Syllabus – Plan de negocio General Course Details: Kurs No.: IBU
Anuncio

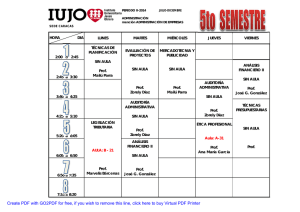
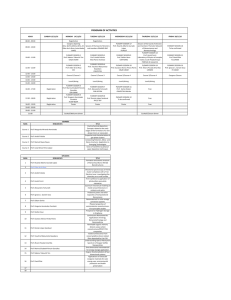
Syllabus – Plan de negocio General Course Details: Kurs No.: IBU 2122 Title: Plan de negocio Language: Spanish Credits: ECTS 5 (4 weekly contact hours) Level: Advanced (Bachelor – 4th semester) Sessions: Friday, 11.30 – 13.00, 13.45 – 15.15 Participants: Students of the IB and ISP track Requirements: Students should have completed all the foundation courses in management taught in Spanish. A high proficiency in Spanish is required. This is not a language course. Lectures Details: Lecturer: Office: Contact: Prof. Dr. Kerstin Bremser / Jorge Enrique Peña Mosquera W2.3.26 Tel: 07231 / 28 6299 or email: [email protected] / [email protected] Colloquium: Wednesday, 11.30 – 13.00 Description of Course: This course provides an introduction to entrepreneurial behavior in the Spanish speaking world. In addition, students apply skills acquired during the first study phase, mainly in cost accounting, marketing and HR management. Main learning goals are: - What different models exist to explain entrepreneurial behavior? - How do you write a business plan? - What are different aspects of the business plan? - How are successful companies started? - How does the investment climate in Spain look like? Learning Objectives: LO Learning Objective / Outcome Contributions to learning objectives Assessment Expert knowledge Students show that they have sound basic knowledge … 1.1 … in Business Administration. Analysis of the importance of business plans in the business world, writing of a business plan Business plans written in teams 1.2 … in Economics. 1.3 … in Business Law. 1.4 … in Quantitative Methods. Use of information technology 2.1 Students demonstrate proficiency in using computer programs to solve business problems. 2.2 Students are able to use information systems effectively in real world business settings. 3. Critical thinking and analytical competence Students are able to apply analytical and critical thinking skills to complex problems. 4. Discussion of causes / consequences / risks associated with the creation of your own company in a foreign environment. Evaluation based on written report and oral contributions Ethical awareness Students are able to develop business ethics strategies and apply them to typical business decision-making problems. Communication skills 5.1 Students are able to express complex problems effectively in writing 5.2 Students demonstrate their oral communication skills in presentations and papers. 6. Capacity for teamwork Students show that they are able to work successfully in a team by performing practical tasks. Write a Business Plan in Spanish Language Present the plan in front of a group of supervisor Elaborate the plan in a team of two to three persons Hand in a written assignment of approx. 30 pages in Spanish Graded oral presentation Tutorials with the professor to steer the teamwork to an effective goal Specific objectives of the class 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 The students demonstrate broad knowledge of business and management tools, methods and know-how, which are used in an international environment. Application of management tools in the set up of the business and evalution on appropriateness The students are able to communicate/negotiate in English and French/Spanish, and are able to use the relevant cultural skills necessary to work successfully in an international environment. Presentation and elaboration of the business plan in Spanish language. Marketing has to be addressed to customers in the foreign market and attract interest from people of a different culture The students understand the business environments, institutions and systems in the Anglo-Saxon and French/Spanish regions and are aware of their implications for International Business. The students are able to analyze problem situations in international business and 7. 1 – 7.3: Oral presentation and written paper on the business idea. Proof of successful operation of the newly founded business in a foreign environment. subsequently develop relevant solutions. Contents of the Course: During a semester approx. 30 sessions are available to consider the following main topics: Session 1/2 07/10/16 3/4 5/6 6/7 7/8 9 / 10 11 / 12 13 / 14 15 / 16 17 / 18 19 / 20 21 / 22 14/10/16 21/10/16 28/10/16 11/11/16 25/11/16 26/11/16 26/11/16 02/12/16 09/12/16 16/12/16 Tbd Topic Business Plan: Introduction to the topic of entrepreneurship / Outline Marketing Plan Operational Planning Own Elevator Pitch Tutorials Financial Planning Financial Planning Financial Planning Tutorials Tutorials Tutorials Student Presentation of Business Plan 23 / 24 Tbd Student Presentation of Business Plan 25 / 26 Tbd Student Presentation of Business Plan 27 / 28 Tbd Student Presentation of Business Plan Teacher Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser Prof. Dr. Bremser / Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Dr. Bremser / Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Dr. Bremser / Prof. Alonso-Almeida Prof. Dr. Bremser / Prof. Alonso-Almeida * for the tutorials students only need to be present during their assigned slot Didactical Approach and Workload: The course consists of 2 sessions of 1 ½ hours per week and awards 5 credits. It is therefore expected that students use at least 60 hours to prepare themselves for the session, to subsequently review the session and write up their business plan. The didactical approach for the course is a mix of formal lecture and case studies that are solved in groups. During the formal lecture it is expected that students are actively involved. In addition, we try to have one guest speaker per term. Attendance to his/her speech is mandatory. In addition, students have to attend several tutorials where the professors check the progress of the groups. Method of Assessment: The final grade is a weighted combination of different assessments. 50 % of the final grade is comprised of the writing of a business plan that students prepare in groups of three, present in class and hand in. Papers are due on February 12th. Absolutely no late papers are accepted, no made up assignment is offered. 30 % is comprised of the presentation of the plan. The remaining 20% are evenly distributed between the three tutorials and class participation. Students are expected to be present at all classes. Absences have to be excused in advance and agreed upon by the lecturer. Unexcused absence during more than two classes leads to failure of the entire course. The grading is as follows: 1.0 Very good, a performance significantly above the average 2.0 Good, an above average performance 3.0 Satisfactory, an average performance 4.0 Adequate, a below average performance with noticeable shortcomings 5.0 Fail, an unacceptable performance Literature: The necessary materials are: A copy of the slides found on the e-learning platform A copy of the distributed articles and case studies found on the e-learning platform Weinberger, K. (2009): Plan de negocios. Nathan Associates Inc. USAID / Perú / Mype competitiva. http://www.uss.edu.pe/uss/eventos/JovEmp/pdf/LIBRO_PLAN_DE_NEGOCIOS.pdf Alcaraz, R. (2001); El emprendedor de éxito, Guía de planes de negocio. McGraw Hill Interamericana editores. In addition to these documents, the following are useful reference books: Almoguera, J. A.: El plan de negocio, http://www.megaconsulting.net/cgivel/megaconsulting1/archivos/PLAN.pdf, 2006 Amat Salas, O.: Comprender la contabilidad y las finanzas, Ediciones Gestión 2000, Capellades (Barcelona), 1998 Amat Salas, O.:Análisis Económico Financiero, Ediciones Gestión 2000, Barcelona, 2005, Barcelona, 2010. Amat Salas, O.; Soldevila, P.: Contabilidad y Gestión de Costes, Editorial Profit, Bueno Campos et al.: Dirección estratégica: Desarrollo de estratégica y análisis de casos, Pirámide, 2006 Cibrán Ferraz P., Villanueva Villar, M., Fernández Rodríguez, M.T.: Planificación financiera, teoría y casos prácticos, Tórculo Edicións, Santiago de Compostela, 2008. Dolan et al.: La gestión de los recursos humanos, 3ª ed., McGraw Hill, 2007 Durbán Oliva, S. irimia Diéguez, A.: Planificación financiera en la práctica empresarial, Ediciones Pirámide, Madrid, 2009. Hollensen, S.: Global Marketing – a decision-oriented approach, 5th edition, Pearson, 2011 Ollé et al.: El plan de empresa: Cómo planificar la creación de una empresa, Marcombo, 2008 Rodríguez Sandiás, A.: Planificación financiera aplicada, Tórculo Edicións, Santiago de Compostela, 2008. Web documents: www.maricopa.edu Guía de un plan de negocio www.circe.es Centro de Información y Red de Creación de Empresas www.barcelonanetactiva.com Barcelona activa www.emprendedores.es Emprendedores www.investinspain.org Invest in Spain www.ipyme.org Pequeña y Mediana Empresa www.planempresa.ipyme.org Plan de Empresa www.infoautonomos.com Como crear una Sociedad ...