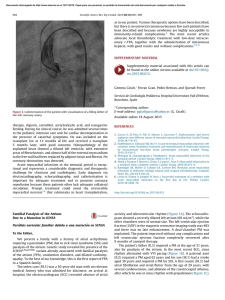
4. LA ONDA P Y SUS ALTERACIONES. ARRITMIAS SUPRAVENTRICULARES FELIPE CAÑAS ORDUZ FELLOW CARDIOLOGIA ICESI 2018 Figure 2: Schematic of normal atrial activation. Atrial activation starts at the sinus node near the right atrial-superior vena cava (SVC) junction. The right atrium is activated first, which is then followed by left atrial activation. For this reason, in general the initial part of the P wave reflects right atrial activation and the terminal portion of the P wave is due to left atrial activation (reprinted with permission from Kusumoto FM, Cardiovascular Pathophysiology, Hayes Barton Press, Raleigh, NC, 1999). CRECIMIENTO AURICULAR 1. Anatomía cardíaca, registro electrocardiográfico y análisis de eje. however, indicates that the finding of a tall, peaked P wave does not consistently correlate with RAA. Fig. 7.1 The normal P wave is usually less than 2.5 mm in pulmo acquire opathy cardiom nary di pu lm o bronch hypert lung di nia). C in clud defects tricusp also be includi stenosi carcino height and less than 0.12 sec in width. Right Atrial Abnormality (Overload) LEFT ABNO Enlarge ONDA P NORMAL Duración 80 – 120 ms Eje 0 - 75° Positiva DI, DII, AVF Bifásica DIII, AVL, V1, V2 Amplitud < 2.5mm.VI: (+) <1.5mm (-) < 1mm P PULMONAR ht atrium (RA) may cause tremity or chest leads. An LA) may cause broad, often mity leads and a biphasic P nent negative component ization of the left atrium. ntheroth WG: How to read uis, Mosby/ Elsevier, 2006.) Atrial Enlargement (Abnormality) LA RA V1 Normal Right Left RA II RA LA LA RA RA LA RA RA V1 LA LA LA ARRITMIAS SUPRAVENTRICULARES ARRITMIAS SUPRAVENTRICULARES ARRITMIAS SUPRAVENTRICULARES 1. Arritmias sinusales 2. Arritmia atriales 3. Nodo sinusal enfermo 4. Ritmos de escape 5. Reentrada intranodal 6. Preexitación 7. Fibrilación auricular 8. Flutter atrial 1. ARRITMIAS SINUSALES BRADICARDIA SINUSAL CAUSAS DE BRADICARDIA SINUSAL Fisiológica SAHOS Medicamentos Infarto Hiperkalemia Endocrinopatías Epilepsia Nodo sinusal enfermo TAQUICARDIA SINUSAL CAUSAS DE TAQUICARDIA SINUSAL Fisiológica Dolor Medicamentos Alcohol Fiebre Hipovolemia Falla cardíaca TEP Infarto Epilepsia Endocrinopatías ARRITMIA RESPIRATORIA SINUSAL 2. ARRITMIAS ATRIALES RITMO ATRIAL BAJO SENO CORONARIO EXTRASISTOLIA ATRIAL 3. NODO SINUSAL ENFERMO Table 9.1 Etiologies of sinus node dysfunction. Categories Specific etiologies Intrinsic Rheumatologic diseases Rheumatic fever, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter’s syndrome, tuberous sclerosis Congenital diseases Correction of congenital heart defects, autosomal dominant sinus node dysfunction Tumors Lymphoma, granular cell tumor SA nodal ischemia Myocardial infarction, embolism Infections Chagas’ disease Trauma After cardiac surgery, penetrating cardiac trauma Infiltrative diseases Sarcoidosis, amyloid, radiation therapy Extrinsic Autonomic responses Normal response, exaggerated vagal tone (carotid sinus hypersensitivity) Electrolytes, hypoxia, and hormones Thyroid disease, hyperkalemia, hypothermia, anorexia nervosa, hypoxia, sleep apnea Medications b-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, chemotherapy, lithium, phenothiazines, cimetidine, tricyclic antidepressants In fact, a number of investigators have demonstrated that the sinus node artery 4. RITMOS DE ESCAPE UNION 5. REENTRADA INTRANODAL ? 6. PRE EXITACIÓN (WPW) WPW en sinusal 3q WPW en taquicardia: Ortodrómica QRS estrecho WPW en taquicardia: Antidrómica QRS ancho 7 FIBRILACION AURICULAR atrial activation leads to irregular ventricular activation. Figure 8: Cartoon showing one of the potential mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. A rotor is a very localized reentrant circuit that appears to propagate “arms” of activation. When the “arms” meet obstacles—a region of refractory tissue, a “hole” such as a valve or vein opening—the arms split into “daughter” rotors. The atrial rate is very rapid, 300 to 1000 beats per minute. Fortunately, the AV node limits the ventricular response rate, although in younger patients fairly rapid 8. FLUTTER FLUTTER ATRIAL ARRITMIAS AURICULARES RESUMEN FORMACION DEL IMPULSO Sinusal Atrial Union CONDUCCION DEL IMPULSO Flutter Reentrada nodal Fibrilación auricular Pre exitación