Basic Rig Components: Petroleum Engineering Fundamentals
Anuncio

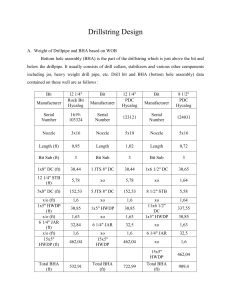
Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering. By: Bilal Shams Memon BASIC RIG COMPONENTS ROTARY DRILLING’S BASIC RIG COMPONENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Derrick & Mast. Substructure. Prime movers. Draw works. Mud pumps. Drill String. Bits. Drilling Line. Auxiliary & Miscellaneous Equipments. 1. DERRICK & MAST i. ii. Structure: Derrick (main component)is a steel structure of sufficient height & strength. Functions: Supports all equipments & provides vertical clearance to raising & lowering the drill string into & out of hole during drilling operations. Types: Standard. Portable. Derrick types i. ii. Standard Derrick: it is of bolted construction, assembled part by part & not raised to a working position as a unit. For transportation, it must be disassembled. Portable Derrick (Mast): it is a complete unit & can’t be disassembled. 2. SUBSTRUCTURE Functions: Support of derrick (derrick’s rest), placement of equipments, working platform for rig crew, installment place of BOPs. Structure: steel platform above the surface at about 10-15ft. 3. PRIME MOVERS a. b. i. ii. iii. Function: generates power about 400-800KW (depending upon rig size, well depth & engine size). Supporting Operations: power consumes in mud pumps, draw works, crew cabins, continuous drilling operations, etc. Bulk of rig power is consumed by: Circulation of drilling fluid. Hoisting. Engines Used: Steam engine – first RD-PM, now rarely used except where continuous and large quantity of water is available. Electric motor – used for special applications like in city drilling where power availability & noise restrictions have made in practical. Internal combustion engine – most drilling rigs are powered by IC engines, burns natural gas, gasoline or diesel. 4. DRAW WORKS (HOISTS) i. ii. Structure: made of steel (like a thread) on which flexible drilling line folded. Functions: Control of centre from which driller operates the rig. It contains clutches, chains, rope sockets, engine throttles & other controls which enables rig power to be diverted to the particular operation. It houses the drum which spools the drilling line during hoisting operations & allows feed off during drilling. Hoisting equipments’ main purpose are to lift & lower pipe out of & into the hole respectively. Hoisting equipments includes the top of derrick mounted with crown block & by means of pulleys travelling block, hook & swivel are suspended & moved on wire ropes. DRAW WORKS Complete Draw-works System Crown Block Travelling Block Rotary Table Hook Swivel 5. MUD PUMPS (SPLASH PUMPS) Function: circulates drilling fluid at desired pressure & volume. Pumps are reciprocating piston, double acting & duplex type. Disadvantage: pulsating discharge flow causes periodic impact loads on discharge lines. This effect will be minimal by air filled surging chambers located on discharge line. These pumps are commonly denoted by bore & stroke. 6. DRILL STRING The portion in between the Kelly & drill bit is drill string. It has the installation of: 1. Kelly. 2. Drill pipes & tool joints. 3. Drill collars. 4. Stabilizer. i. kelly Configuration: It is square or hexagonal steal manufactured suspended from tip of swivel through rotary table (fixed with it) & is connected to drill pipe. Kelly applies rotational force to drill pipe via rotary table’s rotation, also bit rotates due drill pipe rotation. Mud hose is at the top of kelly, passes the drilling mud into the drill string. Kelly is visible portion during drilling whilst marking its rotational rate helps in observing bit’s penetration rate. ii. Drill pipes & tool joints Function: DP gives necessary length to drill string, serve as conduit for drilling fluid & also gives weight to drill bit. Configuration: DP sections are hollow, seamless tubes; manufactured from high grade steel usually in length of 20, 30 & 40 ft having dia varying from 2 to 9 inches & may have weight 25 lb/ft. Tool joints & connectors of DS are separate component & attached to pipe after its manufacture. DP & tubular goods (joints) have API specifications according to their outer diameter, weight per foot, steel grade & range (length). iii. Drill collars Function: Increases penetration power of drill bit via increasing weight on bit & reduces the tendency of DP to bend and divert to bit. Configuration: Heavy steel shafts of about 30ft length & ½ to 2 tons weight (heavier & thicker than drill pipes). iv. Stabilizer Function: Keeps the drill string / bottom hole assembly centered and stabilized (mechanically) in the hole. Configuration: composed of hollow cylindrical body & stabilizing blades (straight or spiral); made up of high strength steel. Placement: Usually 2 to 3 stabilizers are fitted into the BHA, including one just above the drill bit (near-bit stabilizer) and one or two among the drill collars (string stabilizers). 7. DRILL BIT Function: bit cuts the rock, make hole into the ground. Construction: made up of special strong hard, resistant steel with teethes, bit body & cones. Classification: • Fish-tail or Drag. • Roller cutter. • Diamond. i. Drag bit (fish tail) Oldest & first used bit, drills soft & sticky formations (but now roller cuter bits are used) Bit has no moving part & drills by shoveling action of their blades on encountered formation, where water courses are placed in a way that drilling fluid is directed on blades & keeping them clean. Blades & bit body is made up of various alloy steels & are hard faced with tungsten carbide. ii. Roller cutter bit Howard R. Hughes in 1909 initially designed the bit for drilling the hard formations (that can’t drilled by drag bits). Classification: a. Steel tooth (milled tooth) bit. b. Tungsten carbide insert bit. c. Jet bit. a. steel (milled) tooth bit Earlier made of two cones, now these soft bits have three cones. For soft formation: widely spaced, long & sharp teeth bits are used. For hard formation: more closely spaced, shorter & stronger teeth bits are used. MT bits are available for all soft, medium & hard formations. b. tungsten carbide insert bit Modern bits are of TCI or buttons instead of teeth, run with high speed of up to 180+ rpm. Having 3 cones with buttons & nozzles are below the cones. Advantages: great durability & good insert burial into formation, drills excellently hardest formations like quartzite or chert. Available for all soft, medium & hard formations (also with 2 cones). iii. • • • Diamond bit 5 times expensive than roller cutter, drills hardest formations with scraping action on stones via steel matrix. Configurations: Double cone bit – having sharp pointed nose, used for soft & medium soft formations. Modified double cone bit – broader nose, drills hard to hardest formations. Round cone bit – allows large amount of diamond coverage in nose area but have slow penetration rate, drills hard to hardest formations. 8. DRILLING (WIRE) LINE Affords means of handling loads suspended from hook during all drilling operations. Maximum load occurs when running casing is done, fishing require line pulls in excess of drill string weight. Size is 6*19 scale construction, fiber drill core, plow steel cable. For high load requirements, premium grade lines with independent wire rope centre are used. 9. MISCELLANEOUS & AUXILLIARY EQUIPMENTS Rotary table. Travelling block. Crown block. Hook. Swivel. Blow out preventers. rotary table • • Rotary table provides rotation to kelly in rotary drilling, powered by its own electric motors. Also accommodates slips mostly used for pipe suspension in hole when kelly disconnected. Two primary functions: Transmits rotation to drill string by turning kelly joint. Suspend pipe weights during connections & trips. travelling & crown block TB has travelling pulley assembly that connects drilling line to hook (as a unit or in separate parts) & swivel. TB assist in raising or lowering kelly to connect additional pipes for increasing the weight & length to drill faster & deeper respectively. CB is top most part on rig, having pulleys for raising & lowering the drilling line & travelling block. Hook & swivel. Hook is attached with travelling block & further with draw works through drilling line. Hook provides support to travelling block through draw works for raising or lowering the drill string, also it hangs the swivel. Swivel connected with hooks & have bearings which provides rotation to drill string (swivel does not rotate) while being suspended by swivel. Swivel also allows drilling fluid passage from mud hose into drill string. blow out preventers An assembly of heavy duty valves attached to top of casing for controlling well pressure. Two basic types: • Annular preventer – rubber element (tested at 1500 psi for its strength) that closes annular space tightly around kelly, drill pipes, drill collars & open hole. • Ram preventers (mostly used in offshore drilling)– large steel valves with sealing elements that cuts the drill pipe completely to seal the hole. Pipe & blind rams are common examples. Note: in sequence, annular preventer, pipe & blind rams are installed on the well to control the kick even if any one fails other will be active & works.