POLICY BRIEF ON PENSIONS
July 2019
–
www.oecd.org/els/public-pensions
Pension systems went through major reforms
Retirement ages are slowly increasing while
gender gaps are being eliminated
–
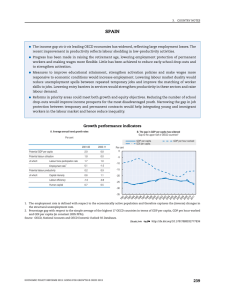
Eligibility age for a full pension for male workers entering the labour market at age 20 and having a full career
1956 (cohort retiring on average about today)
1940 (~ past)
1996 (~ future)
75
73
71
69
67
65
63
61
59
57
45
55
Rising share of adult life spent in retirement
–
Difference between men and women, full-career workers entering the labour market at age 20
1956 (cohort retiring on average about today)
1940 (~ past)
Years
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Large impact of systemic reforms and of big
changes in retirement ages
–
1996 (~ future)
For men of three selected birth cohorts
1956 (cohort retiring on average about today)
1940 (~ past)
1996 (~ future)
57
55
%
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
–
Full-career average earners retiring at the normal retirement age of the respective cohort, men
1956 (cohort retiring on average about today)
1940 (~ past)
1996 (~ future)
1940 (~ past)
1996 (~ future)
%
100
80
60
40
20
0
1956 (cohort retiring on average about today)
%
100
Increasing replacement rate
Stable replacement rate
80
60
40
20
0
–
Other*
References
Citation
Authors
Contacts
Endnotes
Financial support and disclaimer
–
POLICY BRIEF ON PENSIONS
Will future pensioners work for longer and retire on
less?
www.oecd.org/els/public-pensions
–