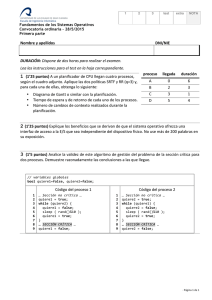
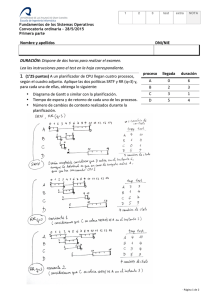
Descargar
Anuncio
Property Based
Testing
(También conocido como Generative Testing)
@guilespi
Guillermo Winkler
Guillermo Winkler
Ingeniero
Guillermo Winkler
Ingeniero
Programador
Guillermo Winkler
Ingeniero
Programador
Tester
Property Based
Testing
O Cómo no escribir mas Unit Tests
Property Based
Testing
O Cómo no escribir mas Unit Tests
Types vs. Tests
Cuál es la mejor forma de
demostrar que nuestros
sistemas son correctos?
(O sea que hacen lo que tienen que hacer)
Cuál es la mejor forma de
demostrar que nuestros
sistemas son correctos?
(O sea que hacen lo que tienen que hacer)
Types
•
Sirven como parte de la especificación
•
Ayudan durante el diseño
•
Ayudan a capturar requerimientos
Tests
•
Sirven como parte de la especificación
•
Sirven como “comentarios ejecutables”
•
Ayudan durante el diseño
•
Ayudan a capturar requerimientos
Una lista de timestamps en
Scala
Un loop en Ruby
“Program testing can be used to show
the presence of bugs, but never to show
their absence”
Edsger Dijkstra
double f1(int x) {
return 1/x;
}
@Test
public void testUnity() {
assertEquals(1, f1(1));
}
double f1(int x) {
return 1/x;
}
@Test
public void testUnity() {
assertEquals(1, f1(1));
}
100% code
coverage!
Patch
Quién se morfo el unit test?
Átomos en la tierra:
1.33 x 10^50
Joe Armstrong
(Erlang)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKXe3HUG2l4
2^k=10^50
k=50log(10)/log(2)
k=166.09
k/32=5.18
Un programa en C con 6 enteros
tiene más estados posibles que
átomos hay en el planeta…
Un programa en C con 6 enteros
tiene más estados posibles que
átomos hay en el planeta…
?
Fred Brooks
Digital computers are more complex than most things that
people build. They have large numbers of states. Software
systems have orders of magnitude more states than
computers do.
No Silver Bullet
Essence and Accidents of Software Engineering
Property based testing
Definir propiedades que tiene
que cumplir nuestro sistema
para cierto dominio de valores.
Property based testing
Poner al sistema en la
mayor cantidad de
estados posibles
Precisamos generar valores
(De ahí lo de generative testing)
Enteros int
0 1 1 0 2 -4 0 5 -7 -8 4 5 3 11 -9 -4 6 -5 -3 0
Vectores de enteros [int]
[] [] [1] [1] [] [] [5 6 6 2 0 1] [3 7 5] [2 0 0 6 2 5 8] [9 1 9 3 8 3 5]
Listas de booleanos (bool)
() () (false) (false true false) (false true) (false true true true) (true)
(false false true true) () (true)
Alfanuméricos (string)
“hZO*3" “m-W2@KL” ",P+po0#2 “ "tlt^[ ui`V"
Estructuras compuestas
{:user-name "kWodcsE2",
:user-id 1,
:email "[email protected]",
:active? true}
QuickCheck
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
C
C++
Chicken Scheme
Clojure
Common Lisp
D
Elm
Erlang
F#
Factor
Io
Java
Javascript
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Node.js
Objective-C
OCaml
Perl
Prolog
Python
R
Ruby
Scala
Scheme
Smalltalk
Standard ML
function sort(values) {
var length = values.length - 1;
do {
var swapped = false;
for(var i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
if (values[i] > values[i+1]) {
var temp = values[i];
values[i] = values[i+1];
values[i+1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
while(swapped == true)
};
sort([7, 4, 5, 2, 9, 1]);
Cómo se define una
propiedad?
Ejemplo:
En un array ordenado el primer elemento
es siempre menor que el último.
Cómo se define una
propiedad?
Ejemplo:
En un array ordenado el primer elemento
es siempre menor que el último.
Promueve una visión de más alto nivel con
restricciones que se deben satisfacer de manera
universal.
Javascript
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Un nombre para la propiedad…
Javascript
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Javascript
Un generador de valores
para la función a testear…
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Javascript
Invocar a la función para el
valor generado…
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Javascript
Validar que la propiedad
se cumple…
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Ejecutar 10 casos…
Javascript
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
Javascript
JSC.reps(10);
JSC.test(
"First is lower than last after sort",
function (verdict, v) {
var sorted = v.sort();
return verdict(sorted[0] < sorted[sorted.length - 1]);
},
[
JSC.array([JSC.integer()]])
]
);
Clojure
(def prop-sorted-first-less-than-last
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(let [s (sort v)]
(< (first s) (last s)))))
(tc/quick-check 10 prop-sorted-first-less-than-last)
=> {:result false,
:failing-size 0,
:num-tests 1,
:fail [[3]],
:shrunk {:total-nodes-visited 5,
:depth 2,
:result false,
:smallest [[0]]}}
Shrinking
(def prop-no-42
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(not (some #{42} v))))
(tc/quick-check 100 prop-no-42)
;; => {:result false,
:failing-size 45,
:num-tests 46,
:fail [[10 1 28 40 11 -33 42 -42 39 -13 13
-44 -36 11 27 -42 4 21 -39]],
:shrunk {:total-nodes-visited 38,
:depth 18,
:result false,
:smallest [[42]]}}
(def prop-no-42
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(not (some #{42} v))))
(tc/quick-check 100 prop-no-42)
;; => {:result false,
:failing-size 45,
:num-tests 46,
:fail [[10 1 28 40 11 -33 42 -42 39 -13 13
-44 -36 11 27 -42 4 21 -39]],
:shrunk {:total-nodes-visited 38,
:depth 18,
:result false,
:smallest [[42]]}}
(def prop-no-42
(prop/for-all [v (gen/vector gen/int)]
(not (some #{42} v))))
(tc/quick-check 100 prop-no-42)
;; => {:result false,
:failing-size 45,
:num-tests 46,
:fail [[10 1 28 40 11 -33 42 -42 39 -13 13
-44 -36 11 27 -42 4 21 -39]],
:shrunk {:total-nodes-visited 38,
:depth 18,
:result false,
:smallest [[42]]}}
Shrink Tree
http://www.slideshare.net/PhilipKoopman/toyota-unintended-acceleration
http://www.quviq.com/volvo-quickcheck/
Property Based Testing
•
Es complementario con unit tests y/o type systems.
•
Promueve una visión de más alto nivel sobre las
definiciones en nuestras pruebas.
•
Permite poner a nuestro sistema en una cantidad de
estados solo alcanzable de forma computacional.
•
Antes que los errores ocurran para prevenir
•
Después que ocurran para diagnosticar