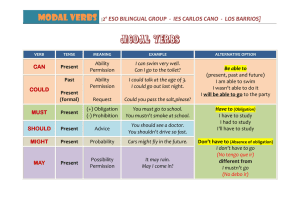
MUST / HAVE TO , MUSTN’T / DON’T HAVE TO Must - express personal obligation. - express what the speaker thinks is necessary. - personal opinion. - written rules / instructions. Have to - express impersonal obligation. - the subject is forced to act by external power ( the Law, school rules,...), facts, no opinions. - external obligation. The teacher is giving the studentes an obligation / instructions. TEACHER: You must complete the homework for Friday. STUDENT: We have to complete the homework for Friday. The teacher has given the obligation / instructions. Mustn’t Don’t have to - It is prohibited. - It is not allowed. - It is important that you do NOT do something. - NEGATIVE OBLIGATION - There is no obligation. - You are not required to do something if you don’t want to. - ABSENCE OF OBLIGATION EXAMPLE: You mustn’t tell John. - Do not tell John. - You are not allowed to tell John. EXAMPLE: You don’t have to tell John. - You can tell John if you want to but it is not necessary. MUST has no past or future forms. Use HAD TO and WILL HAVE TO. Use HAD TO to talk about the past. Use WILL HAVE TO for the future. Yesterday I must go to the dentist. I will must speak to her tomorrow. Yesterday I had to go the dentist. I will have to speak to her tomorrow.