PRETERITO PERFECTO (UNIDAD 11)
Anuncio

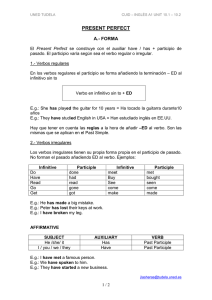
UNED TUDELA – AULA MILAGRO CAD – INGLÉS PRETERITO PERFECTO (UNIDAD 11) A.- FORMA El Present Perfect se construye con el auxiliar have / has + participio de pasado. El participio varía según sea el verbo regular o irregular. 1.- Verbos regulares En los verbos regulares el participio se forma añadiendo la terminación – ED al infinitivo sin to Verbo en infinitivo sin to + ED E.g.: She has played the guitar for 10 years = Ha tocado la guitarra durante10 años E.g.: They have studied English in USA = Han estudiado inglés en EE.UU. Hay que tener en cuenta las reglas a la hora de añadir –ED al verbo. Son las mismas que se aplican en el Past Simple. 2.- Verbos irregulares Los verbos irregulares tienen su propia forma propia en el participio de pasado. No forman el pasado añadiendo ED al verbo. Ejemplos: Infinitive Do Have Read Go Get Participle done had read gone got Infinitive meet Buy See come make Participle met bought seen come made E.g.: He has made a big mistake. E.g.: Peter has lost their keys at work. E.g.: I have broken my leg. AFFIRMATIVE SUBJECT He /she/ it I / you / we / they AUXILIARY Has Have VERB Past Participle Past Participle E.g.: I have met a famous person. E.g.: We have spoken to him. E.g.: They have started a new business. [email protected] 1/2 UNED TUDELA – AULA MILAGRO CAD – INGLÉS NEGATIVE En la forma negativa al igual que en la interrogativa no hay que añadir ningún auxiliar al tener ya el auxiliar have / has. SUBJECT He /she/ it I / you / we / they AUXILIARY Has not / hasn’t Have not / haven’t VERB Past Participle Past Participle E.g.: I haven’t been to New York. E.g.: She hasn’t typed the letter yet. E.g.: They haven’t attended classes regularly. QUESTIONS AUXILIARY Has Have SUBJECT he /she/ it I / you / we / they VERB Past Participle? Past Participle? E.g.: Have you ever been to Moscow? E.g.: Have they found a new flat? E.g.: Have you ever written a poem? B. USOS Los usos de este tiempo verbal en inglés difieren bastante con los usos en castellano: • Para describir acciones que empiezan en el pasado y continúan hasta el presente E:g.: This morning I haven’t drunk coffee. E.g.: Where have you been? I have been very worried. Con este uso suele ir acompañado de SINCE y FOR. SINCE se utiliza para un punto de tiempo y FOR para un periodo de tiempo. E.g.: I have lived in this house for years. (period of time) (vive todavía allí) E.g.: She has written her several e-mails since September. (point of time) • Para acciones en el pasado sin especificar cuándo han ocurrido. E.g.: They have been to London several times. (when?) • Para acciones recientes. En este uso puede ir acompañado de: JUST: se puede traducir por “acabar deH” E.g.: Tom has just read the exercise = Tom acaba de leer el ejercicio ALREADY: en frases afirmativas. Se coloca delante del participio. E.g.: This author has already written two books. YET: en frases negativas o interrogativas. Se coloca al final de la frase. E.g.: Have you passed your driving license yet? E.g.: He hasn’t seen the movie yet [email protected] 2/2