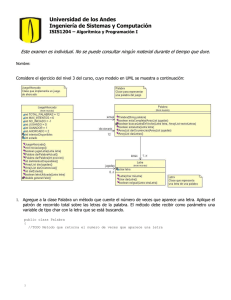
Graficos Y Java 2D
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Introducción
Contextos y objetos gráficos
Colores
Fuentes
Pintar Líneas, Rectángulos y Óvalos
Pintar Arcos
Pintar Polígonos and Polilíneas
Java2D API
Ejemplo
1 Introducción
Capacidades gráficas de JAVA
−
−
−
Pintar figuras de 2D
Uso y control colores
Uso y control de fuentes
Java 2D API
−
Uso más sofisticado de primitivas de
dibujo en 2D
Uso de formar y polígonos 2D personalizados
Relleno de figuras con colores, gradientes,
patrones y texturas.
Jerarquía de algunas clases e interfaces del Java2D API.
Object
Color
Component
Font
FontMetrics
Graphics
Polygon
Clases e interfaces del Java2D API que aparecen en el
paquete java.awt
Graphics2D
interface
java.awt.Paint
BasicStroke
GradientPaint
TexturePaint
interface
java.awt.Shape
interface
java.awt.Stroke
Clases e interfaces del Java2D API que aparecen en
el paquete java.awt.geom
GeneralPath
Line2D
RectangularShape
Arc2D
Ellipse2D
Rectangle2D
RoundRectangle2D
1 Introducción
Sistema de coordenadas de JAVA
−
−
−
Identifica todos los puntos disponibles de
la pantallas
Origen de coordenadas (0,0) en la
esquina superior izquierda
Sistema de coordenadas compuestas por
componentes X e Y.
Sistema de coordenadas de Java. Unidad de medida en pixels.
+x
(0, 0)
(x , y )
+y
Y a xis
X a xis
2 Contextos y objetos gráficos
Contexto Graphics
Permite pintar en la pantalla.
– El objeto Graphics controla el contexto de
graficos
−
−
Controla como se pinta en la pantalla
La Clase Graphics es abstracta
No se puede instanciar
Contribuye a la portabilidad de Java
−
La el método paint de la lase Component emplea
el objeto Graphics
public void paint( Graphics g )
−
Se puede invocar por medio del método repaint
3 Colores
Clase Color
−
−
Define los métodos y las constantes para
manipular los colores.
Los colores se crean en base al esquema
de rojo/verde/azul (RGB).
Constantes de colores definidas en la clase Color
Color constant
public final static Color ORANGE
Color
RGB value
public final static Color PINK
orange
pink
255, 200, 0
255, 175, 175
public final static Color CYAN
cyan
0, 255, 255
public final static Color MAGENTA
magenta
255, 0, 255
public final static Color YELLOW
yellow
255, 255, 0
public final static Color BLACK
black
0, 0, 0
public final static Color WHITE
white
255, 255, 255
public final static Color GRAY
gray
128, 128, 128
public final static Color LIGHT_GRAY
light gray
192, 192, 192
public final static Color DARK_GRAY
dark gray
64, 64, 64
public final static Color RED
red
255, 0, 0
public final static Color GREEN
green
0, 255, 0
public final static Color BLUE
blue
0, 0, 255
Métodos de la clase Color y métodos de relacionados de la
clase Graphics
Method
Description
Color constructors and methods
public Color( int r, int g, int b )
Creates a color based on red, green and blue components expressed as integers
from 0 to 255.
public Color( float r, float g, float b )
Creates a color based on red, green and blue components expressed as floatingpoint values from 0.0 to 1.0.
public int getRed()
Returns a value between 0 and 255 representing the red content.
public int getGreen()
Returns a value between 0 and 255 representing the green content.
public int getBlue()
Returns a value between 0 and 255 representing the blue content.
Graphics methods for manipulating Colors
public Color getColor()
Returns a Color object representing the current color for the graphics context.
public void setColor( Color c )
Sets the current color for drawing with the graphics context.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// Fig. 12.5: ShowColors.java
// Demonstrating Colors.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ShowColors extends JFrame {
// constructor sets window's title bar string and dimensions
public ShowColors()
{
Pinta la ventana cuando
super( "Using colors" );
setSize( 400, 130 );
setVisible( true );
}
comienza la ejecución de
la aplicación
El método setColor establece el color
de pintura en base a un color RGB
// draw rectangles and Strings in different colors
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
// call superclass's paint method
El método fillRect crea un
super.paint( g );
rectángulo relleno en el color de
pintura actual.
// set new drawing color using integers
g.setColor( new Color( 255, 0, 0 ) );
g.fillRect( 25, 25, 100, 20 );
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 40 );
El método drawString escribe un
String en el color actual en las
coordenadas especificadas
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
// set new drawing color using floats
g.setColor( new Color( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f ) );
g.fillRect( 25, 50, 100, 20 );
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 65 );
// set new drawing color using static Color objects
g.setColor( Color.BLUE );
g.fillRect( 25, 75, 100, 20 );
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 90 );
Empleamos las constantes de
la clase Color
// display individual RGB values
Color color = Color.MAGENTA;
g.setColor( color );
g.fillRect( 25, 100, 100, 20 );
g.drawString( "RGB values: " + color.getRed() + ", " +
color.getGreen() + ", " + color.getBlue(), 130, 115 );
} // end method paint
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
ShowColors application = new ShowColors();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class ShowColors
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// Fig. 12.6: ShowColors2.java
// Choosing colors with JColorChooser.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ShowColors2 extends JFrame {
private JButton changeColorButton;
private Color color = Color.LIGHT_GRAY;
private Container container;
// set up GUI
public ShowColors2()
{
super( "Using JColorChooser" );
container = getContentPane();
container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
// set up changeColorButton and register its event handler
changeColorButton = new JButton( "Change Color" );
changeColorButton.addActionListener(
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
new ActionListener() {
// anonymous inner class
// display JColorChooser when user clicks button
JColorChooser presenta
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
un diálogo para
{
seleccionar colores
color = JColorChooser.showDialog(
ShowColors2.this, "Choose a color", color );
// set default color, if no color is returned
if ( color == null )
color = Color.LIGHT_GRAY;
// change content pane's background color
container.setBackground( color );
}
} // end anonymous inner class
); // end call to addActionListener
container.add( changeColorButton );
setSize( 400, 130 );
setVisible( true );
} // end ShowColor2 constructor
static showDialog
muestra el cuadro de
diálogo
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
ShowColors2 application = new ShowColors2();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class ShowColors2
ShowColors2.java
Fig. 12.7 HSB and RGB tabs
of the JColorChooser dialog
4 Fuente
Clase Font
−
−
Contiene métodos y constantes para el
control de las fuentes.
El constructor de la clase Font tiene tres
argumentos
Font name
– Monospaced, SansSerif, Serif, etc.
Font style
– Font.PLAIN, Font.ITALIC y Font.BOLD
Font size
−
Medido en puntos
Métodos y constantes relacionados con la clase Font
Method or constant
Description
Font constants, constructors and methods for drawing polygons
public final static int
PLAIN
A constant representing a plain font style.
public final static int
BOLD
A constant representing a bold font style.
public final static int
ITALIC
A constant representing an italic font style.
public Font( String name,
int style, int size )
Creates a Font object with the specified font, style and size.
public int
getStyle()
public int
getSize()
Returns an integer value indicating the current font style.
Returns an integer value indicating the current font size.
public String getName()
Returns the current font name as a string.
public String getFamily()
Returns the font’s family name as a string.
public boolean
isPlain()
public boolean
isBold()
public boolean
isItalic()
Tests a font for a plain font style. Returns
Tests a font for a bold font style. Returns
Tests a font for an italic font style. Returns
true if the font is plain.
true if the font is bold.
true if the font is italic.
Method or constant
Description
Graphics methods for manipulating Fonts
public Font getFont()
Returns a Font object reference representing the current font.
public void setFont( Font f )
Sets the current font to the font, style and size specified by the
object reference f.
Font
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// Fig. 12.9: Fonts.java
// Using fonts.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Fonts extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar and dimensions
public Fonts()
{
super( "Using fonts" );
setSize( 420, 125 );
setVisible( true );
}
// display Strings in different fonts and colors
public void paint( Graphics g )
El método setFont
{
// call superclass's paint method
super.paint( g );
establece la fuente a usar
// set font to Serif (Times), bold, 12pt and draw a string
g.setFont( new Font( "Serif", Font.BOLD, 12 ) );
g.drawString( "Serif 12 point bold.", 20, 50 );
Escribe
el texto con la
configuración actual de
fuente
26
27
// set font to Monospaced (Courier), italic, 24pt and draw a
string
28
29
30
31
g.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.ITALIC, 24 ) );
g.drawString( "Monospaced 24 point italic.", 20, 70 );
// set font to SansSerif (Helvetica), plain, 14pt and draw a
string
32
33
34
35
g.setFont( new Font( "SansSerif", Font.PLAIN, 14 ) );
g.drawString( "SansSerif 14 point plain.", 20, 90 );
// set font to Serif (Times), bold/italic, 18pt and draw a
string
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
g.setColor( Color.RED );
g.setFont( new Font( "Serif", Font.BOLD + Font.ITALIC, 18 ) );
g.drawString( g.getFont().getName() + " " +
g.getFont().getSize() +
" point bold italic.", 20, 110 );
} // end method paint
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Fonts application = new Fonts();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class Fonts
Control de fuentes
Parámetros de medida y posición de
las Fuentes
−
−
−
−
Height - Altura
Descent (puntos por debajo de la linea
base)
Ascent (puntos por encima de la linea
base)
Leading (diferencia entre Ascent y
Descent)
Control y medidas
he ight
Xy1Õ
le ading
asce nt
ba seline
descent
Fig. 12.11 FontMetrics and
Graphics methods for
obtaining font metrics
Method
Description
FontMetrics methods
public int getAscent()
Returns a value representing the ascent of a font in points.
public int getDescent()
Returns a value representing the descent of a font in points.
public int getLeading()
Returns a value representing the leading of a font in points.
public int getHeight()
Returns a value representing the height of a font in points.
Graphics methods for getting a Font’s FontMetrics
public FontMetrics getFontMetrics()
Returns the FontMetrics object for the current drawing Font.
public FontMetrics getFontMetrics( Font f )
Returns the FontMetrics object for the specified Font argument.
1
// Fig. 12.12: Metrics.java
2
// FontMetrics and Graphics Metrics.java
methods useful for obtaining font Line 22
Line 23
metrics.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
Set font to SansSerif 12-point bold
6
public class Metrics extends
Obtain FontMetrics
JFrame {
object for current font
7
8
// set window's title bar
String and dimensions
9
public Metrics()
25
Use FontMetrics to
obtain ascent, descent,
height and leading
Metrics.java
g.drawString( "Ascent: " +
metrics.getAscent(), 10, 55 );
Repeat same process for
Lines 25-28
26
g.drawString( "Descent:Serif
" 14-point
italic font
+ metrics.getDescent(), 10, 70 ); Lines 30-37
27
g.drawString( "Height: " +
metrics.getHeight(), 10, 85 );
28
g.drawString( "Leading: "
+ metrics.getLeading(), 10, 100 );
29
30
Font font = new
Font( "Serif", Font.ITALIC, 14 );
31
metrics =
g.getFontMetrics( font );
Metrics.java
5 Pintar Líneas, Rectángulos y Óvalos
Clase Graphics
−
Provee métodos para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
Todos lo métodos de pintar estas figuras
requieren el ancho y alto que ocuparan
Existen los métodos para pintar figuras con o
sin rellene (draw* y fill*)
Métodos de la clase Graphics para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
Method
Description
public void drawLine( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Draws a line between the point (x1, y1) and the point (x2, y2).
public void drawRect( int x, int y, int width, int height )
Draws a rectangle of the specified width and height. The top-left corner of the
rectangle has the coordinates (x, y).
public void fillRect( int x, int y, int width, int height )
Draws a solid rectangle with the specified width and height. The top-left
corner of the rectangle has the coordinate (x, y).
public void clearRect( int x, int y, int width, int height )
Draws a solid rectangle with the specified width and height in the current
background color. The top-left corner of the rectangle has the coordinate ( x, y).
public void drawRoundRect( int x, int y, int width, int height,
int arcWidth, int arcHeight )
Draws a rectangle with rounded corners in the current color with the specified
width and height. The arcWidth and arcHeight determine the rounding of
the corners (see Fig. 12.15).
public void fillRoundRect( int x, int y, int width, int height,
int arcWidth, int arcHeight )
Draws a solid rectangle with rounded corners in the current color with the
specified width and height. The arcWidth and arcHeight determine the
rounding of the corners (see Fig. 12.15).
Métodos de la clase Graphics para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
Method
Description
public void draw3DRect( int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean b )
Draws a three-dimensional rectangle in the current color with the specified
width and height. The top-left corner of the rectangle has the coordinates ( x,
y). The rectangle appears raised when b is true and lowered when b is false.
public void fill3DRect( int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean b )
Draws a filled three-dimensional rectangle in the current color with the specified
width and height. The top-left corner of the rectangle has the coordinates ( x,
y). The rectangle appears raised when b is true and lowered when b is false.
public void drawOval( int x, int y, int width, int height )
Draws an oval in the current color with the specified width and height. The
bounding rectangle’s top-left corner is at the coordinates ( x, y). The oval touches
all four sides of the bounding rectangle at the center of each side (see
Fig. 12.16).
public void fillOval( int x, int y, int width, int height )
Draws a filled oval in the current color with the specified width and height.
The bounding rectangle’s top-left corner is at the coordinates ( x, y). The oval
touches all four sides of the bounding rectangle at the center of each side (see
Fig. 12.16).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// Fig. 12.14: LinesRectsOvals.java
// Drawing lines, rectangles and ovals.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class LinesRectsOvals extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
public LinesRectsOvals()
{
super( "Drawing lines, rectangles and ovals" );
setSize( 400, 165 );
setVisible( true );
}
// display various lines, rectangles and ovals
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
g.setColor( Color.RED );
g.drawLine( 5, 30, 350, 30 );
g.setColor( Color.BLUE );
g.drawRect( 5, 40, 90, 55 );
g.fillRect( 100, 40, 90, 55 );
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
g.setColor( Color.CYAN );
g.fillRoundRect( 195, 40, 90, 55, 50, 50 );
g.drawRoundRect( 290, 40, 90, 55, 20, 20 );
Draw filled rounded rectangle
Draw (non-filled) rounded rectangle
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
g.draw3DRect( 5, 100, 90, 55, true );
g.fill3DRect( 100, 100, 90, 55, false );
g.setColor( Color.MAGENTA );
g.drawOval( 195, 100, 90, 55 );
g.fillOval( 290, 100, 90, 55 );
Draw 3D rectangle
Draw filled 3D rectangle
Draw oval
Draw filled oval
} // end method paint
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
LinesRectsOvals application = new LinesRectsOvals();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class LinesRectsOvals
Altura y anchura del arco necesario para construir
RoundedRectangle
(x, y)
arc height
a rc width
width
height
Medidas para construir un óvalo en base al rectángulo que lo
contiene
(x , y)
height
width
6 Pintar Arcos
Arco
−
−
−
−
Porción de un óvalo
Se miden en grados
Barre (Sweeps) el número de grados que
indique el ángulo de arco
Sweep empieza en el inicio de medida de
los ángulos
Barre en sentido contrario a las agujas del
reloj si el ángulo es positivo
Barre en sentido de las agujas del reloj para
ángulos negativos.
Ángulos positivos y negativos
Positive angles
Negative angles
90°
180°
90°
0°
270°
180°
0°
270°
Métodos de la clase Graphics para el pintado de arcos
Method
Description
public void drawArc( int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle,
int arcAngle )
Draws an arc relative to the bounding rectangle’s top-left coordinates (x, y) with
the specified width and height. The arc segment is drawn starting at
startAngle and sweeps arcAngle degrees.
public void fillArc( int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle,
int arcAngle )
Draws a solid arc (i.e., a sector) relative to the bounding rectangle’s top-left
coordinates (x, y) with the specified width and height. The arc segment is
drawn starting at startAngle and sweeps arcAngle degrees.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// Fig. 12.19: DrawArcs.java
// Drawing arcs.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
DrawArcs.java
Lines 24-26
public class DrawArcs extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
public DrawArcs()
{
super( "Drawing Arcs" );
setSize( 300, 170 );
setVisible( true );
}
// draw rectangles and arcs
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
// start at 0 and sweep 360 degrees
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
g.drawRect( 15, 35, 80, 80 );
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
g.drawArc( 15, 35, 80, 80, 0, 360 );
Draw first arc that
sweeps 360 degrees and
is contained in rectangle
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
// start at 0 and sweep 110 degrees
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
g.drawRect( 100, 35, 80, 80 );
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
g.drawArc( 100, 35, 80, 80, 0, 110 );
// start at 0 and sweep -270 degrees
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
g.drawRect( 185, 35, 80, 80 );
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
g.drawArc( 185, 35, 80, 80, 0, -270 );
// start at 0 and sweep 360 degrees
g.fillArc( 15, 120, 80, 40, 0, 360 );
Draw second arc that
sweeps 110 degrees and
is contained in rectangle
Draw third arc that
sweeps -270 degrees and
is contained in rectangle
Draw fourth arc that is filled, has starting
angle 0 and sweeps 360 degrees
// start at 270 and sweep -90 degrees
g.fillArc( 100, 120, 80, 40, 270, -90 );
Draw fifth arc that is filled, has starting
angle 270 and sweeps -90 degrees
// start at 0 and sweep -270 degrees
g.fillArc( 185, 120, 80, 40, 0, -270 );
Draw sixth arc that is filled, has starting
angle 0 and sweeps -270 degrees
} // end method paint
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
DrawArcs application = new DrawArcs();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class DrawArcs
7 Pintar Polígonos y Polilíneas
Clases Polygon
−
Polígonos
−
Figuras de varios lados
Polilíneas
Series de puntos conectados
Métodos Graphics para pintar poligonos y métodos de la
clase Polygon
Method
Description
Graphics methods for drawing polygons
public void drawPolygon( int xPoints[], int yPoints[], int points )
Draws a polygon. The x-coordinate of each point is specified in the xPoints
array and the y-coordinate of each point is specified in the yPoints array. The
last argument specifies the number of points . This method draws a closed
polygon. If the last point is different from the first point, the polygon is closed
by a line that connects the last point to the first point.
public void drawPolyline( int xPoints[], int yPoints[], int points )
Draws a sequence of connected lines. The x-coordinate of each point is specified
in the xPoints array and the y-coordinate of each point is specified in the
yPoints array. The last argument specifies the number of points. If the last
point is different from the first point, the polyline is not closed.
public void drawPolygon( Polygon p )
Draws the specified polygon.
public void fillPolygon( int xPoints[], int yPoints[], int points )
Draws a solid polygon. The x-coordinate of each point is specified in the
xPoints array and the y-coordinate of each point is specified in the yPoints
array. The last argument specifies the number of points. This method draws a
closed polygon. If the last point is different from the first point, the polygon is
closed by a line that connects the last point to the first point.
public void fillPolygon( Polygon p )
Draws the specified solid polygon. The polygon is closed.
Métodos Graphics para pintar poligonos y métodos de la
clase Polygon
Method
Description
Polygon constructors and methods
public
Polygon()
Constructs a new polygon object. The polygon does not contain any points.
public
Polygon(
int xValues[],
int yValues[],
int numberOfPoints )
Constructs a new polygon object. The polygon has
with each point consisting of an
x-coordinate from
from yValues .
public
void addPoint(
numberOfPoints sides,
xValues and a y-coordinate
int x, int y )
Adds pairs of x- and y-coordinates to the
Polygon .
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// Fig. 12.21: DrawPolygons.java
// Drawing polygons.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class DrawPolygons extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
public DrawPolygons()
{
super( "Drawing Polygons" );
setSize( 275, 230 );
setVisible( true );
}
// draw polygons and polylines
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
int xValues[] = { 20, 40, 50, 30, 20, 15 };
int yValues[] = { 50, 50, 60, 80, 80, 60 };
Polygon polygon1 = new Polygon( xValues, yValues, 6 );
g.drawPolygon( polygon1 );
int arrays specifying
Polygon polygon1 points
Draw polygon1 to screen
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
int xValues2[] = { 70, 90, 100, 80, 70, 65, 60 };
int yValues2[] = { 100, 100, 110, 110, 130, 110, 90 };
int arrays specifying
Polyline points
g.drawPolyline( xValues2, yValues2, 7 );
int xValues3[] = { 120, 140, 150, 190 };
int yValues3[] = { 40, 70, 80, 60 };
Draw Polyline to screen
g.fillPolygon( xValues3, yValues3, 4 );
Specify points and draw (filled)
Polygon to screen
Polygon polygon2 = new Polygon();
polygon2.addPoint( 165, 135 );
polygon2.addPoint( 175, 150 );
polygon2.addPoint( 270, 200 );
polygon2.addPoint( 200, 220 );
polygon2.addPoint( 130, 180 );
Method addPoint adds pairs of
x-y coordinates to a Polygon
g.fillPolygon( polygon2 );
} // end method paint
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
DrawPolygons application = new DrawPolygons();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class DrawPolygons
8 Java2D API
Java 2D API
−
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Proporciona capacidades gráficas avanzas 2D
java.awt
java.awt.image
java.awt.color
java.awt.font
java.awt.geom
java.awt.print
java.awt.image.renderable
−
Usa la clase java.awt.Graphics2D
Extiende la clase java.awt.Graphics
12.8 Java2D API
Java 2D formas
−
Paquetes java.awt.geom
• Ellipse2D.Double
• Rectangle2D.Double
• RoundRectangle2D.Double
• Arc3D.Double
• Lines2D.Double
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// Fig. 12.22: Shapes.java
// Demonstrating some Java2D shapes.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Shapes extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
public Shapes()
{
super( "Drawing 2D shapes" );
setSize( 425, 160 );
setVisible( true );
}
// draw shapes with Java2D API
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
Graphics2D g2d = ( Graphics2D ) g; // cast g to Graphics2D
Shapes.java
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
// draw 2D ellipse filled with a blue-yellow gradient
g2d.setPaint( new GradientPaint( 5, 30, Color.BLUE, 35, 100,
Color.YELLOW, true ) );
g2d.fill( new Ellipse2D.Double( 5, 30, 65, 100 ) );
// draw 2D rectangle in red
g2d.setPaint( Color.RED );
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 10.0f ) );
g2d.draw( new Rectangle2D.Double( 80, 30, 65, 100 ) );
// draw 2D rounded rectangle with a buffered background
BufferedImage buffImage = new BufferedImage( 10, 10,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB );
Graphics2D gg = buffImage.createGraphics();
gg.setColor( Color.YELLOW ); // draw in yellow
gg.fillRect( 0, 0, 10, 10 ); // draw a filled rectangle
gg.setColor( Color.BLACK ); // draw in black
gg.drawRect( 1, 1, 6, 6 ); // draw a rectangle
gg.setColor( Color.BLUE ); // draw in blue
gg.fillRect( 1, 1, 3, 3 ); // draw a filled rectangle
gg.setColor( Color.RED ); // draw in red
gg.fillRect( 4, 4, 3, 3 ); // draw a filled rectangle
Use GradientPaint to
fill shape with gradient
Fill ellipse with gradient
Use BasicStroke to draw
2D red-border rectangle
BufferedImage produces
image to be manipulated
Draw texture into
BufferedImage
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
// paint buffImage onto the JFrame
g2d.setPaint( new TexturePaint( buffImage,
new Rectangle( 10, 10 ) ) );
g2d.fill( new RoundRectangle2D.Double( 155, 30, 75, 100, 50, 50 ) );
// draw 2D pie-shaped arc in white
g2d.setPaint( Color.WHITE );
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 6.0f ) );
g2d.draw( new Arc2D.Double( 240, 30, 75, 100, 0, 270, Arc2D.PIE ) );
// draw 2D lines in green and yellow
g2d.setPaint( Color.GREEN );
g2d.draw( new Line2D.Double( 395, 30, 320, 150 ) );
Use BufferedImage as texture
for painting rounded rectangle
Use Arc2D.PIE to
draw white-border
2D pie-shaped arc
Draw solid green line
float dashes[] = { 10 };
g2d.setPaint( Color.YELLOW );
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 4, BasicStroke.CAP_ROUND,
BasicStroke.JOIN_ROUND, 10, dashes, 0 ) );
g2d.draw( new Line2D.Double( 320, 30, 395, 150 ) );
} // end method paint
Draw dashed yellow line
that crosses solid green line
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
// execute application
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Shapes application = new Shapes();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
} // end class Shapes
Shapes.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// Fig. 12.23: Shapes2.java
// Demonstrating a general path.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Shapes2 extends JFrame {
// set window's title bar String, background color and dimensions
public Shapes2()
{
super( "Drawing 2D Shapes" );
getContentPane().setBackground( Color.WHITE );
setSize( 400, 400 );
setVisible( true );
}
// draw general paths
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
int xPoints[] = { 55, 67, 109, 73, 83, 55, 27, 37, 1, 43 };
int yPoints[] = { 0, 36, 36, 54, 96, 72, 96, 54, 36, 36 };
x-y coordinates that comprise star
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
Graphics2D g2d = ( Graphics2D ) g;
GeneralPath star = new GeneralPath(); // create GeneralPath object
// set the initial coordinate of the General Path
star.moveTo( xPoints[ 0 ], yPoints[ 0 ] );
// create the star--this does not draw the star
for ( int count = 1; count < xPoints.length; count++ )
star.lineTo( xPoints[ count ], yPoints[ count ] );
star.closePath(); // close the shape
GeneralPath is a shape
constructed from straight
lines and complex curves
Shapes2.java
Line 28
Create star
Lines 31-37
Lines 42-50
g2d.translate( 200, 200 ); // translate the origin to (200, 200)
// rotate around origin and draw stars in random colors
for ( int count = 1; count <= 20; count++ ) {
g2d.rotate( Math.PI / 10.0 ); // rotate coordinate system
// set random drawing color
g2d.setColor( new Color( ( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ),
( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ),
( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ) ) );
g2d.fill( star ); // draw filled star
}
Draw filled, randomly colored
star 20 times around origin
Shapes2.java