Interrupciones en Modo Protegido
Anuncio

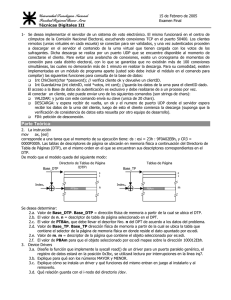
Interrupciones Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Organizacion del Computador II Departamento de Computacion Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales Universidad de Buenos Aires Javier Pimás → Dana Tilve Segundo Cuatrimestre, 2016 Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Interrupciones / Excepciones Son eventos que indican que existe una condición (no necesariamente errónea) en alguna parte del sistema, procesador o el programa que se está ejecutando, que requieren la atención del procesador. Llamamos handler a la acción tomada por el procesador en respuesta a alguna de ellas. Interrupciones aleatoriamente durante la ejecución responden a señales del hardware por software se pueden emular usando INT n Excepciones condición de error ejecutando una instrucción Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Refresco de Memoria Soporta 256 tipos de interrupciones Se utiliza una tabla denominada IDT La IDT almacena descriptores de interrupcion El registro IDTR almacena la direccion de la IDT Ref: Intel Software developer’s manual (vol. 3) capı́tulo 6, interrupciones (tan sólo 10 pags) Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria IDTR e IDT INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING IDTR Register 47 16 15 IDT Base Address 0 IDT Limit + Interrupt Descriptor Table (IDT) Gate for Interrupt #n (n−1)∗8 Gate for Interrupt #3 16 Gate for Interrupt #2 8 Gate for Interrupt #1 31 0 0 Figure 5-1. Relationship of the IDTR and IDT Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Segment Selector Refresco de Memoria Interrupciones INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING Gate Descriptors Trap Gate 31 16 15 14 13 12 Offset 31..16 Task Gate 31 31 16 15 14 13 12 P 31 D P L 0 8 7 Offset 15..0 P D P L 8 7 0 D 1 1 1 5 4 0 0 0 16 15 Segment Selector Offset 15..0 4 0 0 1 0 1 16 15 0 0 TSS Segment Selector DPL Offset P Selector D Descriptor Privilege Level Offset to procedure entry point Segment Present flag Segment Selector for destination code segment Size of gate: 1 = 32 bits; 0 = 16 bits Reserved Figure 5-2. IDT Gate Descriptors Interrupt Gate 31 16 15 14 13 12 Offset 31..16 31 P D P L 8 7 0 D 1 1 0 5 4 0 0 0 5.12 4EXCEPTION AND INTERRUPT HANDLING The processor handles calls to exception- and interrupt-handlers simila handles calls with a CALL instruction a procedure or a task. When res 0 Ojo con los to DPLs (hay 3 en juego) exception or interrupt, the processor uses the exception or interrupt v • Campo (privilegios necesarios parato hacer INT n) index to a descriptor in theDPL IDT. If the index points an interrupt gate 0 "DPL" Segment Selector (debe ser 0) the processor calls •the exception or interrupt handler in a manner sim • DPL descriptor apuntado por Segment Selector to a call gate (see Section 4.8.2, “Gate Descriptors,” through Section 4 16 15 Segment Selector 0 Offset 15..0 Trap Gate 31 16 15 14 13 12 Offset 31..16 31 P D P L 8 7 0 D 1 1 1 16 15 Segment Selector DPL Offset Descriptor Privilege Level Offset to procedure entry point 5 4 0 4 0 0 0 0 Offset 15..0 0 Interrupciones en Modo Protegido 5.12.1 Exception- or Interrupt-Handler Procedures Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria An interrupt gate or trap gate references an exception- or interrupt-handler procedure that runs in the context of the currently executing task (see Figure 5-3). The segment selector for the gate points to a segment descriptor for an executable code segment in either the GDT or the current LDT. The offset field of the gate descriptor points to the beginning of the exception- or interrupt-handling procedure. Interrupt Procedure Call Destination Code Segment IDT Interrupt Vector Interrupt or Trap Gate Offset + Interrupt Procedure Segment Selector GDT or LDT Base Address Segment Descriptor Figure 5-3. Interrupt Procedure Call Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Interrupt Task Switch INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING IDT Interrupt Vector Refresco de Memoria TSS for InterruptHandling Task Task Gate TSS Selector GDT TSS Base Address TSS Descriptor Figure 5-5. Interrupt Task Switch 5.13 ERROR CODE Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Tipos de Interrupciones Fault: Excepción que puede corregirse permitiendo al programa retomar la ejecucion de esa instrucción sin perder continuidad. El procesador guarda en la pila la dirección de la instrucción que produjo la falla (cuando retoma el programa, vuelve a ejecutarla). Traps: Excepción producida inmediatamente a continuación de una instrucción de trap. Algunas permiten al procesador retomar la ejecución sin perder continuidad. Otras no. El procesador guarda en la pila la dirección de la instrucción a ejecutarse luego de la instrucción trapeada. Aborts: Excepción que no siempre puede determinar la instrucción que la causo, ni permite recuperar la ejecución de la tarea que la causo. El handler suele recoger información de diagnósitco y reportar errores severos de hardware o inconsistencias en tablas del sistema. Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING Interrupt Table (see Section 5.2, “Exception and Interrupt Vectors”). Asserting the NMI pin signals a non-maskable interrupt (NMI), which is assigned to interrupt vector 2. Table 5-1. Protected-Mode Exceptions and Interrupts Vector No. Mne- Description monic Type Error Code Source 0 #DE Divide Error Fault No DIV and IDIV instructions. 1 #DB RESERVED Fault/ Trap No For Intel use only. 2 — NMI Interrupt Interrupt No Nonmaskable external interrupt. 3 #BP Breakpoint Trap No INT 3 instruction. 4 #OF Overflow Trap No INTO instruction. 5 #BR BOUND Range Exceeded Fault No BOUND instruction. 6 #UD Invalid Opcode (Undefined Opcode) Fault No UD2 instruction or reserved opcode.1 7 #NM Device Not Available (No Math Coprocessor) Fault No Floating-point or WAIT/FWAIT instruction. 8 #DF Double Fault Abort Yes (zero) Any instruction that can generate an exception, an NMI, or an INTR. Coprocessor Segment Overrun (reserved) Fault No Floating-point instruction.2 9 10 #TS Invalid TSS Fault Yes Task switch or TSS access. 11 #NP Segment Not Present Fault Yes Loading segment registers or accessing system segments. 12 #SS Stack-Segment Fault Fault Yes Stack operations and SS register loads. 13 #GP General Protection Fault Yes Any memory reference and other protection checks. Interrupciones en Modo Protegido or an INTR. Interrupciones Fault Refresco deFloating-point Memoria instruction.2 No 9 Coprocessor Segment Overrun (reserved) Interrupt Table 10 #TS Invalid TSS Fault Yes Task switch or TSS access. 11 #NP Segment Not Present Fault Yes Loading segment registers or accessing system segments. 12 #SS Stack-Segment Fault Fault Yes Stack operations and SS register loads. 13 #GP General Protection Fault Yes Any memory reference and other protection checks. 14 #PF Page Fault Fault Yes Any memory reference. 15 — (Intel reserved. Do not use.) 16 #MF x87 FPU Floating-Point Error (Math Fault) Fault No 17 #AC Alignment Check Fault Yes Any data reference in (Zero) memory.3 No INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING x87 FPU floating-point or WAIT/FWAIT instruction. Table 5-1. Protected-Mode Exceptions and Interrupts (Contd.) 18 #MC Machine Check Abort No 3 5-3 Error codes (if any) andVol. source are model dependent.4 19 #XM SIMD Floating-Point Exception Fault No SSE/SSE2/SSE3 floating-point instructions5 20-31 — Intel reserved. Do not use. 32255 — User Defined (Nonreserved) Interrupts Interrupt External interrupt or INT n instruction. NOTES: 1. The UD2 instruction was introduced in the Pentium Pro processor. 2. Processors after the Intel386 processor do not generate this exception. 3. This exception was introduced in the Intel486 processor. 4. This exception was introduced in the Pentium processor and enhanced in the P6 family processors. 5. This exception was introduced in the Pentium III processor. The processor’s local APIC is normally connected to a system-based I/O APIC. Here, external interrupts received at the I/O APIC’s Interrupciones pins can be directed to theProtegido local APIC en Modo Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Stack Stack Usage with No Privilege-Level Change +∞ Interrupted Procedure’s and Handler’s Stack EFLAGS CS EIP Error Code ESP Before Transfer to Handler ESP After Transfer to Handler 0 Stack Usage with Privilege-Level Change +∞ Interrupted Procedure’s Stack Handler’s Stack ESP Before Transfer to Handler 0 ESP After Transfer to Handler SS ESP EFLAGS CS EIP Error Code Figure 5-4. Stack Usage on Transfers to Interrupt and Exception-Handling Routines Interrupciones en Modo Protegido current LDT. Interrupciones TI Refresco de Memoria GDT/LDT (bit 2) — Only used when the IDT flag is clear. When set, the TI flag indicates that the index portion of the error code refers to a segment or gate descriptor in the LDT; when clear, it indicates that the index refers to a descriptor in the current GDT. Error Code 31 3 2 1 0 Reserved Segment Selector Index T I E I D X T T Figure 5-6. Error Code The segment selector index field provides an index into the IDT, GDT, or current LDT to the segment or gate selector being referenced by the error code. In some cases the error code is null (that is, all bits in the lower word are clear). A null error code indicates that the error was not caused by a reference to a specific segment or that a null segment descriptor was referenced in an operation. EXT: (External Event) Se setea para indicar que la excepción ha sido causada por un evento externo al procesador IDT: (Descriptor Location) Cuando seteado The format of the error code is different for page-faultesta exceptions (#PF).indica See the que el “Interrupt 14—Page-Fault Exception (#PF)” section in this chapter. campo Segment Selector Index se refiere a un descriptor de The error code is pushed on the stack as a doubleword or word (depending on the puerta en latrap, IDT. Cuando esta en the cero indica dicho default interrupt, or task gate size). To keep stack alignedque for doubleword pushes, the upper half of the error code is reserved. Note that the error code is not campo se refiere a un descriptor en la GDT o en la LDT de la popped when the IRET instruction is executed to return from an exception handler, so the handler must remove the error code before executing a return. tarea actual. Error codes are not pushed on the stack for exceptions that are generated externally TI: the (GDT/LDT) Tiene significado cuando elif bit anterior (with INTR or LINT[1:0] pins) or the INT n instruction, even an error code is esta normally produced for those exceptions. en cero. Indica a que tabla de descriptores corresponde el selector del campo Indice. (GDT=0 , LDT=1) 5.14 EXCEPTION AND INTERRUPT HANDLING IN 64-BIT Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria ¿Preguntas? Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Gracias!!! Recuerden: Ref: Intel Software developer’s manual (vol. 3) capı́tulo 6, interrupciones Interrupciones en Modo Protegido Interrupciones Refresco de Memoria Ejercicios 1 Construir un handler para la interrupción #13 que presente en pantalla la leyenda “General Protection”. 2 Configurar la entrada correspondiente a la IDT para resolver la interrupción #13. 3 Armar una rutina que escriba en memoria, utilizando cualquier segmento. 4 Disfrutar como explota en pedazos Interrupciones en Modo Protegido