BACTERIAL AND MYCOTIC DISEASES
Anuncio
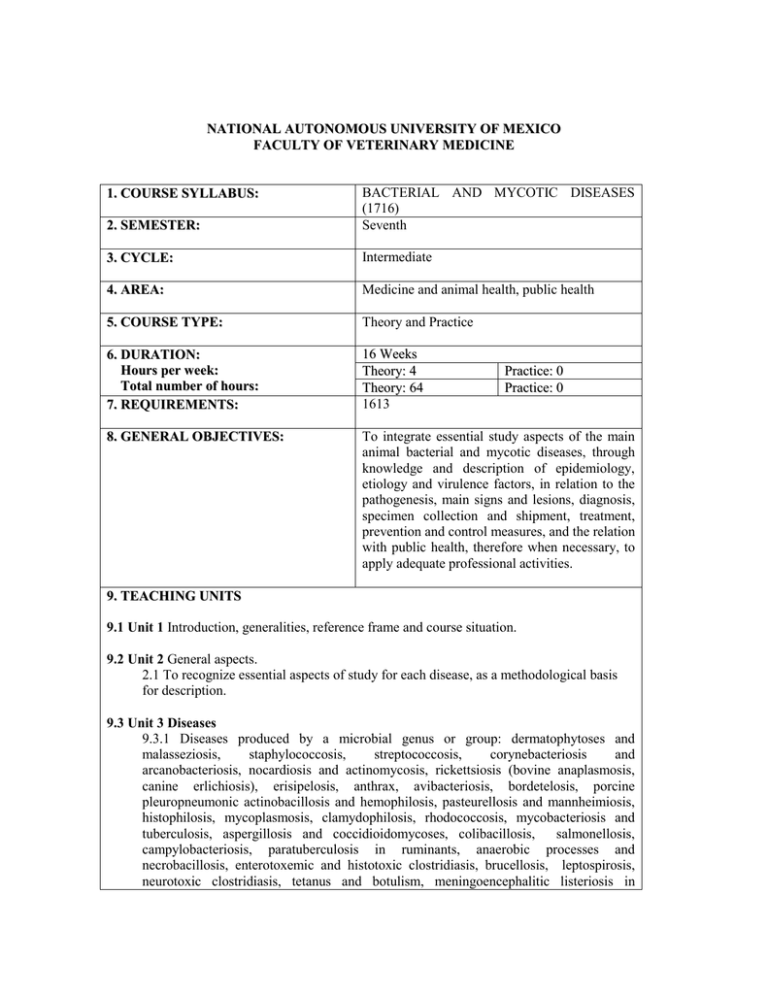
NATIONAL AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MEXICO FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE 2. SEMESTER: BACTERIAL AND MYCOTIC DISEASES (1716) Seventh 3. CYCLE: Intermediate 4. AREA: Medicine and animal health, public health 5. COURSE TYPE: Theory and Practice 6. DURATION: Hours per week: Total number of hours: 7. REQUIREMENTS: 16 Weeks Theory: 4 Theory: 64 1613 8. GENERAL OBJECTIVES: To integrate essential study aspects of the main animal bacterial and mycotic diseases, through knowledge and description of epidemiology, etiology and virulence factors, in relation to the pathogenesis, main signs and lesions, diagnosis, specimen collection and shipment, treatment, prevention and control measures, and the relation with public health, therefore when necessary, to apply adequate professional activities. 1. COURSE SYLLABUS: Practice: 0 Practice: 0 9. TEACHING UNITS 9.1 Unit 1 Introduction, generalities, reference frame and course situation. 9.2 Unit 2 General aspects. 2.1 To recognize essential aspects of study for each disease, as a methodological basis for description. 9.3 Unit 3 Diseases 9.3.1 Diseases produced by a microbial genus or group: dermatophytoses and malasseziosis, staphylococcosis, streptococcosis, corynebacteriosis and arcanobacteriosis, nocardiosis and actinomycosis, rickettsiosis (bovine anaplasmosis, canine erlichiosis), erisipelosis, anthrax, avibacteriosis, bordetelosis, porcine pleuropneumonic actinobacillosis and hemophilosis, pasteurellosis and mannheimiosis, histophilosis, mycoplasmosis, clamydophilosis, rhodococcosis, mycobacteriosis and tuberculosis, aspergillosis and coccidioidomycoses, colibacillosis, salmonellosis, campylobacteriosis, paratuberculosis in ruminants, anaerobic processes and necrobacillosis, enterotoxemic and histotoxic clostridiasis, brucellosis, leptospirosis, neurotoxic clostridiasis, tetanus and botulism, meningoencephalitic listeriosis in ruminants 9.3.2 Diseases and select syndromes affecting several animal species, produced by one or more microbial genera: mastitis, respiratory and digestive complexes, abortion, foot rod and necrobacillosis. 9.4 Diseases and select syndromes in fish and bees. 9.4.1 Bees 9.4.2 Fishes 10. BASIC BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Radostits, O.M., et al.: Veterinary Medicine 10th. ed. New York: Saunders elsevier 2007. 2. Acha, P.N. y Cifres, B.: Zoonosis y Enfermedades Transmisibles Comunes al Hombre y a los Animales. 3ª. ed. Vol. I Bacteriosis y micosis. Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Washington, D.C. 2001. 3. Gillespie, J.H., Timoney, J.F.: Hagan and Bruner’s Infectious Diseases of Domestic Animals. 7th. ed. Cornell University Press, Ithaca. 1994. 11. SUPLEMENTARY BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Smith, B.P.: Large Animal Internal Medicine. Mosby. St. Louis. 2001. 2. Andrews ,A.H.: Bovine Medicine. Blackwell. London. 1992. 3. Smith, C.M., Sherman, D.M.: Goat Medicine. Lippincot Williams and Wilkins. Philadelphia. 1994. 4. Mair T, et al.: Equine Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction. WB Saunders, Philadelphia. 1998. 5. Straw B et al.: Diseases of Swine. 8th.ed. Iowa State University Press. Ames, 1999. 6. Taylor, D.J.: Pig Diseases. 7th. ed. Taylor, Glasgow, 1999. 7. Saif, Y.M. et al.: Diseases of Poultry. 11th. ed. Iowa State University Press, Ames 2003. 8. Green, C.E.: Enfermedades Infecciosas en Perros y Gatos. 2ª ed. McGraw-HillInteramericana, México. 1998. 9. Ettinger, S.J., Feldman, E.C.: Veterinary Internal Medicine. 4th. ed. WB. Saunders, Philadelphia. 1995. 10. Nelson, R.W., Couto, C.G.: Small Animal Internal Medicine. Mosby. St. Louis. 1998. 11. Marín. J.: Enfermedades de los Gatos y su Manejo Clínico. Jaiser, México. 2003. 12. Fowler ME, Miller RE.: Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine. 5th. ed. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 2003. 13. Williams, E.S., Baker, I.K.: (eds). Infectious Diseases of Wild Animals. 3 rd. ed. Iowa State University Press, Ames. 2001. 14. Benenson, A.S.: El Control de las Enfermedades Transmisibles en el Hombre. Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Washington, D.C. 1992. 15. Gyles CL et al. Pathogenesis of bacterial infections in animals 3rd. Ed. Ames, Iowa: Blackwell 2004. 16. Mims, C.: Pathogenesis of Infectious Disease. 5th ed. Academic Press. London. 2000. 17. Jones, T.C., Hunt, R.D.: Veterinary Pathology. 6th. ed. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia. 1997. 18. Quinn, PJ et al. Clinical veterinary microbiolgy Edinburgh: Mosby 1999. 19. Quinn, PJ et al. Microbiology and microbial diseases Ames, Iowa: Balckwell 2002. 20. OIE Manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals: Mammals, birds and bees Paris: Office international des epizooties 2004. Journals: Veterinary Bulletin Index Veterinarius Comparative Immunology Microbiology & Infectious Diseases Infection and Immunity Journal of Infectious Diseases Veterinary Microbiology Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association Veterinaria México Bovine Practitioner Pig News and Information Avian Diseases Canine Practice Journal of Small Animal Practice Feline Practice Journal of Wildlife Diseases Preventive Veterinary Medicine Internet interesting sites: www.senasica.sagarpa.gob.mx www.salud.gob.mx www.oie.int/esp/es_index.htm. www.cdc.gov/spanish/default.htm. www.bacterio.cict.fr/ www.fmvz.unam.mx/fmvz/p_estudios/plan_estudios_2006.pdf 12. TEACHING METHODOLOGY Lecture with discussion and interaction. Guest speakers. Select readings. Seminars. Problem based exercises. 13. COURSE EVALUATION Partial exams, and other activities during the semester. Final Exam. 14. REQUIREMENTS FOR TEACHING THE COURSE Veterinarian with postgraduate studies in microbiology, pathology, infectious diseases, and clinical experience.