el archivo con el nombre IPI.xls Para trabajar los datos en EViews se realiza lo siguiente: Pasos a dar: a) Creamos un Workfile en Eviews. En el MENÚ PRINCIPAL File/New/Workfile Workfile structure ty/Dated-regular frequency Frequency/Monthly Start date 1975:01 End date 2005:12 b) Cargamos los datos de la serie IPI En el MENÚ PRINCIPAL File/Import/Read Text-Lotus-Excel Ficheros a recuperar: a:\IPI.xls Donde dice Upper left data poner la celda de excel en donde empiezan los datos de la serie. En Names for series escriban IPI 1. Predecir el modelo IMA(1,1) para la serie Gasto en el consumo de EUA y compararlo con el modelo de tendencia determinista Trabajaremos con la serie en logaritmos así que calcularemos el logaritmo del consumo En GENR Lconsumo=log(consumo) Primero estimaremos el modelo de tendencia determinista Pasos a dar: a) Generamos una variable t Tendencia En GENR Tendencia=@trend + 1 b) Estimar el modelo y representar ajuste del modelo y los residuos. En el MENÚ PRINCIPAL Quick/Estimate equation/ En Equation Specification, escribir en este orden: Lconsumo C Tendencia Se obtiene lo siguiente Dependent Variable: LCONSUMO Method: Least Squares Date: 03/09/06 Time: 00:05 Sample: 1948 2005 Included observations: 58 Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C TENDENCIA 4.913827 0.074400 0.030566 0.000901 160.7627 82.56223 0.0000 0.0000 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.991852 0.991706 0.114889 0.739169 44.21903 0.039445 Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 7.108626 1.261533 -1.455829 -1.384779 6816.522 0.000000 10 9 8 7 6 5 0.2 4 0.1 0.0 -0.1 -0.2 50 55 60 65 70 75 Residual 80 85 Actual 90 95 00 05 Fitted EL PROCESO IMA(1,1) Vamos analizar el proceso IMA(1,1). Se denomina proceso IMA(1,1) a un proceso tipo: y t y t1 t 1 t1 con | 1 | 1 y t proceso ruido blanco. o y t t 1 t1 con | 1 | 1. Pasos a dar: En el MENÚ PRINCIPAL Quick/Estimate equation/ En Equation Specification, escribir en este orden: D(CONSUMO) C MA(1) Obteniendo lo siguiente: Dependent Variable: D(LCONSUMO) Method: Least Squares Date: 03/21/06 Time: 17:16 Sample(adjusted): 1949 2005 Included observations: 57 after adjusting endpoints Convergence achieved after 12 iterations Backcast: 1948 Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C MA(1) 0.068435 0.411524 0.003646 0.119395 18.77119 3.446746 0.0000 0.0011 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.227662 0.213620 0.019563 0.021049 144.3836 1.696797 Inverted MA Roots Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 0.068621 0.022060 -4.995916 -4.924230 16.21235 0.000175 -.41 0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.00 -0.02 -0.04 -0.06 50 55 60 65 70 75 Residual 80 85 Actual Estimar ahora el modelo IMA(1,2) Pasos a dar: En el MENÚ PRINCIPAL 90 95 00 Fitted 05 Quick/Estimate equation/ En Equation Specification, escribir en este orden: D(CONSUMO) C MA(1) MA(2) Obteniendo lo siguiente: Dependent Variable: D(LCONSUMO) Method: Least Squares Date: 03/21/06 Time: 17:38 Sample(adjusted): 1949 2005 Included observations: 57 after adjusting endpoints Convergence achieved after 11 iterations Backcast: 1947 1948 Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C MA(1) MA(2) 0.069634 0.650778 0.435630 0.004781 0.079862 0.096354 14.56619 8.148754 4.521150 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.409373 0.387498 0.017265 0.016096 152.0284 2.208507 Inverted MA Roots -.33+.57i Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 0.068621 0.022060 -5.229065 -5.121536 18.71411 0.000001 -.33 -.57i 0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.00 -0.02 -0.04 50 55 60 65 70 Residual 75 80 85 Actual 90 95 00 Fitted 05 PREDECIR LOS MODELOS Se tomarán en cuenta solo los datos hasta 1994 y se predecirán a partir de 1995 hasta 2005 a) Para el modelo IMA(1,1) En el MENÚ de la ecuación del modelo para consumo Pulsar Forecast/ En Forecast sample escribir 1995 hasta 2005 Se genera la serie lconsumof Obteniendo lo siguiente 9.6 Forecast: LCONS UMOF A ctual: LCONS UMO S ample: 1995 2005 Include observations: 11 9.4 9.2 Root Mean S quared E rror0.087910 Mean A bsolute E rror 0.078059 Mean A bs. P ercent E rror0.878974 Theil Inequality Coefficient 0.004974 B ias P roportion 0.788450 V ariance P roportion 0.199118 Covariance P roportion0.012432 9.0 8.8 8.6 8.4 95 96 97 98 99 00 LCONS UMOF 01 02 03 04 05 ± 2 S .E . En el Workfile se seleccionan las series lconsumof y lconsumo dando al botón derecho del ratón se selecciona Open/ as Group En el MENU View seleccionar Graph/line 10 9 8 7 6 5 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 LCONS UMO 85 90 95 00 05 LCONS UMOF b) Para el modelo con tendencia determinística En el MENÚ de la ecuación del modelo para consumo Pulsar Forecast/ En Forecast sample escribir 1995 hasta 2005 En forecast name escribir lconsumof2 Se genera la serie lconsumof2 Obteniendo lo siguiente 9.6 Forecast: LCONS UMOF2 A ctual: LCONS UMO S ample: 1995 2005 Include observations: 11 9.4 9.2 Root Mean S quared E rror0.085562 Mean A bsolute E rror 0.068377 Mean A bs. P ercent E rror0.766802 Theil Inequality Coefficient 0.004846 B ias P roportion 0.524786 V ariance P roportion 0.460946 Covariance P roportion0.014268 9.0 8.8 8.6 8.4 8.2 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 LCONS UMOF2 02 03 04 05 ± 2 S .E . En el Workfile se seleccionan las series lconsumof2 y lconsumo dando al botón derecho del ratón se selecciona Open/ as Group En el MENU View seleccionar Graph/line 10 9 8 7 6 5 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 00 05 LCONS UMO LCONS UMOF2 c) Para el modelo IMA(1,2) En el MENÚ de la ecuación del modelo para consumo Pulsar Forecast/ En Forecast sample escribir 1995 hasta 2005 En forecast name escribir lconsumof3 Obteniendo lo siguiente 9.6 Forecast: LCONS UMOF3 A ctual: LCONS UMO S ample: 1995 2005 Include observations: 11 9.4 9.2 Root Mean S quared E rror0.084318 Mean Absolute E rror 0.072210 Mean Abs. P ercent Error0.811734 Theil Inequality Coefficient 0.004773 B ias P roportion 0.733428 V ariance P roportion 0.252369 Covariance P roportion0.014203 9.0 8.8 8.6 8.4 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 LCONS UMOF3 02 03 04 05 ± 2 S .E. En el Workfile se seleccionan las series lconsumof3 y lconsumo dando al botón derecho del ratón se selecciona Open/ as Group En el MENU View seleccionar Graph/line 10 9 8 7 6 5 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 00 05 LCONS UMO LCONSUMOF3