Presente Simple - Ganando Con Inglés Online
Anuncio

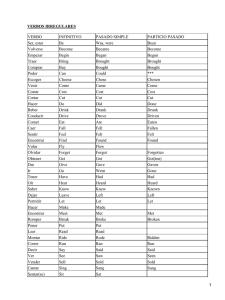
Índice tIntroducción ..................1 tPresente Simple ..................2 tPresente Progresivo ..................4 tFuturo Simple ..................6 tPasado Simple ..................8 tPasado Progresivo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 tPresente Perfecto . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 tPasado Perfecto . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 tVerbos Modales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 tLista de Verbos Irregulares . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 tExamen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 Copyright C 2008 Inglés Sin Barreras, Inc. todos los derechos reservados. Inglés Sin Barreras así como hablemosingles.com son marcas registradas propiedad de Inglés Sin Barreras, Inc. Los contenidos de esta Guía son propiedad de Inglés Sin Barreras, Inc. Qued estrictamente prohibido la reproducción de, parcial o total, sin el permiso correspondiente. Introduction Introducción Congratulations! Felicidades! If you are reading this guide is because you wish to learn English. Believe it, this is a huge step forward and we can help you. We compiled the most practical verbal tenses in English, and made it simple and easy for you to remember. However, be aware that even when the expressions herein are basic and understandable, you need a previous knowledge of English language. This guide begins with easy topics and gradually increases its level of complexity. In the last part, you will find a short test so you can know if you have reached an adequate learning. We suggest practice. Realize that this guide does not use the same natural learning method as used in Ganando con Inglés. Moreover, it do es not comprise material from the course. This guide has been created with a different purpose. We do not want that you lose great opportunities just because you do not speak English. Get the promotion you are looking forward, change your job, travel to other countries, know different cultures and give your life emotion and success: Si estás leyendo esta guía seguramente es porque tienes el deseo de aprender inglés, y créelo, este es un importante paso hacia adelante. Nosotros te vamos a ayudar. Hicimos una recopilación sobre los tiempos verbales más utilizados en inglés y los explicamos de una manera sencilla y fácil de recordar para ti. Sin embargo, queremos aclararte que aunque las expresiones utilizadas son básicas y muy entendibles, es necesario un conocimiento previo del idioma inglés. La guía inicia por los temas más sencillos y el nivel aumenta gradualmente. Al final encontrarás un pequeño test que medirá sí has aprendido lo suficiente. Te recomendamos practicar. Debes saber que esta guía no utiliza el mismo método de aprendizaje natural de Ganando con Inglés, ni incluye contenido del curso. Ha sido realizada con un objetivo diferente. No queremos que dejes pasar ninguna oportunidad más por no hablar inglés. Llévate ese ascenso que deseas, cambia de trabajo, viaja a otros países, conoce otras culturas, y dale a tu vida mucha más emoción y éxito: Learn English once and for all! ¡Aprende inglés de una vez por todas! www.ganandoconingles.com 1 CONVERSACIONES My Hobby Alan Caroline, what's your hobby? Caroline Well, I play the guitar. Alan Really? Caroline Yes, I like playing the guitar. Alan How often do you play? Caroline I play twice a week. What about you? Do you have a hobby? Alan I'm interested in video games. Caroline That's interesting! Alan Yes, I play video games almost every day. Useful Expressions tReally ( ¿De verdad? ) Mi Pasatiempo Alan Carolina, ¿cuál es tu hobby? Carolina Bueno, yo toco la guitarra. Alan ¿De verdad? Carolina Sí, a mi me gusta tocar la guitarra. Alan ¿Qué tan seguido tocas la guitarra? Carolina Yo toco la guitarra 2 veces por semana. ¿Y tú? ¿Tú tienes algún hobby? Alan Yo estoy interesado en los videojuegos. Carolina ¡Eso es interesante! Alan Sí, yo juego videojuegos casi todos los días. www.ganandoconingles.com tWell ( Bueno ) tI Like To ( Me gusta ) tHow often? ( ¿Qué tan seguido? ) tWhat about you? ( ¿Qué hay sobre ti? ) 2 PRESENTE SIMPLE Presente de los Verbos Auxiliares Presente Simple tTo be: - I am (´m), You/we/they are (´re), he/she/it is (´s). El tiempo Presente Simple se utiliza, entre otras cosas, para expresar acciones, eventos o situaciones habituales que transcurren con cierta frecuencia. - I am not (´m not), You/we/they are not (´re not / arent´t), he/she/it is is (´s not / isn´t). tTo have: I/you/we/they have (´ve), he/she/it has. - Have not (don´t haven´t), does not have (hasn´t). have not (don't have), does not have (doesn't have) Por ejemplo: tI'm a teacher. Yo soy un maestro. tAnne is a teacher. Ana es maestra. tShe lives in London. Ella Vive en Londres. tAnne gets up at 7 a.m. Ana se despierta a las 7 a.m. tShe usually has breakfast at 8 a.m. Usualmente desayuna a las 8 a.m. Forma Afirmativa Forma Negativa Sujeto + Verbo + Complemento Sujeto + Verbo + Complemento I am a student (Yo soy un estudiante) I am not a student (Yo no soy un estudiante) Recordemos: Al conjugar los verbos regulares en tiempo presente, debe You are an engineer (Tú eres un ingeniero) You are not an engineer (Tú no eres un ingeniero) agregarse para la tercera persona del singular (He / She / It) una "s" al verbo base, mientras que para las demás personas el verbo permanece igual. FormaInterrogativa Sujeto + Verbo + Complemento ? Am I a student? (¿Soy yo un estudiante?) Are you an engineer? (¿Eres tú un ingeniero?) www.ganandoconingles.com 3 CONVERSACIONES At the party Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Hi, How are you doing? I’m ok, what about you? I’m good. Is Janet at the party? Yes, she is. She’s at the garden. What is she doing? She’s talking with Patty right now. Where are Peter and Sue? They’re dancing now. Are they singing too? No, they aren’t. They´re drinking some soda, but Alice is singing a romantic song. And who’s playing the guitar? Maybe Alex is. It’s nice talking to you! En la fiesta Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Joe Ricky Useful Expressions tHi, Hello ( Hola ) tHow are you doing? Hola, ¿Cómo te va? Bien, ¿Y tú? Bien. ¿Está Janet en la fiesta? Si. Está en el jardín. ¿Qué está haciendo? Está platicando con Patty en este momento. ¿Dónde están Pedro y Susana? Están bailando ahora. ¿Están cantando también? No. Están tomando refresco, pero Alicia está cantando una canción romántica. ¿Y quién está tocando la guitarra? Quizá es Alex. ¡Es agradable platicar contigo! www.ganandoconingles.com ( ¿Cómo te ha ido? ) tWhere are ( ¿Dónde están? ) tI'm ok/ I'm good ( Estoy bien) tMaybe ( Quizás ) tIt's nice talking to you ( Es agradable platicar contigo ) 4 PRESENTE PROGRESIVO Presente Progresivo Forma Afirmativa Ejemplo: Forma Negativa Sujeto + To Be + Verbo + ING + Complemento Sujeto + To Be + Not + Verbo + ING + Complemento I am doing the homework (Estoy haciendo la tarea) They are not drinking coffe. (Ellos no están tomando café) You are playing the guitar (Tu estás tocando la guitarra) He is not buying that car (El no está comprando ese auto) tI am working at home (Estoy trabajando en casa) tYou are doing the homework (Estas/Estan haciendo la tarea) tWe are sitting next to Mr. Lee. (Estamos sentados junto al Sr. Lee) tI'm not having fun (No me estoy divirtiendo) tAre you doing your homework? (¿Estás haciendo tu tarea?) Forma Interrogativa To Be + Sujeto + Verbo + ING + Complemento ? Am i eating too much? (¿Estoy comiendo demasiado?) Are you doing yoga? (¿Estás haciendo yoga?) El presente progresivo es usado para expresar que una actividad está sucediendo al momento de hablar. Este tiempo verbal se construye utilizando como auxiliar el verbo TO BE (am, is, are) y como verbo principal en infinitivo con la terminación ING. www.ganandoconingles.com 5 CONVERSACIONES Cleaning your room Mom Daughter Mom Daughter Mom Daughter Mom Daughter Mom Daughter Mom Are you going to clean your room today? I don’t know, mom. I have a lot of homework to do. Really? When are you going to do it then? Well… Remember that your friends are coming tonight. Oh, I had forgotten that! I’ll clean it right now. Good! Wait! Mom! Where are you going? I’ll go to buy some snacks to your friends. Aren’t you going to help me? I won’t have enough time, I’m going to the supermarket, sorry! Daughter Never mind. Useful Expressions tGood ( Bien ) tWait ( Espera ) Limpiando tu cuarto Mamá Hija Mamá Hija Mamá Hija Mamá Hija Mamá Hija Mamá Hija t I don't know ¿Vas a limpiar tu cuarto hoy? No lo sé mamá. Tengo que hacer mucha tarea. ¿De verdad? Entonces, ¿cuándo lo vas a limpiar? Bueno… Recuerda que tus amigos van a venir esta noche. ¡Híjole, se me había olvidado! Lo limpiaré ahora mismo. Bien. ¡Espera! ¡Mamá!, ¿adónde vas? Iré a comprar algunos bocadillos para tus amigos. ¿No me vas a ayudar? Lo siento, pero no tendré tiempo suficiente, me voy al supermercado. No te preocupes. www.ganandoconingles.com ( No lo se ) tReally? ( ¿De verdad? ) tWhere are you going? ( ¿A dónde vas? ) tSorry ( Lo siento ) tNever mind ( No hay problema ) 6 FUTURO SIMPLE Futuro con Will Recordemos: El tiempo futuro se forma con los verbos auxiliares will, más el Forma Afirmativa Forma Negativa Sujeto + Will + Verbo + Complemento Sujeto + Will not + Verbo + Complemento She will clean her room (Ella limpiará su cuarto) Contracción: She'll clean her room (Ella limpiará su cuarto) She will not clean her room (Ella no limpiará su cuarto) Contracción: She won't clean her room (Ella no limpiará su cuarto) infinitivo del verbo principal. Se puede contraer el auxiliar will. Will -> 'll, Will not -> Won't Futuro con Be going to Forma Afirmativa Sujeto + To be + going to + Complemento She is going to clean her room (Ella va a limpiar su cuarto) Forma Negativa Sujeto + To be + not going to + Verbo + Complemento She is not going to clean her room (Ella no va a limpiar su cuarto) Forma Interrogativa Will + Sujeto + Verbo + Complemento ? Forma Interrogativa To be + Sujeto + Going To + Verbo + Complemento Will she clean her room? (¿Limpiará ella su cuarto?) Is she going to clean her room? (¿Va a limpiar ella su cuarto?) El tiempo futuro se utiliza, entre otras cosas, para expresar promesas, determinación, dar énfasis o situaciones condicionales. tI will clean my room. Limpiaré mi cuarto. tI will clean it right now! ¡Lo limpiaré ahora mismo! tI will clean it if you help me. Lo limpiaré si tú me ayudas. tShe will do it. Ella lo hará. Cuando queremos indicar el propósito de realizar alguna acción futura o se planea algo, la frase going to es muy común. El uso de la forma verbal going to es mucho más generalizado que will para indicar acción futura o para expresar intención de realizarla en el futuro. www.ganandoconingles.com 7 CONVERSACIONES Enjoying vacations Edward How’s it going? Lillian Not bad, everything is ok, what about you? Edward I’m fine and a lot to talk. Lillian Tell me, how was your vacation? Edward It was great. My family and I went to the beach. Lillian Wow, that’s terrific!! And what did you do there? Edward Well, I swam at the beach, my mom prepared sandwiches, and then we went fishing. Tell me about your vacation! Lillian We went to the mountains. We left home around 5 o’clock in the morning. We went skating and my brother climbed a small mountain. Edward Did you go to the Rocky Mountains? Lillian No, we didn’t. We traveled to YellowStone. Did you travel to Puerto Vallarta? Edward Yes, we did. We stayed there for two weeks, also we visited the aquarium. Disfrutanto las vacaciones Useful Expressions tHow's it going? ( ¿Qué tal? ) tNot bad ( No está mal ) Edward ¿Qué tal? Lillian No me puedo quejar, todo muy bien, ¿y tú? Edward Bien y mucho que platicar. Lillian Dime, ¿Cómo estuvieron tus vacaciones? Edward Estuvieron fantásticas. Mi familia y yo fuimos a la playa. Lillian ¡Wow, eso es genial! ¿Y que hicieron ahi? Edward Bueno, nadé en la playa, mi mamá preparó emparedados y luego fuimos de pesca. ¡Platícame de tus vacaciones! Lillian Fuimos a las montañas, caminamos alrededor del bosque, fuimos a esquiar y mi hermano escaló una montaña pequeña. Edward ¿Fueron a las Montañas Rocallosas? Lilian No. Viajamos a Yellowstone. ¿Viajaron a Puerto Vallarta? Edward Sí. Permanecimos por dos semanas, y también visitamos el acuario. www.ganandoconingles.com tWe went to ( Fuimos a) tThat's terrific! ( ¡Es genial! ) tIt was great ( Estubo muy bien ) tTell me ( Dime ) 8 PASADO SIMPLE El tiempo pasado es usado para hablar acerca de actividades o situaciones que comenzaron y terminaron en un tiempo particular en el pasado, y a su vez traduce el pretérito simple en español: Comí, jugué, nadé, corrí, etc., y notaremos que este tiempo, en inglés, tiene una sola forma para todas las personas. Pasado de los verbos auxiliares tTo be: I / he / she / it was, you/we/they were - Was not (wasn´t), were not (´weren´t). tTo have: had; en una pregunta: did + sujeto + have. - Did not have (didn't have) Forma Afirmativa Forma Negativa Sujeto + Verbo en pasado + Complemento Sujeto + did not +Verbo en pasado + Complemento I went to the beach (Fui a la playa) I didn't go to the beach (Yo no fui a la playa) We traveled to YellowStone (Nosotros viajamos a YellowStone) We didn't traveled to YellowStone (Nosotros no viajamos a YellowStone) Forma Interrogativa Did + Sujeto + Verbo en presente + Complemento ? Did I tell you? (¿Te lo dije?) tIt was great. Fue genial Fue muy bueno. tMy family and I went to the beach. Mi familia y yo fuimos a la playa. Para cambiar un verbo a pasado basta con agregar una -ed al final si es regular. Ejemplo: tPlay (jugar) -> Played (jugó). tClean (Limpiar) -> Cleaned (Limpió). Al final de la guía se incluye una lista de verbos irregulares. Ejemplo: tTell (Decir) -> Told (Dijo), tTeach (Enseñar) -> Taught (Enseñó). Did you find your cellphone? (¿Encontraste tu teléfono celular?) www.ganandoconingles.com 9 CONVERSACIONES Talking in the school Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose Edward Rose What were you doing at the store yesterday? I was waiting for David. What was he doing? He was buying things for school. He was looking for special sales. What was he buying? Pens, some paper, a notebook. Where were you? How did you see me? I was in the store too. What were you doing there? I was with Lisa. Was Lisa buying things? No, she wasn’t. She was working. Oh, I didn’t see you. I saw you pass, but you were looking something. Rose, sorry but I have to go to classes, can we talk later? Sure, don’t worry. See you after class. Hablar en la Escuela Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Eduardo Rosa Useful Expressions tWhat were you doing? ( ¿Qué estabas haciendo? ) tI was waiting for ( Estaba esperando a ) ¿Qué estaban haciendo en la tienda ayer? Estaba esperando a David. ¿Qué estaba haciendo él? El estaba comprando artículos para la escuela. Estaba buscando ofertas. ¿Qué estaba comprando? Plumas, algo de papel, un cuaderno. ¿Dónde estabas? ¿Cómo me viste? Estaba en la tienda también. ¿Qué estabas haciendo ahí? Estaba con Lisa. ¿Estaba Lisa comprando cosas? No, ella estaba trabajando. Oh, no las vi. Los vi pasar, pero estaban buscando algo y decidí no interrumpirlos. Rosa, lo siento, pero me tengo que ir a clases, ¿podemos hablar después? Claro, no te preocupes. Te veo después de clase. www.ganandoconingles.com tI was with ( Estaba con ) tIt's fine ( Está bien) tSure ( Seguro ) tDon't worry ( No te preocupes ) 10 PASADO PROGRESIVO Pasado Progresivo Forma Afirmativa Forma Negativa Sujeto + To be (was, were) + verbo + ING + Complemento Sujeto + To be (was, were) + not + verbo + ING + Complemento I was talking with lisa (Estaba hablando con lisa) She was not talking with Tom (Ella no estaba hablando con Tom) They were waiting for David (Ellos esperaban a David) You were looking for a new car (Ustedes buscaban un auto nuevo) El pasado continuo se forma con el pasado simple del verbo (to) be: was o were como auxiliar más el gerundio (ing) del verbo principal. Describe una acción que ocurría en cierto momento o época en el pasado. Usualmente el pasado continuo está complementado por un pasado simple. tI was sleeping when you called. Estaba durmiendo cuando llamaste. t It was nice talking to you. Fue divertido hablar contigo. tShe was thinking what to do. Ella estaba pensando que hacer. tWe were living in New York in 2006. Nosotros vivimos en Nueva York en 2006. Forma Interrogativa To be (was, were) + Sujeto + Verbo + ING + Complemento ? Was I buying things? (¿Estaba yo comprando cosas?) Forma Interrogativa Did + Sujeto + Verbo en presente + Complemento Were they waiting for ?David? (¿Esperaban ellos a David?) www.ganandoconingles.com 11 CONVERSACIONES S CHIAPA My beautiful car Sandy Saul Sandy Saul Sandy I love this car! It´s so much fun to drive and it´s very comfortable. Have you driven a sports Focus car? No, I haven´t, but please slow down a little, Sandy, you ´re doing nearly 100! Am I? Oh, sorry, but don´t worry. I´ve never gotten a speeding ticket. Um, how long till we get there? You know, I´ve never been to Chiapas before. Oh, we´ll be there in about an hour. Useful Expressions tI love this ( Yo amo este ) tHave you? Mi precioso auto ( Has tu? ) tNo. I haven´t Sandy Saúl Sandy Saúl Sandy ¡Yo amo este auto! es muy divertido y cómodo conducirlo, ¿has conducido un automóvil Focus deportivo? No, no lo he hecho, pero por favor baja un poco la velocidad, Sandra, ¡ya estás casi en los 100 kms! ¿Lo estoy? Oh, lo siento, pero no te preocupes. Yo nunca he recibido una multa por alta velocidad. Um, ¿cuánto nos falta para llegar? Sabes, Yo nunca he estado en Chiapas antes. Oh, estaremos ahí mas ó menos en una hora. www.ganandoconingles.com ( No no lo he hecho ) tUntil / Till ( Hasta que / Mientras ) tYou Know ( Tu sabes ) tAbout an hour ( Cerca de una hora ) 12 PRESENTE PERFECTO Presente Perfecto Forma Afirmativa Sujeto + have/has + verbo en particio pasado + Complemento que es igual para todas las personas. Forma Negativa Sujeto + have/has + not + verbo en participio pasado + complemento We have played tennis for two hours (Hemos jugado tenis por dos horas) You have not studied a lot (Tu no has estudiado mucho) She has arrived late again (Ella ha llegado tarde de nuevo) He has not buyed that car (El no ha comprado ese carro) Los verbos irregulares tienen su propio participio pasado y la única manera de aprenderlos es memorizarlos. Normalmente son los que aparecen en la tercera columna de los listados de verbos irregulares en los diccionarios de inglés. Por ejemplo el participio pasado del verbo TO SEE (ver) es "seen". Siempre es igual para todas las personas. tWe have seen many people around here. Nosotros hemos visto mucha gente por aquí. tShe has seen many people around here. Ella ha visto mucha gente por aquí. Forma Interrogativa Have/has + Sujeto + Verbo en participio pasado + Complemento ? Para realizar preguntas usando este tiempo, se usa HAVE (conjugado para la persona correspondiente), seguido del sujeto, luego el participio pasado y finalmente el resto de la oración. Have i gone to the mall? (¿He ido al centro comercial?) Has he cleaned his room? (¿Ha limpiado el su habitación?) tHave you had lunch? Has almorzado? El tiempo Present Perfect se usa para hablar de acciones comenzadas en el pasado y que aún continúan en el presente. La forma negativa se compone del auxiliar HAVE en su forma negativa (conjugado para la persona correspondiente), seguido del participio pasado, que es igual para todas las personas. tI haven't seen him yet. Aún no lo he visto. Ejemplo: tI have been here since Monday. Yo he estado aquí desde el lunes. Para formarlo, se usa el auxiliar HAVE, conjugado para la persona correspondiente (cambia solamente para la tercera persona del singular), seguido del participio pasado, www.ganandoconingles.com 13 CONVERSACIONES I steal in house Sally Hi Donna, what happened to you! Look at your face! Donna Oh! I’m really scared! I’m going to the police station. Sally Why? What happened? Donna Well, I arrived to my house this evening, and I realized that somebody had broken into it. Somebody had been in my house and had taken my new computer! Sally Really? How did you realize it? Donna Because I tried to open the door but somebody had opened it before. Then, when I came in, I looked that all my stuff were in a mess. I had left the computer on the table, but it wasn’t there anymore: a thief had stolen my computer! Sally Oh, what a shame! Donna Yes, I had bought that computer just a week ago. Sally Oh well, I’ll go with you to the police station. Donna Thank you. Robo en casa Useful Expressions tWhat happened to you? ( ¿Qué te pasó? ) tI'm really scared ( Estoy muy asustado ) Sally Donna Sally Donna Hola Donna, ¿qué te pasó? ¡Mira la cara que traes! Oh! ¡Estoy muy asustada! Voy a la estación de policía. ¿Por qué? ¿Qué pasó? Resulta que llegué a mi casa esta tarde y me di cuenta de que alguien se había introducido. ¡Alguien había estado en mi casa y se había llevado mi nueva computadora! Sally ¿De veras? ¿Cómo te diste cuenta? Donna Porque traté de abrir la puerta pero alguien la había abierto antes. Luego, cuando entré, vi que todas mis cosas estaban en desorden. ¡Yo había dejado la computadora sobre la mesa, pero ya no estaba allí: un ladrón se había robado mi computadora! Sally ¡Oh, qué pena! Donna Sí, había comprado esa computadora hace sólo una semana. Sally Bueno, te acompaño a la estación de policía. Donna Gracias. www.ganandoconingles.com tWhy? ( ¿Por qué? ) tHow did you realize? ( ¿Cómo te diste cuenta?) tWhat a shame! ( ¡Qué pena! ) tThank you ( Gracias ) 14 PASADO PERFECTO Pasado Perfecto Forma Afirmativa Sujeto + had + verbo en particio pasado + Complemento A thief had taken my computer (Un ladrón se había llevado mi computadora) Forma Negativa Sujeto + had + not + verbo en participio pasado + complemento A thief had not (hadn't) take my computer (El ladrón no se había llevado mi computadora) tSomebody had been in my house.Alguien había estado en mi casa. tHe had been doing his homework almost every day. El había estado haciendo su tarea casi todos los días. tShe had been looking for you. Ella había estado buscandote. tWe had taken the bus to Picadilly. Nosotros habíamos tomado el bus a Picadilly. tI had studied chinese before getting this job. Yo había estudiado chino antes de obtener este trabajo. Forma Interrogativa Had + Sujeto + Verbo en participio pasado + Complemento ? Had a thief taken my computer (¿Se había llevado mi computadora un ladrón?) El pasado perfecto se forma con el tiempo pasado del verbo have (had) como verbo auxiliar, para todas las personas (I, you, he, etc.) más el participio pasado del verbo principal conjugado. Se utiliza para describir acciones ocurridas y terminadas: www.ganandoconingles.com 14 CONVERSACIONES Preparing a cake William Peter William Freddy Sally Peter Fredy Hi guys, what are you doing? We are preparing this cake for my mom’s birthday. May I help you? I could pass you the ingredients. No, I don’t think so. You should sit and be quiet. Well, I think he could help us to prepare the cake. O.K, you could read the instructions for making the cake. Hurry up guys! We don’t have much time. It’s late and Mommy might get back earlier. Mom Hello, children! I’m already here. William Uh, oh! Hey mom, how was your shopping? Mom It was perfect! Sally Mom, you look stressed. I think you ought to go to bed and take a nap. All Brothers Yeeesssss Moommmm! Go to bed and take a rest. Mom O.K, please be good. See you later. Preparando un pastel William Peter William Freddy Sally Peter Fredy Hola muchachos, ¿qué están haciendo? Estamo preparando este pastel para el cumpleaños de mi mamá. ¿Me dan permiso de ayudarlos? Podría pasarles los ingredientes. No, no lo creo. Sólo deberías sentarte y estar callado. Bueno, yo creo que podría ayudarnos a preparar el pastel. O.k. Podrías leer las instrucciones para hacer el pastel. ¡Apresúrense chicos! No tenemos mucho tiempo. Es tarde y mami posiblemente regrese más temprano. Mami ¡Hola niños! Ya estoy aquí. William ¡Hey mami! ¿cómo estuvieron tus compras? Mami Estuvo perfecto. Sally Mami, te ves estresada. Creo que deberías ir a la cama y tomar una siesta Todos los Hermanos ¡Siiiiiiii mamiii! Ve a la cama y descansa. Mami O.K. Por favor, pórtense bien. Nos vemos luego. www.ganandoconingles.com Keyphases tWhat are you doing? ( ¿Qué están haciendo? ) tMay I help you? ( ¿Puedo ayudarle? ) tI don't think so ( No lo creo ) tPlease be good ( Por favor comportate ) 15 VERBOS MODALES Verbos Modales (Auxiliares Especiales) Can, May, Should, Ought, Must, Would, etc. CAN – COULD Can es un verbo defectivo o incompleto, ya que sólo tiene dos tiempos, can en presente y could en el pasado. Can tampoco tiene infinitivo y siempre se emplea como auxiliar especial con el otro verbo en infinitivo. Can puede expresar: Habilidad, Posibilidad, Permiso, aunque también se considera más correcto usar May. tYou can't miss it. No te lo puedes perder. tCould you please tell me where the bank is? ¿Podría decirme dónde está el banco? WOULD Es un verbo auxiliar que se usa para expresar un deseo, preferencia, para solicitar ayuda amablemente, o para expresar un deseo insatisfecho. En estas situaciones también se pueden usar los verbos can o could. MAY, MIGHT May, como el auxiliar can, también es verbo defectivo y solamente tiene dos tiempos. May en presente y might en pasado. Tampoco tiene en infinitivo. May se emplea para expresar permiso, duda o posibilidad, propósito. tMay I use your pen? ¿Puedo usar tu pluma? tYou may sit next to John. Usted puede sentarse junto a Juan. tThe train may arrive a little late. Puede que el tren llegue un poco retrasado. Might, se emplea cuando se requiere la forma pasada del auxilia may. Ejemplos: t He thought I might go with him to the party. Él pensó que yo podía ir a la fiesta con él. SHOULD, OUGHT Seguidos de un infinitivo, sirven para expresar una especie de obligación leve, similar al uso de debiera o debería en español. Ejemplos: tYou should see a doctor. Usted debería ver a un doctor. tEdward ought to study harder. Eduardo debería estudiar más. tI would like to go to the movies. Me gustaría ir al cine. tI would rather stay home than go to work. Preferiría quedarme en casa en vez de ir a trabajar. tWould you please help me with this task? ¿Podría ayudarme con esta tarea? tI would have liked to receive a promotion. Me habría gustado recibir una promoción (ascenso en el trabajo) www.ganandoconingles.com 16 www.ganandoconingles.com grew hung had heard hid hit held hurt kept knew laid led learnt* left lent let lay lit* lost made meant met paid put quit read rode rang rose ran said saw sought sold sent set shook PASADO PARTICIPIO grow crecer hang colgar have tener hear oír hide esconder hit golpear hold sostener hurt herir keep guardar know saber lay colocar lead guiar learn aprender leave abandonar lend prestar let dejar lie acostarse light iluminar lose perder make hacer mean significar meet encontrar pay pagar put meter quit dejar read leer ride cabalgar ring sonar rise levantarse run correr say decir see ver seek buscar sell vender send enviar set poner shake sacudir PRETERITO been borne beaten become begun bet bitten bled blown broken brought built burnt* burst bought caught chosen come cost cut dealt done drawn dreamt* drunk driven eaten fallen fed felt fought found flown forbidden fogotten frozen got, gotten given gone INFINITO was, were bore beat became began bet bit bled blew broke brought built burnt* burst bought caught chose came cost cut dealt did drew dreamt* drank drove ate fell fed felt fought found flew forbade forgot froze got gave went PASADO PARTICIPIO be ser ó estar bear soportar beat pelear become convertirse begin comenzar bet apostar bite morder bleed sangrar blow soplar break romper bring llevar build construir burn quemar burst estallar buy comprar catch aptrapar choose escoger come venir cost costar cut cortar deal tratar do hacer draw dibujar dream soñar drink beber drive conducir eat comer fall caer feed alimentar feel sentir fight pelear find encontrar fly volar forbid prohibir forget olvidar freeze congelar get obtener give dar go ir PRETERITO INFINITO VERBOS IRREGULARES grown hung had heard hidden hit held hurt kept known laid led learnt* left lent let lain lit* lost made meant met paid put quit read ridden rung risen run said seen sought sold sent set shaken 17 shone shot showed shrank shut sang sank sat slept smelt* spoke spelt* spent spoilt* spread stood stole stuck stung struck swore swam took taught tore told thought threw woke wore wept won PASADO PARTICIPIO shine brillar shoot disparar show mostrar shrink encoger shut cerrar sing cantar sink cantar sit sentarse sleep dormir smell oler speak hablar spell deletrear spend gastar spoil estropear spread extender stand estar de pie steal robar stick pegar sting picar strike golpear swear jurar swim nadar take tomar teach enseñar tear desgarrar tell decir think pensar throw lanzar wake despertarse wear llevar puesto weep llorar win ganar PRETERITO INFINITO VERBOS IRREGULARES shone shot shown shrunk shut sung sunk sat slept smelt* spoken spelt* spent spoilt* spread stood stolen stuck stung struck / stricken sworn swum taken taught torn told thought thrown woren worn wept won www.ganandoconingles.com * Las formas regulares también se emplean. 1 Pero born en el sentido de nacido o como objetivo. 2 Forma regular hanged cuando se trata de persona. 18 EXAMEN 4. Time expression used in present progressive tense. a. Last year. b. Tomorrow. c. 3 weeks ago. d. Now. 5. Peter ________ his homework right now. Guide's Test This test is intended to help you determine how much you have learned studying this guide. The test has 30 multiple choise questions. Each question is worth one point. Complete the test and then have a look to the answers in the last page of this guide. Study in the topics you have failed. Good luck. Examen de la guía Este examen está hecho para ayudarte a determinar cuanto has aprendido estudiando esta guia. El examen tiene 30 preguntas de opción multiple. Cada pregunta cuenta como un punto. Completa el examen y después mira las respuestas en la última pagina de esta guía. Estudia en los temas que hayas fallado. Suerte. 1. Is Louis mad? a. Yes, it’s. b. No, he isn’t. c. No, he is. d. Yes, he’s. 2. The boys ____________ very noisy. a. Is not b. Aren’t c. Isn’t d. ‘ren’t 3. Is the dog sick? a. Yes, it’s. b. No, it’s. c. No, isn’t. d. Yes, it is. a. is doing b. did c. was doing d. done 6. ______ you __________ overtime tonight? Yes, I _______. a. Do – study – do. b. Are – playing – am. c. Did – talk – did. d. Are – working – am. 7. Do you live in Rome? a. Yes, I do. b. Yes, I am. c. Yes, I am live in Rome. d. No, I am. 8. Does Anna study English? a. Yes, she does. b. Yes, she is. c. Yes, she do. d. No, she aren’t. 9. Does Peter go to school everyday? a. No, he does not. b. No, he don’t. c. No, he isn’t. d. Yes, she was. 10. My grandparents _________ at home in the morning. a. were not b. was not c. no were d. not were 19 11. _______Michael at the beach on Sunday __________? 18. According to the conversation: Did Edward get fun? a. Were--Saturday b. Was--afternoon c. Were--tomorrow d. Was--moorning a.Yes, he does. b.No, he didn’t. c.Yes, he did. d.No, he doesn’t. 12. My uncle and my aunt ______ at the movies __________. 19.What’s the right answer for this question: Will you clean your room? a. Were--a day after tomorrow b. Were--tomorrow c. Were--three days ago d. Was--last week a. Yes, I did. b. Yes, I have cleaned my room. c. I am tired, I won’t do it. d. No, I wasn’t. 13. The children _______________ at the park yesterday. 20. What’s the correct sentence? a. was playing b. wear playing c. were playing d. were playin a. She going to buy some snacks. b. She is not going buy some snacks. c. She is goes to buy some snacks. d. She is going to buy some snacks. 14. My parents and my sister _______________ cleaning up the house last week 21. According to the text, the phrase “never mind” is close in meaning to: a. did not b. were not c. wasen’t d. were nat a. “It doesn’t matter”. b. “Good luck”. c. “See you later”. d. “Congratulations!” 15. ______ the students ____________ the car in the garage a day before? 22. Has Richard washed his car? a. Where--washin b. Were--washing c. Wear--washing d. Was--washes a.No, he hasn’t washed it for months. b.No, he washed it yesterday. c.No, he didn’t. d.Yes, they do. 16. My friends and I ________ to the movies last weekend. 23. Have you seen this movie before? a. are going b. went c. didn’t went d. go a.Yes, I did. b.Yes, I have. c.Yes, I do. d.No, she does. 17. What does “How’s it going” mean? 24. Have you ever been to London? a. Something that it’s passing. b. Something to greet people. c. Something that it’s good. d. Something to ask the time. a.Yes, I was. b.Yes, I have. c.Yes, I did. d.No, they did. 20 25. What’s the correct sentence? a. I had leave my computer on the table. b. I had leaved my computer on the table. c. I hasn’t left my computer on the table. d. I had left my computer on the table. 26. According to the text, what’s the correct answer for this question: How did you know that somebody had taken your computer? a. Because I had bought it yesterday! b. Because I had saved money to buy it. c. Because I had left the computer on the table, and it wasn’t there anymore. d. Because I had taken a taxi to get home early. 27. The expression “what a shame!” means: a. Feeling really sorry. b. Nice to meet you. c. That’s great! d. Let’s go to the police station. 28. The boys are preparing a birthday cake because… a. They like cakes. b. It’s her mother’s cake. c. They are her mother’s ingredients. d. It’s their mother’s birthday. 29. Why are they in a hurry? a. Because their mom will gets back soon. b. Because their mom is a good runner. c. Because their mother might get back sooner. d. Because their mom might gets back sooner. 30. What advice did the guys give their mom? a. You should go to buy more things. b. You should go to bed and jump. c. You ought go to bed and take a nap. d. You ought to go to bed and rest. Test's answers Here you have the correct answers, compare them with yours and finally study the topics where you have failed. Respuestas del examen Aquí tienes las respuestas correctas, comparalas con las tuyas y finalmente estudia en los temas donde no acertaste. 1.b 2.b 3.d 4.d 5.a 6.d 7.a 8.a 9.a 10.a 11.b 12.c 13.c 14.b 15.b 16.b 17.b 18.c 19.c 20.d 21.a 22.a 23.b 24.b 25.d 26.c 27.a 28.d 29.c 30.d 21