Bolivia - weforum.org - World Economic Forum
Anuncio

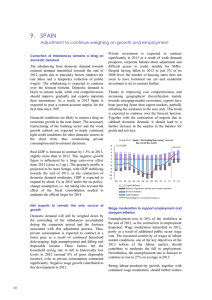
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles Bolivia Key indicators, 2013 GDP (PPP) per capita (int’l $), 1990–2013 Population (millions) ........................................ 11.0 GDP (US$ billions) .......................................... 29.8 GDP per capita (US$) ................................... 2,700 GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total ............ 0.07 Bolivia 15,000 Latin America and the Caribbean 12,000 9,000 6,000 3,000 0 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 Global Competitiveness Index Rank (out of 144) Stage of development Score (1–7) GCI 2014–2015 .................................................... 105 ..... 3.8 Transition 1–2 1 GCI 2013–2014 (out of 148) ..................................... 98 ......3.8 GCI 2012–2013 (out of 144) ................................... 104 ......3.8 GCI 2011–2012 (out of 142) ................................... 103 ......3.8 Factor driven Transition 2–3 2 3 Efficiency driven Innovation driven Institutions Basic requirements (46.0%) .......................................93 ......4.2 7 Innovation Institutions ................................................................ 90 ......3.5 Infrastructure .......................................................... 109 ......3.0 Macroeconomic environment ................................... 35 ......5.5 Health and primary education ................................. 109 ......4.9 Infrastructure 6 5 Business sophistication Macroeconomic environment 4 3 2 Efficiency enhancers (45.5%) ...................................116 ......3.4 Market size Higher education and training ................................... 97 ......3.7 Goods market efficiency ........................................ 132 ......3.6 Labor market efficiency .......................................... 127 ......3.6 Financial market development ................................ 121 ......3.3 Technological readiness .......................................... 118 ......2.8 Market size ............................................................... 84 ......3.4 Health and primary education 1 Higher education and training Technological readiness Financial market development Goods market efficiency Labor market efficiency Innovation and sophistication factors (8.5%) .............94 ......3.4 Business sophistication ......................................... 103 ......3.6 Innovation ................................................................. 83 ......3.1 Bolivia Latin America and the Caribbean The most problematic factors for doing business Access to financing ...........................................................20.8 Restrictive labor regulations ...............................................18.5 Foreign currency regulations ..............................................13.0 Inefficient government bureaucracy ...................................10.7 Inadequate supply of infrastructure ....................................10.3 Corruption ...........................................................................7.1 Inadequately educated workforce ........................................5.2 Poor work ethic in national labor force ................................3.7 Tax regulations ....................................................................2.9 Policy instability ...................................................................1.9 Insufficient capacity to innovate ...........................................1.7 Tax rates..............................................................................1.6 Government instability/coups ..............................................1.0 Inflation ................................................................................0.9 Crime and theft ...................................................................0.8 Poor public health ...............................................................0.1 0 Note: 5 10 15 Percent of responses From the list of factors above, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country and to rank them between 1 (most problematic) and 5. The bars in the figure show the responses weighted according to their rankings. 130 | The Global Competitiveness Report 2014–2015 © 2014 World Economic Forum 20 25 30 2.1: Country/Economy Profiles Bolivia The Global Competitiveness Index in detail INDICATOR VALUE RANK/144 INDICATOR 1st pillar: Institutions VALUE RANK/144 6th pillar: Goods market efficiency (cont’d.) 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Property rights ....................................................... 3.5 ..........111 Intellectual property protection ............................... 3.3 ............89 Diversion of public funds ........................................ 3.5 ............55 Public trust in politicians ......................................... 3.3 ............51 Irregular payments and bribes ................................ 2.6 ..........133 Judicial independence............................................ 3.3 ............94 Favoritism in decisions of government officials ....... 3.6 ............40 Wastefulness of government spending ................... 3.3 ............62 Burden of government regulation ........................... 3.6 ............57 Efficiency of legal framework in settling disputes .... 3.7 ............66 Efficiency of legal framework in challenging regs. ... 3.4 ............67 Transparency of government policymaking............. 3.6 ..........106 Business costs of terrorism .................................... 4.0 ..........122 Business costs of crime and violence..................... 3.6 ..........108 Organized crime ..................................................... 3.7 ..........123 Reliability of police services .................................... 3.5 ..........109 Ethical behavior of firms ......................................... 3.9 ............80 Strength of auditing and reporting standards ......... 3.8 ..........123 Efficacy of corporate boards .................................. 4.1 ..........113 Protection of minority shareholders’ interests ......... 3.7 ............96 Strength of investor protection, 0–10 (best)* .......... 4.0 ..........113 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 Quality of overall infrastructure ............................... 3.6 ............99 Quality of roads ...................................................... 3.3 ............95 Quality of railroad infrastructure .............................. 2.5 ............70 Quality of port infrastructure ................................... 2.0 ..........141 Quality of air transport infrastructure....................... 3.2 ..........120 Available airline seat km/week, millions* ............... 75.6 ............91 Quality of electricity supply ..................................... 3.9 ............94 Mobile telephone subscriptions/100 pop.* ........... 97.7 ............98 Fixed telephone lines/100 pop.* ............................. 8.2 ............98 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 Government budget balance, % GDP*................... 0.1 ............19 Gross national savings, % GDP* .......................... 25.5 ............39 Inflation, annual % change* .................................... 5.7 ..........101 General government debt, % GDP* ..................... 33.1 ............45 Country credit rating, 0–100 (best)* ...................... 37.2 ............86 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 Malaria cases/100,000 pop.* ............................. 104.8 ............34 Business impact of malaria .................................... 3.9 ............56 Tuberculosis cases/100,000 pop.* ..................... 127.0 ..........100 Business impact of tuberculosis ............................. 3.5 ..........139 HIV prevalence, % adult pop.* ............................... 0.3 ............59 Business impact of HIV/AIDS ................................. 3.2 ..........140 Infant mortality, deaths/1,000 live births* .............. 32.8 ..........103 Life expectancy, years*......................................... 66.9 ..........108 Quality of primary education ................................... 3.0 ..........111 Primary education enrollment, net %* .................. 83.4 ..........123 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 Secondary education enrollment, gross %* .......... 77.3 ............96 Tertiary education enrollment, gross %*................ 37.7 ............71 Quality of the education system ............................. 3.3 ............93 Quality of math and science education .................. 3.1 ..........116 Quality of management schools ............................. 3.0 ..........131 Internet access in schools ...................................... 3.6 ............99 Availability of research and training services ........... 3.7 ............97 Extent of staff training ............................................ 3.5 ..........115 2nd pillar: Infrastructure 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 No. procedures to start a business* ........................ 15 ..........141 No. days to start a business* ............................... 49.0 ..........130 Agricultural policy costs.......................................... 3.6 ............87 Prevalence of trade barriers ................................... 3.7 ..........137 Trade tariffs, % duty* .............................................. 8.8 ............97 Prevalence of foreign ownership............................. 3.5 ..........121 Business impact of rules on FDI ............................. 3.6 ..........120 Burden of customs procedures .............................. 3.8 ............82 Imports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 38.6 ............96 Degree of customer orientation .............................. 3.5 ..........130 Buyer sophistication ............................................... 3.6 ............51 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 Cooperation in labor-employer relations ................. 3.7 ..........120 Flexibility of wage determination ............................. 4.0 ..........124 Hiring and firing practices ....................................... 3.5 ............98 Redundancy costs, weeks of salary* ........ not possible ..........143 Effect of taxation on incentives to work .................. 3.6 ............76 Pay and productivity............................................... 3.8 ............89 Reliance on professional management ................... 3.8 ............97 Country capacity to retain talent............................. 3.8 ............48 Country capacity to attract talent ........................... 3.4 ............75 Women in labor force, ratio to men* ..................... 0.80 ............72 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 Availability of financial services ............................... 3.8 ..........105 Affordability of financial services ............................. 3.7 ..........105 Financing through local equity market .................... 3.3 ............76 Ease of access to loans ......................................... 3.6 ............24 Venture capital availability ....................................... 3.4 ............30 Soundness of banks .............................................. 4.0 ..........120 Regulation of securities exchanges ........................ 3.7 ............98 Legal rights index, 0–10 (best)* ................................. 1 ..........143 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 Availability of latest technologies ............................ 3.8 ..........128 Firm-level technology absorption ............................ 3.7 ..........130 FDI and technology transfer ................................... 3.6 ..........129 Individuals using Internet, %* ............................... 39.5 ............83 Fixed broadband Internet subscriptions/100 pop.* ... 1.3 ..........100 Int’l Internet bandwidth, kb/s per user* .................. 9.0 ..........105 Mobile broadband subscriptions/100 pop.*.......... 13.9 ............91 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 Domestic market size index, 1–7 (best)*................. 3.1 ............87 Foreign market size index, 1–7 (best)* .................... 4.2 ............82 GDP (PPP$ billions)* ............................................ 59.2 ............84 Exports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 42.3 ............64 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 Local supplier quantity ........................................... 3.7 ..........134 Local supplier quality.............................................. 3.8 ..........111 State of cluster development.................................. 3.5 ............94 Nature of competitive advantage ............................ 3.3 ............85 Value chain breadth................................................ 3.6 ............91 Control of international distribution ......................... 3.9 ............84 Production process sophistication.......................... 3.5 ............98 Extent of marketing ................................................ 3.7 ..........107 Willingness to delegate authority ............................ 3.5 ............93 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 Capacity for innovation........................................... 3.5 ............92 Quality of scientific research institutions ................. 3.2 ..........101 Company spending on R&D................................... 3.5 ............41 University-industry collaboration in R&D ................. 3.5 ............72 Gov’t procurement of advanced tech products ...... 3.5 ............64 Availability of scientists and engineers .................... 3.6 ............94 PCT patents, applications/million pop.* .................. 0.1 ..........102 7th pillar: Labor market efficiency 8th pillar: Financial market development 3rd pillar: Macroeconomic environment 4th pillar: Health and primary education 5th pillar: Higher education and training 6th pillar: Goods market efficiency 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 Intensity of local competition .................................. 3.8 ..........139 Extent of market dominance .................................. 3.8 ............66 Effectiveness of anti-monopoly policy ..................... 3.5 ..........114 Effect of taxation on incentives to invest................. 3.6 ............77 Total tax rate, % profits* ....................................... 83.4 ..........140 9th pillar: Technological readiness 10th pillar: Market size 11th pillar: Business sophistication 12th pillar: Innovation Notes: Values are on a 1-to-7 scale unless otherwise annotated with an asterisk (*). For further details and explanation, please refer to the section “How to Read the Country/Economy Profiles” on page 101. © 2014 World Economic Forum The Global Competitiveness Report 2014–2015 | 131