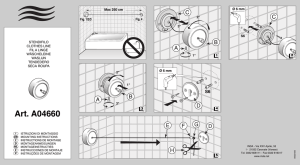
w LB p - Biotech Dental
Anuncio

NOTICE D’INSTRUCTIONS SYSTEMES D’IMPLANTS DENTAIRES BIOTECH DENTAL KONTACT , B.I.S. , B.I.S. Conic et Weego.fr. Les systèmes d’implants dentaires BIOTECH DENTAL doivent être manipulés par des personnes FORMEES, QUALIFIEES et AYANT PRIS CONNAISSANCE de la présente notice. 1. DESCRIPTION GÉNÉRALE Les systèmes d’implants dentaires BIOTECH DENTAL sont constitués : - d’implants dentaires en titane / alliage de titane conformes aux normes en vigueur ISO 5832-2 / ISO 5832-3, - de piliers en titane, alliage de titane ou en céramique conformément aux normes correspondantes en vigueur, - de composants prothétiques annexes en titane, alliages de titane ou métalliques et polymères conformes aux normes correspondantes en vigueur, - d’une instrumentation ancillaire en acier inoxydable de grade médical, alliage de titane et titane. Afin de permettre l’identification, la majorité des instruments portent de manière visible une référence et un numéro de lot de fabrication. Les produits stériles sont identifiés au niveau de l’emballage. En l’absence de mention spécifique ‘stérile’, les produits sont fournis non stériles et doivent être stérilisés avant utilisation par le personnel concerné. Les systèmes d’implants dentaires sont radio-opaques. 2. CONDITIONS GÉNÉRALES D’UTILISATION Les systèmes d’implants dentaires doivent exclusivement être utilisés par des chirurgiens expérimentés: - formés à l’implantologie et aux techniques d’utilisation des dispositifs médicaux BIOTECH DENTAL, - dans le respect des indications, contre indications et précautions à indiquer au patient en post –opératoire mentionnées dans la présente notice et dans les protocoles chirurgicaux et prothétiques disponibles sur demande, - dans des locaux compatibles avec les conditions d’asepsie requises dans la présente notice d’instructions. En aucun cas ils ne doivent être utilisés avec des dispositifs d’un autre fabricant. BIOTECH DENTAL s’engage, durant une période allant de l’implantation à la mise en charge à remplacer tout implant ou composant prothétique si les conditions ci-dessus ont été respectées. Le praticien est responsable des complications pouvant résulter d’une utilisation ne respectant pas les recommandations ou d’une faute d’asepsie. Ces complications ne peuvent en aucun cas être imputées à BIOTECH DENTAL et ont pour effet le rejet de tout recours formulé à l’encontre de BIOTECH DENTAL en matière de garantie ou visant un remplacement de produit. 3. INDICATIONS Les implants dentaires BIOTECH DENTAL sont utilisés comme base d’ancrage des remplacements à la mandibule comme au maxillaire. Les restaurations vont du remplacement unitaire à complet afin de redonner tout ou partie des fonctions des dents naturelles. Cette technique n’est envisagée que lorsque toute autre thérapie moins invasive est considérée comme moins appropriée. Le volume et la qualité osseux doivent être suffisants pour supporter des implants dentaires. 4. CONTRE-INDICATIONS Les implants dentaires ne doivent pas être utilisés chez des patients présentant des contre-indications locales et/ou générales pour toute intervention chirurgicale dentaire. Ces contre-indications doivent être évaluées soigneusement lors de la décision prise par le chirurgien. En font partie entre autres : - facteurs interférant avec le processus de cicatrisation et de régénération osseuse et tissulaire comme troubles du métabolisme osseux, du tissu conjonctif, diabète gras, thérapie stéroïdienne, infections osseuses, abus de tabac, d’alcool, - pathologies ou thérapies immunosuppressives telles que la chimiothérapie, radiothérapies, - volume osseux et qualité osseuse insuffisants pour accepter des implants en nombre et dimension suffisants et supporter les charges fonctionnelles, - bruxisme, habitudes parafonctionnelles, troubles de l’occlusion et/ou des articulations temporo-mandibulaires, - infections et inflammations buccales telles que parodontite, gingivite, - allergie au titane, alliage de titane ou hygiène bucco-dentaire insuffisante. 5. PRÉCAUTIONS D’UTILISATION - Afin d’éviter toute déglutition ou inhalation de petits composants, il est recommandé si possible de les sécuriser - Tout incident ou problème relatif à un implant ou instrument doit être signalé à BIOTECH DENTAL. Précautions pré-opératoires : - l’utilisateur doit s’assurer du bon état et du bon fonctionnement du matériel avant son utilisation. Il ne doit en aucun cas être utilisé si des détériorations de surface ou de forme sont visibles, - une évaluation du patient est nécessaire pour déterminer tout facteur susceptible de l’exposer à un risque résultant de la pose de l’implant, ou pouvant influer sur les facultés de cicatrisation de l’os/ du tissu mou, Certains critères doivent être pris en compte dans l’indication opératoire et le choix des implants : - la surface occlusale de l’implant doit idéalement être plus petite que la dent prothétique pour assurer l’évasement des tissus mous et le profil d’émergence de la prothèse, - un espace minimum de 1,5mm entre l’implant et la racine adjacente, 1,5mm entre 2 implants, et une épaisseur d’os de 1mm autour des faces vestibulaires et linguales de l’implant (> pour les gros diamètres), - en cas de suspicion d’hypersensibilité ou d’hypersensibilité avérée à des corps étrangers, il est recommandé de contrôler la tolérance au titane et à l’alliage de titane TA6V ELI avant d’implanter le matériel, - une évaluation radiographique et/ou tomodensitométrique et un plan de traitement clinique sont impératifs pour une sécurité absolue. Précautions per-opératoires : - la stabilité primaire de l’implant est indispensable, - le choix du type d’implant et de sa taille incombe au chirurgien; il dépend de chaque patient et de sa pathologie. C’est la taille et la nature des structures osseuses qui définissent le choix du chirurgien. Il devra aussi tenir compte des efforts exercés sur l’implant après l’intervention, - les implants ne doivent pas être déformés. Au risque d’entraîner une fatigue anormale de l’implant, les manœuvres doivent être progressives. Un effort excessif exercé sur l’implant pourrait induire des contraintes provoquant une fracture ou une déformation de l’implant responsables d’effets secondaires, - il appartient au praticien de définir les réglages de son matériel en fonction des cas cliniques et de vérifier le bon état de celui-ci avant chaque intervention. Il est préconisé de réaliser les séquences de forage à vitesse lente, sous irrigation externe profuse et constante. La vitesse de rotation recommandée est de 700 à 1200 tr/min pour le forage, ne dépassant pas 1500 tr/min, et 200 tr/min pour l’alésage, - les forets sont très coupants, il est recommandé d’être prudent lors de leur préhension afin d’éviter toute coupure. De même, du fait de leurs conceptions à goujures hélicoïdales, ils peuvent induire, lors de leurs usages, un phénomène d’entrainement préjudiciable à la précision du perçage. Afin de remédier à cette éventualité, il est recommandé d’utiliser les butées de forets prévues à cet effet, - l’usage de tous les instruments coupants (Fraise, forets, tarauds et alésoirs) doit être limité à 20 utilisations afin d’éviter les problèmes d’usure. Une fiche de suivi spécifique pour les forets est mise à disposition. Précautions post-opératoires : Après mise en place de l’implant, l’ostéointégration s’effectue dans les 4 mois (mandibule) et les 6 mois (maxillaire). Le chirurgien devra mettre en place le suivi post-opératoire. La responsabilité lui incombe d’informer le patient concernant : - les actions à éviter suite à la pose d’un implant et les précautions à prendre au cours de l’activité journalière normale. Le patient devra comprendre qu’avant complète consolidation osseuse, un matériel métallique ne peut être aussi résistant que les structures osseuses saines et que celui-ci cassera en cas d’efforts intenses ou anormaux, - l’effectivité de l’implantation qui dépend de son comportement et de son hygiène buccale, - des potentiels risques et effets indésirables liés à la mise en place d’un implant dentaire, - de la possibilité d’un échec de l’ostéointégration de l’implant, - de la nécessité de déclarer toute sensibilité apparaissant au niveau du secteur opéré en per / post-opératoire, - des interactions potentielles avec d ‘autres procédures, dispositifs thérapeutiques ou diagnostiques. 6. EFFETS INDÉSIRABLES ÉVENTUELS Les techniques d’implantation s’accompagnent de contre-indications et risques d’usage. Ils peuvent aussi bien être liés à l’utilisation du dispositif qu’à l’intervention chirurgicale et peuvent inclure (liste non exhaustive) : - sensibilité, problèmes d’élocution, œdèmes, hématomes, - descellement, rupture ou perte d’un composant, - lésion nerveuse locale transitoire ou permanente, - infection, lésion des dents adjacentes, problèmes esthétiques, - réaction allergique à l’égard des différents matériaux constitutifs des implants de BIOTECH DENTAL. 7. STÉRILITÉ ET TRAÇABILITÉ - Dispositifs livrés stériles : Les implants dentaires, livrés seuls avec une vis de couverture et/ou une vis de cicatrisation dans le packaging de l’implant, sont stériles (stérilisation par rayonnement gamma). L’intégrité des emballages doit être contrôlée avant utilisation pour s’assurer que la stérilité du contenu n’est pas altérée. Dans des conditions de stockage adéquates, l’emballage permet de maintenir l’état de stérilité jusqu’à la date de péremption. Si l’emballage est endommagé, ne pas utiliser. Des étiquettes sur les différents niveaux d’emballage ainsi que des étiquettes libres permettent une parfaite traçabilité basée sur la référence et le numéro de lot de l’implant. Les dispositifs stériles à usage unique ne doivent en aucun cas être réutilisés et re-stérilisés. En cas de restérilisation d’un dispositif médical non re-stérilisable, l’absence de transmission iatrogène d’organismes pathogènes par ces dispositifs n’est plus garantie et un accident relevant du domaine de la matériovigilance peut se produire. Dispositifs livrés non stériles : L’instrumentation ancillaire et les pièces prothétiques sont livrés dégraissés non stériles. Il est de la responsabilité du personnel concerné de procéder à la décontamination, au nettoyage et à la stérilisation avant et après (pour les produits réutilisables) chaque intervention, selon les recommandations en vigueur (cf §8). 8. NETTOYAGE ET STÉRILISATION DES DISPOSITIFS NON STÉRILES Les opérations de décontamination et de nettoyage sont impératives avant toute stérilisation. - Pour ne pas détériorer les composants, utiliser uniquement des produits de nettoyage et de décontamination compatibles avec les matériaux. Proscrire les produits alcalins et corrosifs pour les dispositifs en acier inoxydable et en aluminium : l’eau de javel, solution aqueuse d’hypochlorite et de chlorure de sodium décolorent et/ou corrodent les instruments, le sérum physiologique a un effet corrosif sur les aciers inoxydables. - L’eau à utiliser pour la pré-désinfection, le nettoyage, la décontamination, les rinçages et la stérilisation doit être en accord avec les réglementations en vigueur. - L’utilisateur doit prêter une attention particulière au nettoyage des saletés, des résidus et dépôts de toutes les parties des instruments (creux, interstices,…). Pré-décontamination : - elle doit être réalisée immédiatement après chaque intervention sur tous les instruments réutilisables démontés, - immerger totalement les instruments préalablement démontés dans une solution décontaminante à pH neutre sans aldéhyde, plus ou moins concentrée selon le taux de contamination et de souillures des instruments. Laisser tremper 15 à 20 minutes. Le trempage en bain à ultrasons est conseillé. - La solution décontaminante doit être renouvelée après chaque utilisation pour éviter sa saturation. Nettoyage : Il peut être effectué par brossage ou par ultrasons et doit être réalisé sur composants démontés. - Le brossage doit être effectué avec une brosse douce (nylon par exemple). - Une durée de trempage de 15 min minimum est nécessaire. Un contact prolongé de plusieurs heures avec certains produits peut induire une corrosion du matériau (ne pas dépasser 2 heures). Rinçage – Séchage : Le nettoyage sera suivi immédiatement d’un rinçage abondant puis les produits devront être séchés avant le lancement du processus de stérilisation. Conditionnement avant stérilisation : Quel que soit le mode de nettoyage, le matériel doit être immédiatement conditionné afin d’éviter toute nouvelle contamination. ® ® ® Dans le cas d’une stérilisation sur plateaux métalliques grillagés, un conditionnement sous double emballage papier doit être réalisé. Dans le cas d’un conditionnement tardif (> à 2 heures), un re-nettoyage pourrait être considéré afin de s’assurer de l’état stérile du matériel. Stérilisation : Préparer les instruments de manière à ce que toutes les surfaces soient en contact direct avec la vapeur d’eau. Le cycle recommandé est le cycle Prion à 134°C pendant 18 minutes. Retour : Après utilisation de l’ancillaire dans le cas d’un prêt, celui-ci devra être retourné à BIOTECH DENTAL , après avoir été nettoyé et décontaminé suivant l’instruction DGS/RI3/3011/449 du 1er décembre 2011. Il incombe à l’établissement de santé ou au praticien de s’assurer que le processus de nettoyage-stérilisation effectivement mis en œuvre (équipement, matériaux et opérateur) atteint le résultat escompté. En aucun cas, le fabricant ne pourra être tenu pour responsable de la stérilité. 9. MANIPULATION ET STOCKAGE La manipulation et le stockage des produits doit être effectué avec précaution pour garantir l’absence de contamination ou de détérioration avant toute intervention chirurgicale. Le stockage doit être réalisé avec soin dans un endroit approprié, sec et propre. Ils ne doivent pas être exposés à la lumière solaire directe, aux rayonnements ionisants, à des températures extrêmes, à une contamination particulaire ou au contact ou à proximité de produits pouvant avoir une action corrosive. La durée de vie des dispositifs peut être compromise par un manque de précautions lors de la manipulation ou une mauvaise protection des instruments. 10. ELIMINATION L’élimination des déchets médicaux doit se conformer à la législation en vigueur. Le tri entre déchets à risques infectieux et déchets assimilables aux ordures ménagères incombe au professionnel producteur du déchet. GB INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE BIOTECH DENTAL DENTAL IMPLANT SYSTEMS KONTACT®, B.I.S.®, B.I.S. Conic® and Weego.fr. These products must be handled by TRAINED, QUALIFIED individuals who HAVE READ these instructions. 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION BIOTECH DENTAL dental implant systems consist of: - titanium/titanium alloy dental implants which comply with applicable standards ISO 5832-2/ISO 5832-3, - titanium, titanium alloy and ceramic abutments which comply with the applicable standards, - additional prosthetic titanium components in titanium, titanium alloy or metal and polymer which comply with the applicable standards, - ancillary medical grade stainless steel instrumentation, titanium/titanium alloy, For the purpose of identification, the majority of the instruments bear a visible reference and manufacturing batch number. The sterile products are identified on the packaging. If the word ‘sterile’ is not specifically stated, the products are supplied non-sterile and must be sterilised before use by the staff concerned. The dental implant systems are radio-opaque. 2. GENERAL CONDITIONS OF USE The dental implant systems must only be used by experienced surgeons: - trained in implantology and techniques for the use of BIOTECH DENTAL medical devices, - in the observance of the indications, contraindications and precautions which are to be indicated to the patient during the postoperative phase and which are mentioned in these instructions as well as in surgical and prosthetic protocols available on request, - on premises compatible with the aseptic conditions required by these instructions, Under no circumstances may the dental implant systems be used with the devices of another manufacturer During the period from implantation to management, BIOTECH DENTAL undertakes to replace any implant or prosthetic component, provided that the above conditions have been observed. The practitioner will be responsible for complications which result from use which has failed to comply with the recommendations or asepsis. These complications may under no circumstances be attributed to BIOTECH DENTAL and will lead to the rejection of any formulated action against BIOTECH DENTAL concerning guarantee or product replacement. 3. INDICATIONS BIOTECH DENTAL dental implants are used as a base for the anchorage of replacements to the mandible as well as the maxillary. Restorations range from unitary replacement to complete replacement for the purposes of reproducing all or some of the functions of the natural teeth. This technique is only considered if other less invasive therapies are regarded as less suitable. The osseous volume and quality must be sufficient for the purposes of supporting the dental implants. 4. CONTRAINDICATIONS Dental implants must be not be used in patients who present with local and/or general contraindications to surgical dental intervention. These contraindications must be carefully assessed when the surgeon makes his decision. Among other things, the contraindications constitute: - factors which interfere with the process of healing and osseous and tissue regeneration such as problems with osseous metabolism, connective tissue, type 2 diabetes, steroid therapy, osseous infections, and nicotine and alcohol abuse, - diseases or immunosuppressive therapies such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, - osseous volume and osseous quality which are not sufficient for the purposes of accepting a sufficient number and size of implants and to support the functional loads, - bruxism, parafunctional habits, problems with occlusion and/or the temporomandibular joints, - buccal infections and inflammation such as paradontitis and gingivitis, - allergy to titanium or titanium alloy or inadequate bucco-dental hygiene. 5. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE - In order to avoid swallowing or inhalation of small components, it is recommended that they be secured where possible. - BIOTECH DENTAL must be informed of any incident or problem concerning an implant or instrument. Preoperative precautions: - The user must ensure that the material is in good condition and working correctly before use. Under no circumstances must the material be used if the packaging is damaged or if surface damage or deformations can be seen. - Evaluation of the patient is necessary for the purposes of determining any factor which is likely to expose him to a risk resulting from insertion of the implant or which might have an influence on healing of the bone/soft tissue. Certain criteria must be taken into consideration with regard to the indication for surgery and the choice of implant: - the occlusal surface of the implant must ideally be smaller than the prosthetic tooth to ensure the flaring of the soft tissue and the emergence profile of the prosthesis, - a minimum space of 1.5 mm between the implant and the adjacent root, 1.5 mm between 2 implants, and a thickness of bone of 1 mm around the vestibular and lingual surfaces of the implant (> in the case of large diameters), - in the event of suspected hypersensitivity or proven hypersensitivity to foreign bodies, it is recommended that titanium and TA6V ELI titanium tolerance be checked prior to implantation of the material. Radiographic and/or CT scan evaluation and a clinical treatment plan are essential for the purposes of ensuring complete safety. Perioperative precautions: - Primary stability of the implant is essential, - The choice of the type of implant and its size will be a matter for the surgeon; this will depend on the particular patient and the patient’s pathology. The size and the nature of the osseous structures will determine the surgeon’s choice. The surgeon will also have to consider the stresses on the implant after the procedure, - Implants must not be deformed. At the risk of causing abnormal fatigue of the implant, the manipulations will have to be progressive. An excessive effort exerted on the implant might induce stresses which could cause a fracture or deformation of the implant responsible for secondary effects, - It is up to the practitioner to determine the settings of his equipment depending on the particular clinical case, and to check that his equipment is working properly prior to every procedure. It is recommended that the drilling sequences be conducted at a slow speed and with profuse and constant external irrigation. The recommended rotation speed is from 700 to 1,200 rpm in the case of drilling, not exceeding 1,500 rpm, and 200 to 400 rpm for boring, - The drills are very sharp; it is recommended that caution be exercised when gripping the drills in order to avoid being cut. Also, because the drills are designed with helicoidal flutes, their use can result in a drag phenomenon which is detrimental to drilling precision. In order to correct this possibility, it is recommended that use be made of the drilling stops provided for this purpose, - Cutting tools (countersinks, drills, taps and borers) must not be used more than 20 times in order to prevent problems with wear. A specific tracking sheet for the drills is available. Postoperative precautions: After insertion of the implant, osteointegration is achieved within 4 months (mandible) 6 months (maxillary). The surgeon must implement postoperative follow-up. He will be responsible for informing the patient with regard to: - actions to avoid following the insertion of an implant and the precautions to be taken in the course of normal daily activity. The patient must understand that prior to complete osseous consolidation, a metallic material is not as strong as healthy osseous structures, and that metallic materials will break if subjected to intense or abnormal stresses, - the efficacy of the implant depends on his behaviour and his buccal hygiene, - potential risks and adverse effects associated with the insertion of a dental implant, - the possibility of failure of implant osteointegration, - the need to report any sensitivity appearing in the operated area, peri- or postoperatively, - potential interaction with other procedures and therapeutic or diagnostic devices. 6. POSSIBLE ADVERSE EFFECTS The implantation techniques are accompanied by contraindications and risks of use. They can also be related to use of the device as well as the surgical intervention and they can include (a non-exhaustive list): - sensitivity, problems with speech, oedema and haematomas, - loosening, rupture or loss of a component, - local nervous lesion, transient or permanent, - infection, lesion of adjacent teeth and aesthetic problems, - an allergic reaction to the different materials which constitute BIOTECH DENTAL implants. 7. STERILITY AND TRACEABILITY Sterile delivered Device: dental implants delivered with a cover screw and a healing screw in the packaging of the implant, are sterile (sterilisation by gamma radiation). Any product which is supplied sterile is for single use and must not be resterilised. The entire packaging must be checked before use to ensure that the sterility of the contents has not altered. In conditions of adequate storage, the packaging maintains sterility until the expiry date. Do not use if the packaging has been damaged. Labels on the different levels of packaging as well as free labels will make it possible to ensure perfect traceability based on the reference number and the batch number of the implant. Sterile single-use devices should under any circumstances be reused and re-sterilized. In case of re-sterilization of a non-re-sterilizable medical device, the absence of iatrogenic transmission of pathogens by these devices is no longer guaranteed and accident in the field of materiovigilance may occur. Non sterile delivered device: the ancillary instrumentation and the prosthetic parts are supplied clean but not sterile. It will be the responsibility of the staff concerned to proceed with decontamination, cleaning and sterilisation before and after every procedure (for reusable products) in accordance with the applicable recommendations. 8. CLEANING AND STERILISATION OF NON-STERILE DEVICES Decontamination and Cleaning operations are imperative before every sterilisation process. - In order to prevent the deterioration of the components, only use cleaning products and decontamination products which are compatible with the materials. Alkaline and corrosive products for stainless steel and aluminium medical devices are prohibited: bleach, aqueous solutions of sodium hypochlorite and sodium chloride discolour and/or corrode the instruments, - The water to be used for pre-disinfection, cleaning, decontamination, rinsing and sterilisation must comply with the applicable regulations, - The user must pay particular attention to the cleaning of dirt, residue and deposits on all parts of the instruments (cavities, interstices, etc.). Pre-decontamination: - this must be done immediately after every procedure in the case of all disassembled reusable instruments, - completely immerse the previously disassembled instruments in a decontaminating solution with a neutral pH, without aldehyde and whose concentration depends on the rate of contamination and the degree of soiling of the instruments. Soak for 15 to 20 minutes. Ultrasound bath soaking is recommended, - the decontamination solution must be renewed each time after use in order to prevent its saturation. Cleaning: - this can be undertaken by brushing and by ultrasound and must be done on disassembled components, - brushing must be carried out with a soft brush (for example, nylon), - soaking for a minimum of 15 minutes is necessary. Prolonged contact with certain products for several hours can cause corrosion of the material (do not exceed 2 hours). Rinsing – Drying: Cleaning must immediately be followed by abundant rinsing and then the products must be dried prior to beginning the sterilisation process. Packaging prior to sterilisation: Whichever method of cleaning is used, the material must be packaged immediately in order to avoid any new contamination. In the event of sterilisation on metal grid trays, double wrapping paper must be used for the packaging. In the event of late packaging (> 2 hours), further cleaning might be considered in order to make sure that the material is sterile. Sterilisation: Prepare the instruments so that all surfaces are in direct contact with the steam. The recommended cycle is the Prion cycle at 134°C for 18 minutes. Return: After using the ancillary in the event of a loan, this must be returned to BIOTECH DENTAL after having been cleaned and decontaminated in accordance with applicable regulations. It is incumbent upon the healthcare establishment or the practitioner to ensure that the cleaning/sterilisation process which is effectively implemented (equipment, materials and operator) achieves the desired result. Under no circumstances will the manufacturer be held responsible for sterility. 9. HANDLING AND STORAGE The products must be handled and stored carefully in order to ensure a lack of contamination and deterioration prior to any surgical intervention. Storage must be done with care in an appropriate, dry and clean environment. They must not be exposed to direct sunlight, ionising radiation, extreme temperatures, specific contamination, or contact or proximity with products that may have a corrosive effect. The lifecycle of the devices can be compromised by a lack of precautions during handling or poor protection of the instruments. 10. ELIMINATION The elimination of medical waste must comply with the applicable legislation. The professional who produces waste will be responsible for sorting waste which carries a risk of infection and waste which is compatible with household waste. DE GEBRAUCHSANWEISUNG BIOTECH DENTAL ZAHN-IMPLANTATSYSTEME KONTACT®, B.I.S.®, B.I.S. Conic® und Weego.fr. Darf dieses Produkt ausschließlich von GESCHULTEN, QUALIFIZIERTEN Personen gehandhabt werden, die diese Anleitung GELESEN HABEN. 1. ALLGEMEINE BESCHREIBUNG Die Zahnimplantatsysteme von BIOTECH DENTAL bestehen aus folgenden Bestandteilen: - zahnimplantate aus Titan/Titanlegierung, die die einschlägigen Normen ISO 5832-2/ISO 5832-3 erfüllen, - abutments aus Titan, Titanlegierung und Keramik, die die einschlägigen Normen erfüllen, - zusätzliche prothetische Titan-Komponenten aus Titan, Titanlegierung oder Metall und Kunststoff, die die einschlägigen Normen erfüllen, - hilfsmittel aus titanlegiertem rostfreiem Stahl für medizinische Einsatzzwecke, Titan/Titanlegierung. Zum Zwecke der Identifikation sind die meisten Instrumente mit ihrer Artikel- und Chargennummer gekennzeichnet. Sterile Produkte sind auf der Verpackung entsprechend gekennzeichnet. Wenn das Wort «steril» nicht explizit angegeben ist, werden die Produkte unsteril geliefert und müssen vor der Verwendung vom betreffenden Personal sterilisiert werden. Zahnimplantatsysteme sind röntgenopak. 2. ALLGEMEINE ANWENDUNGSBEDINGUNGEN Zahnimplantatsysteme dürfen nur von erfahrenen Kieferchirurgen angewandt werden. Diese müssen: - auf dem Gebiet der Implantologie und in der Anwendung von BIOTECH DENTAL -Medizinprodukten geschult sein, - und die Indikationen, Kontraindikationen und Vorsichtsmaßnahmen, die für die postoperative Phase der Patientenversorgung gelten und in der vorliegenden Gebrauchsanweisung sowie in den chirurgischen und prothetischen Protokollen aufgeführt sind auf Anfrage verfügbar, - des Weiteren darf die Anwendung nur in Einrichtungen erfolgen, in denen die in dieser Gebrauchsanweisung geforderten aseptischen Bedingungen gewährleistet sind. In keinem Fall dürfen die Zahnimplantatsysteme gemeinsam mit Produkten anderer Hersteller angewandt werden. Im Zeitraum von der Implantation bis zum Management verpflichtet sich BIOTECH DENTAL zum Ersatz sämtlicher Implantate und prothetischer Komponenten, sofern die oben genannten Bedingungen eingehalten wurden. Im Falle von Komplikationen, die aufgrund der Nichtbeachtung dieser Empfehlungen und der Nichteinhaltung aseptischer Bedingungen eintreten, haftet der Arzt. Die genannten Komplikationen können unter keinem Umständen BIOTECH DENTAL angelastet werden und haben die Rückweisung sämtlicher gegen BIOTECH DENTAL erhobener Garantie- oder Ersatzforderungen zur Folge. 3. INDIKATIONEN Die Zahnimplantate von BIOTECH DENTAL können als Träger zur Verankerung von Zahnersatz im Unterund Oberkiefer verwendet werden. Ihr Anwendungsgebiet reicht vom Einzelzahnersatz bis zur Versorgung des zahnlosen Kiefers zum Zweck der Wiederherstellung aller oder bestimmte Funktionen des natürlichen Gebisses. Dieses Verfahren ist nur dann in Erwägung zu ziehen, wenn andere, weniger invasive Therapien als ungeeignet eingeschätzt wurden. Für den Einsatz von Zahnimplantaten müssen ein ausreichendes Knochenvolumen und eine entsprechende Knochenqualität gegeben sein. 4. KONTRAINDIKATIONEN Zahnimplantate dürfen nicht bei Patienten eingesetzt werden, die lokale und/oder allgemeine Kontraindikationen für kieferchirurgische Eingriffe aufweisen. Diese Kontraindikationen muss der Kieferchirurg bei seiner Entscheidung sorgfältig beurteilen. Es können z.B. folgende Kontraindikationen bestehen: - faktoren, die den Heilungsprozess und die Knochen- und Geweberegeneration beeinträchtigen, z.B. Knochenstoffwechselerkrankungen, Bindegewebserkrankungen, Diabetes Typ 2, Steroidtherapien, Knocheninfektionen sowie Nikotin- und Alkoholabusus, - bestehende Erkrankungen und immunsuppressive Therapien, z.B. Chemotherapie und Strahlentherapie, - unzureichende Knochenmasse und –qualität, um eine entsprechende Anzahl und Größe von Implantaten aufzunehmen und eine entsprechende funktionale Belastbarkeit zu gewährleisten, - bruxismus, Parafunktionen, Okklusionsstörungen und/oder Kiefergelenksprobleme, - infektionen und Entzündungen der Mundhöhle, z.B. Parodontitis und Gingivitis, - allergische Reaktionen auf Titan oder Titanlegierungen sowie unzureichende Mund- und Zahnhygiene. 5. VORSICHTSMASSNAHMEN BEI DER ANWENDUNG - Um das Verschlucken oder Einatmen von Kleinteilen zu verhindern, empfiehlt es sich, diese möglichst zu befestigen. - BIOTECH DENTAL ist über sämtliche Zwischenfälle oder Probleme, die bezüglich eines Implantats oder Instruments auftreten, zu informieren. Präoperative Vorsichtsmaßnahmen: - der Anwender muss sich vor dem Einsatz vergewissern, dass sich das Material in ordnungsgemäßem Zustand befindet und korrekt funktioniert. Das Material darf unter keinen Umständen verwendet werden, wenn die Verpackung beschädigt ist oder Oberflächenschäden oder Verformungen sichtbar sind, - bei der Untersuchung des Patienten sind alle Faktoren zu ermitteln, die beim Einsetzen des Implantats zu gesundheitlichen Risiken führen oder den Heilungsprozess von Knochen/Weichteilgewebe beeinflussen könnten. Im Hinblick auf die chirurgische Indikation und die Implantatauswahl sind bestimmte Kriterien zu berücksichtigen: - die Okklusionsfläche des Implantats muss idealerweise kleiner sein als die Zahnprothese, damit das Weichteilgewebe und das Emergenzprofil der Prothese genügend Platz haben, - 1,5 mm Mindestabstand zwischen dem Implantat und der benachbarten Wurzel; 1,5 mm Mindestabstand zwischen zwei Implantaten und 1 mm Knochendicke an der bukkalen und lingualen Seite des Implantats (> bei größeren Durchmessern) sind einzuhalten, - falls eine Fremdkörperüberempfindlichkeit vermutet wird oder nachweislich besteht, empfiehlt es sich, vor Implantation des Materials einen Verträglichkeitstest auf Titan und TA6V ELI durchzuführen. Zur Gewährleistung umfassender Sicherheit sind Röntgen- und/oder CT-Untersuchungen sowie ein klinischer Behandlungsplan unerlässlich. Perioperative Vorsichtsmaßnahmen: - die Primärstabilität des Implantats ist Grundvoraussetzung, - die Auswahl des Implantattyps und der Implantatgröße obliegt dem Kieferchirurgen und ist vom Einzelfall und von der Pathologie des betreffenden Patienten abhängig. Größe und Art der Knochenstruktur sind für die Entscheidung des Kieferchirurgen ausschlaggebend. Der Kieferchirurg hat außerdem auch die Belastungen zu berücksichtigen, denen das Implantat nach dem Einsetzen ausgesetzt ist. - Implantate dürfen nicht verbogen werden. Um eine zu hohe Beanspruchung des Implantats zu vermeiden, muss die Belastung allmählich erfolgen. Eine zu starke Krafteinwirkung auf das Implantat kann Spannungen erzeugen, die zum Bruch oder zur Verformung führen und Nebenwirkungen hervorrufen. - Vor jedem Einsatz muss der Arzt seine Geräteeinstellungen im Hinblick auf den vorliegenden klinischen Einzelfall kontrollieren und überprüfen, ob seine Geräte ordnungsgemäß funktionieren. Es wird empfohlen, die Bohrsequenzen mit langsamer Geschwindigkeit sowie reichlicher und konstanter externer Kühlung vorzunehmen. Die empfohlenen Rotationsgeschwindigkeiten sind 700 bis 1200 (nicht über 1500) U/min beim Pilotbohrer und 200 bis 400 U/min beim Erweiterungsbohrer. - Die Bohrer sind äußerst scharf, daher empfiehlt es sich, diese mit Vorsicht zu handhaben, um Schnittverletzungen zu vermeiden. Die spiralförmigen Rillen der Bohrer können bewirken, dass der Bohrer von der Bohrrichtung abweicht, wodurch die Bohrgenauigkeit beeinträchtigt werden könnte. Um dies zu vermeiden empfiehlt es sich, für diesen Zweck spezielle Stopper zu verwenden. - Schneidwerkzeuge (Countersinks, Pilotbohrer, Gewindeschneider und Erweiterungsbohrer) dürfen nicht mehr als 20 Mal eingesetzt werden, um Abnutzungsprobleme zu verhindern. Für diese Bohrer gibt es ein spezielles Erfassungsblatt. Postoperative Vorsichtsmaßnahmen Nach dem Einsetzen des Implantat dauert die Osseointegration 4 Monate (Unterkiefer) 6 Monate (Oberkiefer). Der Kieferchirurg ist für die postoperative Nachsorge verantwortlich. Er muss den Patienten darüber informieren: - was dieser nach Einsetzen eines Implantats zu vermeiden und welche Vorsichtsmaßnahmen er im Alltag zu beachten hat. Der Patient muss darüber aufgeklärt werden, dass Metallwerkstoffe vor der vollständigen Verbindung mit dem Knochen nicht so widerstandsfähig wie gesunde Knochenstrukturen sind und brechen, wenn sie zu stark oder anormal belastet werden, - dass der Erfolg des Implantats vom Verhalten und der Mundhygiene des Patienten abhängig ist;- dass mit dem. Einsetzen eines Zahnimplantats potenzielle Risiken und Nebenwirkungen verbunden sind: - dass die Osseointegration fehlschlagen kann, - dass der Arzt über peri- und postoperative Beschwerden im Operationsbereich informiert werden muss, - dass Wechselwirkungen mit anderen Verfahren und therapeutischen oder diagnostischen Geräten auftreten können. 6. MÖGLICHE NEBENWIRKUNGEN Die Implantationstechniken unterliegen bestimmten Kontraindikationen und Risiken. Diese können sowohl mit dem Einsatz der Instrumente als auch mit dem chirurgischen Eingriff in Zusammenhang stehen, z.B. (Aufzählung erhebt keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit): - empfindlichkeit, Sprachprobleme, Ödeme und Hämatome, - lockern, Brechen oder Verlust eines Bestandteils, - vorübergehende oder dauerhafte lokale Nervenschädigungen, - infektion, Beschädigung von Nachbarzähnen und ästhetische Probleme, - allergische Reaktion auf die einzelnen Implantatwerkstoffe von BIOTECH DENTAL. 7. STERILITÄT UND RÜCKVERFOLGBARKEIT Steril gelieferte Produkte: Zahnimplantate sind mit einem Abdeckungsschraube und eine heilende Schraube in der Verpackung des Implantats sind steril (Gamma-Sterilisation). Alle steril gelieferten Produkte sind zum Einmalgebrauch bestimmt und dürfen nicht resterilisiert werden. Vor der Verwendung muss die gesamte Verpackung überprüft werden, um sicherzustellen, dass die Sterilität des Inhalts nicht beeinträchtigt ist. Bei sachgemäßer Lagerung bleibt die Packung bis zum Verfalldatum steril. Verwenden Sie das Produkt nicht, wenn die Verpackung beschädigt ist. Etiketten auf den einzelnen Verpackungen sowie freie Etiketten gewährleisten eine lückenlose Rückverfolgbarkeit anhand der Artikelnummer und Chargennummer des Implantats. Unsteril gelieferte Produkte: Hilfsmittel und prothetische Teile werden gereinigt, aber nicht steril geliefert. Es obliegt dem betreffenden Anwender, die Dekontamination, Reinigung und Sterilisierung vor und nach jedem Einsatz (bei Mehrwegprodukten) gemäß den geltenden Empfehlungen vorzunehmen. 8. REINIGUNG UND STERILISATION VON UNSTERILEN GERÄTEN Vor jedem Sterilisationsprozess sind die Produkte zu dekontaminieren und zu reinigen. - Um eine Beschädigung der Komponenten zu verhindern sind nur solche Reinigungs- und Dekontaminationsmittel zu verwenden, die für die betreffenden Werkstoffe geeignet sind. Alkalische und korrosive Produkte für medizinische Geräte aus rostfreiem Stahl und Aluminium dürfen nicht verwendet werden. Entfärber, wässrige Lösungen von Natriumhypochlorit und Natriumchlorid führen zum Ausbleichen und/oder zur Korrosion der Instrumente. - Das zur Prädesinfektion, Reinigung, Dekontamination, Spülung und Sterilisation verwendete Wasser muss die geltenden Vorschriften erfüllen. - Der Anwender muss besonders sorgfältig darauf achten, dass Schmutz, Reste und Ablagerungen von allen Instrumententeilen (Hohl- und Zwischenräumen usw.) entfernt werden. Prädekontamination: - diese muss sofort nach jedem Einsatz wiederverwendbarer Instrumente, die zu diesem Zweck zu demontieren sind, erfolgen, - tauchen Sie die zuvor demontierten Instrumente in eine aldehydfreie Dekontaminationslösung mit neutralem pH-Wert. Die Konzentration der Lösung ist in Abhängigkeit vom Kontaminations- und Verschmutzungsgrad festzulegen. 15 bis 20 min im Desinfektionsbad belassen. Empfohlen wird ein Ultraschallbad, - die Dekontaminationslösung muss nach jeder Anwendung erneuert werden, um eine Sättigung zu verhindern. Reinigung: - diese kann durch Abbürsten oder Ultraschall erfolgen. Die Instrumente müssen zuvor demontiert werden, - abbürsten mit einer weichen Bürste (z.B. Nylon), - mindestens 15 min im Tauchbad belassen. Wenn Produkte längere Zeit, z.B. mehrere Stunden, im Tauchbad bleiben, kann dies zur Korrosion des Materials führen (2 Stunden nicht überschreiten). Spülen – Trocknen: Unmittelbar nach der Reinigung muss gründlich gespült werden. Danach müssen die Produkte getrocknet werden, ehe mit der Sterilisation begonnen werden kann. Verpackung vor Sterilisation: Um eine erneute Kontamination zu verhindern, muss das Material, unabhängig vom angewandten Reinigungsverfahren, sofort verpackt werden. Falls bei der Sterilisation Gittertrays aus Metall zum Einsatz kommen, ist doppellagiges Papier zum Verpacken zu verwenden. Falls das Verpacken zu spät erfolgt (> 2 Stunden), sollte das Produkte erneut gereinigt werden, damit der sterile Zustand gesichert ist. Sterilisation: Die Instrumente sind so vorzubereiten, dass alle Flächen mit dem Dampf in direkten Kontakt kommen. Empfohlen wird das Prion-Programm, 18 min bei 134 °C. Rückgabe: Zubehörinstrumenten sind nach Gebrauch gemäß geltenden Vorschriften zu reinigen und zu dekontaminieren und an BIOTECH DENTAL zurückzugeben. Die Gesundheitseinrichtung bzw. der Arzt haben dafür zu sorgen, dass wirksame Reinigungs-/ Sterilisationsverfahren (Ausrüstung, Materialien, Personal) angewandt werden und zum gewünschten Ergebnis führen. Der Hersteller haftet in keinem Fall für die Sterilität. 9. HANDHABUNG UND AUFBEWAHRUNG Die Produkte sind sorgfältig zu behandeln und aufzubewahren, damit diese vor ihrem chirurgischen Einsatz nicht kontaminiert oder beschädigt werden. Sie müssen in einer geeigneten, trockenen und sauberen Umgebung sachgemäß gelagert werden. Sie dürfen nicht direktem Sonnenlicht, ionisierender Strahlung oder extremen Temperaturen ausgesetzt werden, nicht kontaminiert werden und nicht in Kontakt oder in die Nähe von Produkten gelangen, die Korrosion verursachen könnten. Die Lebensdauer der Instrumente kann sich durch unsachgemäße Handhabung oder ungenügende Schutzmaßnahmen verkürzen. 10. ENTSORGUNG Die Entsorgung medizinischer Abfälle muss unter Einhaltung der einschlägigen Gesetze erfolgen. Die Gesundheitseinrichtungen sind als Erzeuger dieser Abfälle für die Trennung von infektiösem und im Hausmüll zu entsorgendem Abfall verantwortlich. PT INSTRUÇÕES DE UTILIZAÇÃO BIOTECH DENTAL SISTEMAS DE IMPLANTES DENTÁRIOS KONTACT®, B.I.S.®, B.I.S. Conic® e Weego.fr. Este produto deve ser manuseado por pessoal FORMADO e QUALIFICADO que TENHA LIDO estas instruções. 1. DESCRIÇÃO GERAL Os sistemas de implantes dentários da BIOTECH DENTAL são compostos por: - implantes dentários de titânio/liga de titânio que estão em conformidade com as normas ISO 5832-2/ISO 5832-3 aplicáveis, - abutments de titânio, liga de titânio e cerâmica em conformidade com as normas aplicáveis, - componentes protéticos adicionais em titânio, liga de titânio ou metal e polímero em conformidade com as normas aplicáveis, - instrumentação auxiliar de qualidade médica, titânio/liga de titânio, em aço inoxidável. Para efeitos de identificação, a maioria dos instrumentos possui uma referência visível e o número do lote de fabrico. Os produtos esterilizados são identificados na embalagem. Se não estiver escrita a palavra «esterilizado», significa que os produtos fornecidos não são esterilizados devendo, portanto, sê-lo pelo pessoal competente antes da respetiva utilização. Os sistemas de implantes dentários são opacos ao raio-X. 2. CONDIÇÕES GERAIS DE UTILIZAÇÃO Os sistemas de implantes dentários apenas devem ser utilizados por cirurgiões experientes: - com formação em implantologia e nas técnicas de utilização dos dispositivos médicos da BIOTECH DENTAL, - no cumprimento das indicações, contraindicações e precauções, as quais devem ser comunicadas ao doente durante a fase do pós-operatório e que estão mencionadas nestas instruções, bem como nos protocolos cirúrgicos e protéticos disponível a pedido, - em instalações compatíveis com as condições asséticas exigidas por estas instruções. Os sistemas de implantes dentários nunca devem ser utilizados com os dispositivos de outro fabricante. Durante o período desde a implante até ao controlo, a BIOTECH DENTAL compromete-se a substituir qualquer implante ou componente protético, desde que as condições supramencionadas tenham sido cumpridas. O médico-dentista será responsável pelas complicações resultantes de utilização que não tenha respeitado as recomendações ou as práticas de assepsia. Estas complicações não devem, em qualquer circunstância, ser atribuídas à BIOTECH DENTAL e levarão à rejeição de qualquer ação movida contra a BIOTECH DENTAL referente à garantia ou à substituição do produto. 3. INDICAÇÕES Os implantes dentários da BIOTECH DENTAL são utilizados como base tanto para a fixação das substituições à mandíbula como ao maxilar. Os restabelecimentos vão desde a substituição unitária até à substituição completa a fim de reproduzir todas ou algumas funções dos dentes naturais. Esta técnica apenas é tida em conta, se outras terapias menos invasivas forem consideradas menos adequadas. A qualidade e o volume ósseos devem ser suficientes para suportarem os implantes dentários. 4. CONTRAINDICAÇÕES Os implantes dentários não devem ser utilizados em doentes que apresentem contraindicações locais e/ou gerais à intervenção dentária cirúrgica. Estas contraindicações devem ser cuidadosamente avaliadas assim que o cirurgião tomar a sua decisão. Entre outras coisas, as contraindicações constituem: - fatores que interferem com o processo de cicatrização e de regeneração óssea e tecidular, tais como problemas com o metabolismo ósseo, tecido conjuntivo, diabetes de tipo 2, terapia com esteroides, infeções ósseas e abuso de nicotina e de álcool, - doenças ou terapias imunossupressoras, como a quimioterapia e a radioterapia, - volume ósseo e qualidade óssea insuficientes para poderem aceitar número e tamanhos suficientes de implantes e suportarem as cargas funcionais, - bruxismo, hábitos parafuncionais, problemas com a oclusão e/ou com as articulações temporomandibulares, - infeções bocais e inflamação, como a periodontite e a gengivite, - alergia ao titânio ou à liga de titânio ou higiene dentária e bocal inadequada. 5. PRECAUÇÕES DE UTILIZAÇÃO - Para evitar a deglutição ou inalação de componentes pequenos, recomenda-se que os mesmos estejam bem fixos, sempre que possível. - A BIOTECH DENTAL deve ser informada de qualquer incidente ou problema relativo a um implante ou instrumento. Precauções pré-operatórias: - o utilizador deve certificar-se de que o material está em perfeitas condições e que funciona corretamente antes da sua utilização. O material nunca deverá ser utilizado, se a embalagem estiver danificada ou se forem visíveis danos ou deformações na superfície. NOTICE D’INSTRUCTIONS SYSTEMES D’IMPLANTS DENTAIRES Fabricant Manufacturer Hersteller Fabricante Fabricante Gyártó Produttore Mm Date de fabrication Date manufactured Herstellungsdatum Data de fabrico Fecha de fabricación Gyártás dátuma Data di produzione Date limite d’utilisation Expiry date Verfalldatum Prazo de validade Fecha de caducidad Felhasználható Data di scadenza h Référence du catalogue commercial Catalogue reference Katalognummer Referência de catálogo Referencia del catálogo Cikkszám Riferimento catalogo g Code du lot Batch code Chargencode Código do lote Código de lote Gy.sz. Numero di lotto Ne pas réutiliser Do not reuse Nicht wiederverwenden Não reutilizar No reutilizar Nem szabad újra Non riutilizzare D i Consulter les précautions d’emploi Read the instructions for use Bitte Gebrauchsanweisung Ler as instruções de utilização Lea las instrucciones de uso Olvassa el a használati utasítást Leggere le istruzioni d’uso Stérilisé par irradiation Sterilised by radiation Sterilisation durch Bestrahlung Esterilizado por irradiação Esterilizado mediante irradiación Besugárzással sterilizált Sterilizzato mediante irradiazione k IK Conserver à l’abri de la lumière du soleil Store away from sunlight Lichtgeschützt aufbewahren Guardar longe da luz solar Guardar apartado de la luz del sol Napfénytől távol tartandó Conservare lontano dalla luce solare w L B p Ne pas utiliser si l’emballage est endommagé Do not use if the packaging is damaged Nicht verwenden, wenn die Verpackung beschädigt ist Não utilizar se a embalagem estiver danificada No usar si el embalaje está dañado Ne használja, ha a csomagolás sérült Non utilizzare se la confezione è danneggiata Ne pas restériliser Do not resterilise Nicht resterilisieren Não voltar a esterilizar No volver a esterilizar Nem sterilizálható újra Non risterilizzare Craint l’humidité Protect from humidity Vor Feuchtigkeit schützen Proteger da humidade Proteger de la humedad Nedvességtől óvni kell Proteggere dall’umidità Non stérile Non sterile Unsteril No estéril Não esterilizado Nem steril Non sterile Pour toute information, contacter le fabricant For additional information please contact the manufacturer Für weitere informationen wenden Sie sich bitte an den Hersteller Para solicitar informacion complementaria, contactar el fabricante Para qualquer informaçäo complementar, contatar ofabricante Per ulteriori informazioni, contattare il produttore responsabile További információért forduljon a gyártóhoz 305, Allées de Craponne - 13300 Salon de Provence - FRANCE Tél. : +33 (0)4 90 44 60 60 - Fax : +33 (0)4 90 44 60 61 [email protected] - www.biotech-dental.com BY_IMPLANTS3_0915_01 FR - é necessário proceder à avaliação do doente a fim de determinar qualquer fator que o possa expor a um risco resultante da inserção do implante ou que possa exercer influência sobre a cicatrização do osso/tecido mole. Devem ser tidos em consideração determinados critérios relativamente à indicação de cirurgia e à escolha do implante: - idealmente, a superfície oclusal do implante deve ser mais pequena do que a prótese dentária para garantir a difusão do tecido mole e do perfil de emergência da prótese. Precauções perioperatórias: - a estabilidade primária do implante é essencial, - a seleção do tipo de implante e do respetivo tamanho será da exclusiva competência do cirurgião. Tal dependerá do doente em questão e da sua patologia. O tamanho e a natureza das estruturas ósseas irão determinar a seleção do cirurgião. O cirurgião também terá de considerar as pressões sobre o implante após o procedimento, - os implantes não devem apresentar deformações. Sob o risco de provocar fadiga anormal do implante, as manipulações terão de ser progressivas. O excesso de esforço exercido sobre o implante poderá induzir pressões, as quais podem provocar uma fratura ou deformações do implante responsáveis por efeitos secundários, - cabe ao médico-dentista determinar as definições do equipamento, dependendo do caso clínico em questão, e verificar se o equipamento funciona corretamente antes de cada procedimento. Recomenda-se que as sequências de perfuração com broca sejam realizadas a baixa velocidade e com irrigação externa abundante e constante. A velocidade de rotação recomendada é de 700 a 1200 rpm durante a perfuração com broca, não excedendo as 1500 rpm, e de 200 a 400 rpm para a perfuração, - as brocas são bastante afiadas. Recomenda-se o máximo cuidado ao agarar nas brocas por forma a evitar cortes. De igual forma, dado que as brocas são concebidas com canais helicoidais, a sua utilização pode resultar num fenómeno de arraste que é prejudicial à precisão da perfuração com broca. Para corrigir esta possibilidade, recomenda-se a utilização dos batentes de perfuração fornecidos para este efeito, - as ferramentas de corte (escareadores, brocas, roscas e perfuradoras) não devem ser utilizadas mais de 20 vezes, de modo a evitar problemas de desgaste. Está disponível uma folha de registo específica para as brocas. Precauções pós-operatórias: Após a inserção do implante, a osteointegração completa-se no prazo de 4 meses (mandíbula) 6 meses (maxilar). O cirurgião deve efetuar o acompanhamento pós-operatório. Será responsável por comunicar ao doente o seguinte: - as ações a evitar após a inserção de um implante e as precauções a tomar no decurso da atividade diária normal. O doente deve compreender que, antes da consolidação óssea completa, um material metálico não é tão forte como as estruturas ósseas saudáveis e que os materiais metálicos irão partir-se caso sejam sujeitos a pressões intensas ou anormais, - a eficácia do implante depende do seu comportamento e da sua higiene bocal, - os riscos potenciais e efeitos adversos associados à inserção de um implante dentário, - a possibilidade de insucesso da osteointegração do implante, - a necessidade de comunicar qualquer sensibilidade que surja na região operada, na fase do perioperatório ou do pós-operatório, - potencial interação com outros procedimentos e dispositivos terapêuticos ou de diagnóstico. 6. EFEITOS ADVERSOS POSSÍVEIS As técnicas de implante são acompanhadas por contraindicações e riscos de utilização. Podem igualmente estar relacionadas com a utilização do dispositivo, bem como com a intervenção cirúrgica, podendo incluir (enumeração não exaustiva): - sensibilidade, problemas da fala, edema e hematomas, - relaxamento, rutura ou perda de um componente, - lesão nervosa local, transitória ou permanente, - infeção, lesão de dentes adjacentes e problemas estéticos, - uma reação alérgica aos diferentes materiais que compõem os implantes da BIOTECH DENTAL. 7. ESTERILIZAÇÃO E RASTREABILIDADE Dispositivo entregue esterilizado: Os implantes dentários vêm com um parafuso da tampa e um parafuso de cicatrização na embalagem do implante, são estéreis (esterilização por radiação gama). Todos os produtos fornecidos esterilizados destinam-se a utilização única e não devem ser novamente esterilizados. É necessário verificar a embalagem na sua totalidade, antes da utilização, por forma a garantir que a esterilização do conteúdo não sofreu alteração. Em condições de armazenagem adequadas, a embalagem mantém a esterilização até à data de validade. Não utilizar em caso de danos na embalagem. Os rótulos nos diferentes níveis de embalagem, bem como os rótulos livres permitirão garantir uma rastreabilidade perfeita com base no número de referência e no número de lote do implante. Dispositivos de uso único estéril deve em nenhum caso ser reutilizados e re-esterilizado. No caso de re-esterilização de um dispositivo que não seja re-esterilização médica, a ausência de transmissão de agentes patogénicos iatrogénica por estes dispositivos não é garantida e acidente no campo de materiovigilance pode ocorrer. Dispositivo entregue não esterilizado: A instrumentação acessória e os elementos protéticos são fornecidos limpos, mas não esterilizados. A equipa envolvida será responsável pelo processo de descontaminação, limpeza e esterilização antes e após cada procedimento (para os produtos reutilizáveis) de acordo com as recomendações aplicáveis. 8. LIMPEZA E ESTERILIZAÇÃO DE DISPOSITIVOS NÃO ESTERILIZADOS As operações de descontaminação e de limpeza são obrigatórias antes de cada processo de esterilização. - Para evitar a deterioração dos componentes, utilizar apenas produtos de limpeza e de descontaminação que sejam compatíveis com os materiais. É proibida a utilização de produtos alcalinos e corrosivos em dispositivos médicos de aço inoxidável e alumínio: a lixívia e as soluções aquosas de hipoclorito de sódio e cloreto de sódio descoloram e/ou corroem os instrumentos. - A água a ser utilizada para a desinfeção prévia, limpeza, descontaminação, lavagem e esterilização deve estar em conformidade com os regulamentos aplicáveis. - O utilizador deve prestar especial atenção à limpeza de sujidade, resíduos e depósitos em todos as peças dos instrumentos (cavidades, interstícios, etc.). Descontaminação prévia: - deve ser realizada imediatamente após cada procedimento relativamente a todos os instrumentos reutilizáveis desmontados, - mergulhar totalmente os instrumentos previamente desmontados numa solução de descontaminação com um pH neutro e sem aldeído, cuja concentração depende da taxa de contaminação e do grau de sujidade dos instrumentos. Deixá-los imersos na solução durante 15 a 20 minutos. Recomenda-se uma imersão em banho de ultrassons, - a solução de descontaminação deve ser sempre renovada após a respetiva utilização por forma a evitar a saturação. Limpeza: - pode ser realizada através da escovagem e por ultrassons e deve ser realizada em componentes desmontados, - a escovagem deve ser efetuada com uma escova macia (por exemplo, nylon), - a imersão deve prolongar-se por um período mínimo de 15 minutos. O contacto prolongado com determinados produtos durante várias horas pode provocar a corrosão do material (não exceder 2 horas). Enxaguamento – Secagem: A limpeza deve ser imediatamente seguida de um enxaguamento abundante e, depois, os produtos devem ser secos antes de se iniciar o processo de esterilização. Acondicionamento antes da esterilização: Independentemente do método de limpeza utilizado, o material deve ser embalado de imediato a fim de evitar novas contaminações. Caso a esterilização seja realizada em tabuleiros de rede metálica, é necessário utilizar papel de embalagem duplo para o acondicionamento. Caso o acondicionamento seja tardio (> 2 horas), há que considerar uma limpeza adicional por forma a garantir a esterilização do material. Esterilização: Preparar os instrumentos para que todas as superfícies estejam em contacto direto com o vapor. O ciclo recomendado é o ciclo Prião a 134° C durante 18 minutos. Devolução: Em caso de empréstimo de um acessório, este deve ser posteriormente devolvido à BIOTECH DENTAL após ter sido limpo e descontaminado de acordo com os regulamentos aplicáveis. Compete ao estabelecimento de cuidados de saúde ou ao médico-dentista garantir que o processo de limpeza/esterilização eficazmente implementado (equipamento, materiais e operador) alcança o resultado desejado. Sob nenhuma circunstância deverá o fabricante ser responsabilizado pela esterilidade. 9. MANUSEAMENTO E ARMAZENAGEM Os produtos devem ser cuidadosamente manuseados e armazenados para garantir a ausência de contaminação e deterioração antes de qualquer intervenção cirúrgica. A armazenagem deve ser feita com cuidado num ambiente adequado, seco e limpo. Não devem ser expostos à luz solar direta, radiação ionizante, temperaturas extremas, contaminação específica ou entrar em contacto com ou estar na proximidade de produtos que possam ter um efeito corrosivo. O ciclo de vida dos dispositivos pode ser comprometido por falta de precauções durante o manuseamento ou proteção insuficiente dos instrumentos. 10. ELIMINAÇÃO A eliminação dos resíduos médicos deve estar em conformidade com a legislação aplicável. O profissional que produz resíduos será responsável pela separação daqueles que comportem risco de infeção e dos que são compatíveis com o lixo doméstico. ES m M m m m NSTRUCC ONES DE USO B OTECH DENTAL S STEMAS DE MPLANTES DENTALES m Ó m W G m m m m m m m m m m m m m número de referencia y el lote de fabricación. Los productos estériles llevan una indicación en su embalaje. Si no aparece expresamente la palabra «estéril», quiere decir que los productos se suministran en condiciones no estériles y que es necesario esterilizarlos antes de proceder a su uso. Los sistemas de implantes dentales son radiopacos. 2. CONDICIONES GENERALES DE USO Los sistemas de implantes dentales solo pueden ser utilizados por cirujanos experimentados: - con formación en implantología y técnicas de utilización de productos sanitarios de BIOTECH DENTAL, - respetando las indicaciones, contraindicaciones y precauciones que se indicarán al paciente durante el postoperatorio y que aparecen en estas instrucciones, así como en los protocolos quirúrgicos y protésicos disponibles a petición, - en instalaciones compatibles con las condiciones asépticas que exigen estas instrucciones. Los sistemas de implantes dentales no podrán utilizarse en ningún caso con los productos de otro fabricante. Durante el periodo que transcurre entre la implantación y el tratamiento, BIOTECH DENTAL se compromete a sustituir cualquier implante o componente protésico siempre que se hayan respetado las condiciones anteriores. El médico asumirá la responsabilidad por las complicaciones que se deriven del hecho de no seguir las recomendaciones o de no mantener las condiciones de asepsia necesarias. Estas complicaciones no podrán atribuirse en ningún caso a BIOTECH DENTAL y se rechazará cualquier acción emprendida contra BIOTECH DENTAL en relación con la garantía o la sustitución del producto. 3. INDICACIONES Los implantes dentales de BIOTECH DENTAL se utilizan como base para el anclaje de sustituciones tanto en la mandíbula como en el maxilar. El tipo de restauración puede ser desde una sustitución unitaria hasta una sustitución completa con el fin de reproducir todas o algunas de las funciones de los dientes naturales. Esta técnica solo deberá considerarse en caso de que un tratamiento menos invasivo no resultara adecuado. El hueso deberá presentar un volumen y una calidad suficientes como para soportar los implantes dentales. 4. CONTRAINDICACIONES No deberán utilizarse implantes dentales en pacientes que presenten contraindicaciones locales y/o generales para una intervención quirúrgica dental. El cirujano deberá evaluar detenidamente las contraindicaciones antes de tomar una decisión. Por contraindicaciones se entiende, a título meramente enunciativo y no exhaustivo: - factores que interfieren en el proceso de cicatrización y de regeneración ósea y tisular, tales como problemas con el metabolismo óseo, tejido conjuntivo, diabetes de tipo 2, tratamientos con corticoides, infecciones óseas y consumo excesivo de nicotina y alcohol, - enfermedades o tratamientos inmunodepresores, tales como la quimioterapia y la radioterapia, - el volumen óseo y la calidad ósea no son suficientes para colocar la cantidad de implantes necesaria, del tamaño requerido, y para soportar las cargas funcionales, - bruxismo, hábitos parafuncionales, problemas de oclusión y/o en las articulaciones temporomandibulares, - inflamaciones e infecciones bucales, tales como periodontitis y gingivitis, - alergia al titanio o a la aleación de titanio o higiene bucodental insuficiente. 5. PRECAUCIONES DE USO - Para evitar tragar o inhalar componentes de reducidas dimensiones, se recomienda sujetarlos en la medida de lo posible, - Deberá comunicarse a BIOTECH DENTAL cualquier incidente o problema relacionado con un implante o un instrumento. Precauciones preoperatorias: - antes de utilizarlo, el usuario deberá asegurarse de que el material está en buen estado y que funciona correctamente. El material no podrá utilizarse bajo ninguna circunstancia si el embalaje que lo contiene está dañado o presenta daños o deformaciones en su superficie, - se requiere una evaluación del paciente para determinar la presencia de factores que pudieran exponerle a un riesgo derivado de la inserción del implante o que pudiera afectar a la cicatrización del hueso o del tejido blando. Deberán tenerse en cuenta unos criterios determinados acerca de la idoneidad de la cirugía y de la elección del implante: - en condiciones ideales, la superficie oclusora del implante será más pequeña que el diente protésico para conseguir una buena transición entre el tejido blando y el perfil de emergencia de la prótesis, - un espacio mínimo de 1,5 mm entre el implante y la raíz adyacente, 1,5 mm entre dos implantes y un grosor óseo de 1 mm alrededor de las superficies vestibulares y linguales del implante (> en el caso de diámetros grandes), - si se sospecha que existe hipersensibilidad o si efectivamente existe hipersensibilidad a cuerpos extraños, se recomienda comprobar la tolerancia al titanio y al titanio TA6V ELI antes de implantar el material, Para garantizar una seguridad total, es fundamental realizar radiografías y/o TC y elaborar un plan de tratamiento clínico. Precauciones perioperatorias: - la estabilidad primaria del implante es esencial, - el cirujano deberá elegir el tipo y el tamaño del implante, que dependerán de cada paciente concreto y de su anatomía patológica. El tamaño y la naturaleza de las estructuras óseas condicionarán la elección del cirujano. El cirujano también deberá considerar las tensiones que soportará el implante tras la intervención, - los implantes no deben ser deformados. Debido al riesgo de causar una fatiga anormal del implante, las manipulaciones deberán ser progresivas. Ejercer un esfuerzo excesivo sobre el implante podría generar tensiones que causarían una fractura o deformación del implante que daría lugar a efectos secundarios, - el médico deberá ajustar su equipo según cada caso clínico concreto y comprobar que funciona correctamente antes de cada intervención. Se recomienda realizar las secuencias de perforación a baja velocidad y con irrigación externa profusa y constante. La velocidad de giro recomendada oscila entre 700 y 1.200 rpm para el perforado, en ningún caso superior a 1.500 rpm, y entre 200 y 400 rpm para el mandrilado, - las fresas están muy afiladas; extreme las precauciones cuando las manipule para no cortarse. Asimismo, dado que las fresas tienen estrías helicoidales, su utilización puede generar una resistencia al avance que resta precisión al perforado. Para evitarlo, se recomienda utilizar los topes de fresado que se incluyen a tal efecto, - las herramientas de corte (avellanadores, fresas, machos de roscar y mandriladoras) no deberán utilizarse más de 20 veces para evitar problemas ocasionados por el desgaste. Existe una hoja de control específica para las fresas. Precauciones postoperatorias: Tras la inserción del implante, la osteointegración se logra entre los 4 meses (mandíbula) 6 meses (maxilar). El cirujano deberá realizar un seguimiento postoperatorio. Él se encargará de informar al paciente respecto a: - acciones que deben evitarse tras la inserción de un implante y precauciones que deben tenerse durante la actividad diaria habitual. El paciente debe entender que, mientras no se logre una consolidación ósea total, el material metálico no tendrá la resistencia de una estructura ósea sana, y por tanto podría romperse si es sometido a tensiones fuertes o anormales, - la eficacia del implante depende del comportamiento del paciente y de su higiene bucal, - posibles riesgos y efectos adversos asociados a la inserción de un implante dental, - la posibilidad de que no se produzca la osteointegración del implante, - la necesidad de comunicar cualquier sensibilidad que aparezca en la zona operada, en el perioperatorio y en el postoperatorio, - posible interacción con otras intervenciones y dispositivos diagnósticos o terapéuticos. 6. POSIBLES EFECTOS ADVERSOS Las técnicas de implantación van acompañadas de contraindicaciones y riesgos de uso, los cuales pueden estar relacionados también con el uso del dispositivo y con la intervención quirúrgica, y pueden incluir, a título meramente enunciativo, pero no exhaustivo: - sensibilidad, problemas al hablar, edema y hematomas, - aflojamiento, rotura o pérdida de un componente, - lesiones nerviosas locales, temporales o permanentes, - infecciones, lesiones en dientes adyacentes y problemas estéticos, - reacciones alérgicas a los distintos materiales de los implantes de BIOTECH DENTAL. 7. ESTERILIDAD Y TRAZABILIDAD Dispositivos suministrados en condiciones estériles: Los implantes dentales vienen con un tornillo de la cubierta y un tornillo de cicatrización en el envase del implante, son estériles (esterilización con rayos gamma). Cualquier producto que se suministre estéril es de un solo uso y no se puede esterilizar de nuevo. El embalaje debe ser inspeccionado antes de utilizar su contenido para verificar que la esterilidad no ha sido alterada. Si se mantienen unas condiciones de almacenamiento correctas, el embalaje preservará la esterilidad hasta la fecha de caducidad. No utilice el dispositivo si el embalaje está dañado. Las etiquetas de los distintos niveles del embalaje, así como las etiquetas sueltas, permiten garantizar una trazabilidad perfecta a través del número de referencia y del número de lote del implante. Dispositivos de un solo uso estériles bajo ninguna circunstancia deberías ser reutilizados y reesterilizados. En caso de re-esterilización de un dispositivo médico no re-esterilizables, la falta de transmisión iatrogénica de patógenos por medio de dispositivos de tesis ya no está garantizada y accidente en el campo de materiovigilance pueden ocurrir. Las etiquetas de los distintos niveles del embalaje, así como las etiquetas sueltas, permiten garantizar una trazabilidad perfecta a través del número de referencia y del número de lote del implante. Dispositivos suministrados en condiciones no estériles: La instrumentación auxiliar y las piezas protésicas se suministran limpias, pero no estériles. El personal pertinente será el encargado de realizar la descontaminación, limpieza y esterilización antes y después de cada intervención (en el caso de los productos reutilizables) de acuerdo con las recomendaciones aplicables. 8. LIMPIEZA Y ESTERILIZACIÓN DE DISPOSITIVOS NO ESTÉRILES Las operaciones de descontaminación y limpieza son obligatorias antes de cada proceso de esterilización. - Para evitar el deterioro de los componentes, utilice solo productos de limpieza y descontaminación que sean compatibles con los materiales. Se prohíbe el uso de productos alcalinos y corrosivos en productos sanitarios de acero inoxidable y aluminio, ya que la lejía y las soluciones acuosas de hipoclorito sódico y cloruro sódico decoloran y/o corroen los instrumentos. - El agua que se utilizará para la predesinfección, limpieza, descontaminación, aclarado y esterilización deberá cumplir con la normativa aplicable. - El usuario deberá prestar especial atención a la limpieza de la suciedad, los residuos y los depósitos de todas las partes de los instrumentos (cavidades, intersticios, etc.). Predescontaminación: - deberá realizarse inmediatamente después de cada intervención en el caso de todos los instrumentos reutilizables desmontados, - sumerja por completo los instrumentos, previamente desmontados, en una solución descontaminante con un pH neutro, sin aldehído, en una concentración adecuada a la tasa de contaminación y el grado de suciedad que presenten los instrumentos. Déjelos en remojo durante 15 o 20 minutos. Se recomienda emplear la inmersión en baño de ultrasonidos, - la solución descontaminante deberá renovarse siempre tras su uso para evitar que se sature. Limpieza: - puede realizarse mediante cepillado y por ultrasonidos, y se llevará a cabo con los componentes desmontados, - para el cepillado, utilice un cepillo suave (de nailon, por ejemplo), - deje los componentes en remojo durante al menos 15 minutos. Un contacto prolongado con determinados productos podría corroer el material (no exceda las dos horas). Aclarado y secado: Inmediatamente después de limpiar los componentes, hay que aclararlos bien y secarlos para proceder a la esterilización. Embalaje previo a la esterilización: Independientemente del método de limpieza utilizado, el material deberá embalarse de inmediato para evitar que vuelva a contaminarse. Si se han utilizado bandejas de rejilla metálica durante la esterilización, el embalaje deberá llevar doble envoltorio. Si el material no va a embalarse de inmediato (> 2 horas), deberá considerarse la posibilidad de realizar una nueva limpieza para garantizar la esterilidad del material. Esterilización: Coloque los instrumentos de tal forma que todas sus superficies estén en contacto directo con el vapor. El ciclo recomendado es el ciclo Prión a 134 °C durante 18 minutos. Devolución: Tras utilizar la instrumentación auxiliar en caso de préstamo, esta deberá ser retornada a BIOTECH DENTAL tras su limpieza y descontaminación de acuerdo con la normativa aplicable. Es responsabilidad del centro sanitario o del médico garantizar que el proceso de limpieza/ esterilización correctamente implementado (equipo, materiales y operario) ha obtenido los resultados deseados. El fabricante no asumirá responsabilidad alguna relacionada con la esterilidad. 9. MANIPULACIÓN Y ALMACENAMIENTO Los productos deberán manipularse y almacenarse con cuidado para evitar que se contaminen o deterioren antes de la intervención quirúrgica. Los instrumentos deberán almacenarse con cuidado en un entorno adecuado, seco y limpio. No deberán exponerse directamente a la luz del sol, a radiaciones ionizantes, a temperaturas extremas, a contaminación específica ni deberán estar en contacto o cerca de productos que pudieran tener un efecto corrosivo. La vida útil de los dispositivos puede acortarse si no se observan las precauciones necesarias durante su manipulación o si no se los protege adecuadamente. 10. ELIMINACIÓN La eliminación de residuos médicos deberá realizarse de conformidad con la legislación aplicable. El profesional que genere los residuos se encargará de clasificar, por una parte, los residuos que comporten un riesgo de infección y, por otra, los que sean compatibles con los residuos domésticos. HU A BIOTECH DENTAL FOGÁSZATI IMPLANTÁCIÓS RENDSZEREK HASZNÁLATI UTASÍTÁSA KONTACT®, B.I.S. ®, B.I.S. Conic® és Weego.fr. Szerint ezt a terméket csak KÉPZETT, MINŐSÍTETT személyek kezelhetik, akik ELOLVASTÁK ezeket az utasításokat. 1. ÁLTALÁNOS LEÍRÁS A BIOTECH DENTAL fogászati implantátum rendszerek a következőkből állnak: - titánból/titánötvözetből készült fogászati implantátumok, amelyek megfelelnek az alkalmazandó ISO 5832-2/ISO 5832-3 szabványoknak, - titán, titánötvözet és kerámia hidak, amelyek megfelelnek az alkalmazandó szabványoknak, - további titánból, titánötvözetből vagy fémből és polimerből készült prosztetikus elemeket, amelyek megfelelnek az alkalmazandó szabványoknak, - titánból/titánötvözetből, orvosi minőségű rozsdamentes acél kiegészítő műszerezést. Azonosítás céljából a műszerek többségén cikkszám és gyártási szám látható. A steril termékek sterilitása a csomagoláson azonosítható. Ha a «steril» szó nem szerepel kifejezett módon, akkor a termékeket nem sterilen szállítják, és az érintett személyzetnek sterilizálni kell azokat a használat előtt. A fogászati implantátum rendszerek röntgensugárzás számára átlátszatlanok. 2. ÁLTALÁNOS FELHASZNÁLÁSI FELTÉTELEK A fogászati implantátum rendszereket csak olyan tapasztalt sebészek használhatják, akik: - képzettek az implantológiában és a BIOTECH DENTAL orvosi eszközök használatában, - betartják a betegeknek a műtét utáni szakaszban, továbbá a jelen utasításokban és a sebészeti és prosztetikus protokollokban felsorolt javallatokat, ellenjavallatokat és óvintézkedéseket;- az ezen utasítások által megkívánt aszeptikus feltételekkel kompatibilis helyszíneken tartózkodnak kérésre elérhető. A fogászati implantátum rendszerek semmilyen körülmények között sem használhatók fel egy másik gyártó eszközeivel együtt. A beültetés és a terhelés közötti időszakban a BIOTECH DENTAL vállalja, hogy minden implantátumot vagy prosztetikus komponenst kicserél, feltéve, hogy a fenti feltételeket betartották. Az ajánlásoknak vagy a sterilitásnak nem megfelelő felhasználásból eredő szövődményekért az orvos viseli a felelősséget. Ezek a szövődmények semmilyen körülmények között sem ruházhatók a BIOTECH DENTAL vállalatra, és a BIOTECH DENTAL felé megfogalmazott bármilyen garanciavállalási vagy termékcsere iránti igény elutasításához vezetnek. 3. JAVALLATOK A BIOTECH DENTAL fogászati implantátumokat a fogpótlások alsó állkapocshoz és a felső állkapocshoz való lerögzítésének alapjaként használják. A helyreállítások az egyedi pótlástól a teljes pótlásig terjednek a természetes fogak összes vagy egyes funkcióinak reprodukálására. Ez a módszer csak akkor vehető számításba, ha egyéb kevésbé invazív terápiák kevésbé tekinthetők alkalmasnak. A csonttérfogatnak és a csont minőségének elegendőnek kell lennie a fogászati implantátumok megtámasztására. 4. ELLENJAVALLATOK Fogászati implantátumok nem használhatók fel olyan betegeknél, akiknél a szájsebészeti beavatkozás helyileg és/vagy általánosan ellenjavallt. Amikor a sebész meghozza döntését, ezeket az ellenjavallatokat gondosan értékelnie kell. Az ellenjavallatok többek között a következők: - a gyógyulási folyamatot, valamint a csontok és a szövetek regenerálódásának folyamatát akadályozó tényezők, mint csontanyagcserével, kötőszövettel, 2-es típusú cukorbetegséggel, szteroid kezeléssel, csontfertőzésekkel, valamint a túlzott nikotinbevitellel és alkoholfogyasztással összefüggő problémák, - egyes immunszupresszív betegségek vagy terápiák, mint például a kemoterápia és a sugárkezelés, - elegendő számú és méretű implantátum befogadásához és a funkcionális terhelés elviseléséhez elégtelen csonttérfogat és csontminőség, - fogcsikorgatás, parafunkcionális szokások, okklúziós és/vagy temporomandibuláris ízületi zavarok, - bukkális fertőzések és gyulladások, mint például paradontitis és gingivitisz, - titán- vagy titánötvözet-allergia, illetve elégtelen szájüregi higiénia. 5. A HASZNÁLATTAL KAPCSOLATOS ÓVINTÉZKEDÉSEK - A kisméretű komponensek lenyelésének vagy belégzésének elkerülése érdekében javasolt ezek lehetőség szerinti lerögzítése, - A BIOTECH DENTAL vállalatot tájékoztatni kell az implantátumot vagy műszert érintő minden incidensről vagy problémáról. Preoperatív óvintézkedések: - a felhasználónak meg kell győződnie az anyagok és eszközök megfelelő állapotáról és működéséről. Semmilyen körülmények között nem szabad felhasználni sérült csomagolású anyagot, illetve ha az anyagon felületi károsodások vagy elváltozások láthatók, - a beteg értékelése szükséges minden olyan tényező megállapításához, amelyek a beteget az implantátum behelyezéséből eredő vagy a csont/lágyszövet gyógyulására kihatással bíró kockázatnak tehetik ki. A műtét indikációjával és az implantátum megválasztásával kapcsolatban figyelembe kell venni a következő kritériumokat: - az implantátum rágófelszínének ideális esetben a prosztetikus fognál kisebbnek kell lennie, hogy biztosítsa a lágyszövet kiterjedését és a protézis kiemelkedési profilját, - az implantátum és a szomszédos gyökér között 1,5 mm-es, 2 implantátum között 1,5 mm-es minimális távolság, továbbá az implantátum vesztibuláris és lingvális felszínei körül a csontvastagság legalább 1 mm-es (> nagy átmérők esetén), - Abban az esetben, ha idegen testekre való túlérzékenység gyanúja vagy bizonyított túlérzékenység áll fenn, akkor ajánlott a titánnal és a TA6V ELI titánötvözettel szembeni tolerancia ellenőrzése az anyag beültetése előtt. A radiológiai és/vagy CT-vizsgálati értékelés és a klinikai kezelési terv elengedhetetlen a teljes biztonság biztosítása érdekében. Perioperatív óvintézkedések: - az implantátum primer stabilitása alapvető fontosságú, - az implantátum típusának és méretének a megválasztása a sebész feladata; ez az adott betegtől és a beteg patológiai jellemzőitől függ. A csontstruktúrák mérete és jellemzője határozza meg a sebész választását. A sebésznek figyelembe kell vennie az implantátumnak az eljárás utáni terhelését is, - az implantátumoknak nem szabad deformálódniuk. Az implantátum rendellenes kifáradásának kockázata miatt a műveleteket fokozatosan kell végezni. Az implantátumra kifejtett túlzott erőhatás az implantátumban másodlagos hatásokat kiváltó törést vagy deformációt okozó feszültségeket okozhat, - az orvos feladata, hogy az adott klinikai esettől függően a felszerelés beállításait meghatározza, és hogy minden eljárás előtt ellenőrizze a felszerelés helyes működését. Ajánlatos, hogy a fúrási szekvenciák alacsony sebességgel, bőséges és állandó külső öblítés mellett legyenek végrehajtva. Az ajánlott forgási sebesség fúrásnál 700-1200 ford./perc, de legfeljebb 1500 ford./perc, furatkészítésnél pedig 200-400 ford/ perc, - a fúrószárak nagyon élesek; ezeket a vágási sérülések elkerülése érdekében óvatosan javasolt megfogni. Mivel a fúrók spirális hornyokkal rendelkeznek, használatuk során a félrecsúszás előfordulhat, ami károsan hat a fúrás pontosságára nézve. Ezen lehetőség kiküszöbölése érdekében ajánlatos az erre a célra rendelkezésre bocsátott mélységbeállítók használata, - a kopási problémák elkerülésére a vágószerszámok (marók, frézerek, csapok és fúrók) nem használhatók több mint 20 alkalommal. A fúrófejekre speciális nyilvántartó lap áll rendelkezésre. Műtét utáni óvintézkedések Az implantátum behelyezése után a csontintegráció 4 hónapon (alsó állkapocs) 6 hónapon (felső állkapocs) belül fejeződik be. A sebésznek a műtét után a beteget nyomon kell követnie. Ő a felelős a beteg következőkről való tájékoztatásáért: - az implantátum behelyezése után elkerülendő tevékenységek, és a napi normális tevékenységben betartandó óvintézkedések. A betegnek meg kell értenie, hogy a csont teljes konszolidációja előtt a fémes anyag nem olyan erős, mint az egészséges csontstruktúrák, és hogy a fémes anyagok intenzív vagy normálistól eltérő, feszültségek esetén eltörnek, - az implantátum hatásossága az ő viselkedésétől és szájhigiéniájától, - az implantátum beültetéséhez kapcsolódó potenciális kockázatoktól és mellékhatásoktól, - az implantátum csontba való beépülésének lehetséges sikertelenségétől, - a műtéti területen a műtét közben vagy után megjelenő bármely érzékenység jelentésének szükségességétől, - más eljárásokkal és terápiás vagy diagnosztikai eszközökkel való lehetséges kölcsönhatásoktól függ. 6. LEHETSÉGES MELLÉKHATÁSOK A beültetési technikáknak ellenjavallatai és alkalmazási kockázatai vannak. Ezek összefüggésben is lehetnek az eszköz használatával, valamint a sebészeti beavatkozással, és magukban foglalhatják az alábbiakat (nem teljes lista): - érzékenység, beszédproblémák, ödéma és vérömlenyek, - egy komponens meglazulása, törése, vagy elvesztése, - helyi idegrendszeri elváltozás, átmeneti vagy állandó, - a szomszédos fogak fertőzése, elváltozása és esztétikai problémák, - a BIOTECH DENTAL implantátumok különböző anyagaira történő allergiás reakció. 7. STERILITÁS ÉS NYOMON KÖVETHETŐSÉG Sterilen szállított eszközök: A fogászati implantátumok jön egy csavarját, és a gyógyulási csavart a csomagolásban az implantátum, steril (gamma sugárzással sterilizálva). Minden sterilen szállított termék egyszer használatos, és nem szabad újrasterilizálni azokat. Használat előtt a teljes csomagolás ellenőrzendő, hogy a tartalom sterilitása nem változott-e meg. Megfelelő tárolási körülmények között a csomagolás fenntartja sterilitását a lejárati dátumig. Ne használja fel, ha a csomagolás megsérült. A csomagolások különböző szintjein lévő címkék és külön címkék teszik lehetővé a teljes nyomon követhetőséget az implantátum cikkszáma és a gyártási száma alapján. Steril, egyszer használatos eszközöket semmilyen körülmények között shoulds kell újra és újra sterilizálni. Abban az esetben, újra sterilizálása nem re-sterilizálható orvosi eszköz hiánya iatrogén átviteli kórokozók dolgozat eszközökkel már nem garantált, és baleset területén materiovigilance előfordulhat. Nem sterilen szállított eszközök: A kiegészítő műszereket és a prosztetikus alkatrészeket tisztán, de nem sterilen szállítják. Az érintett személyzet felelőssége a vonatkozó ajánlások szerint a fertőtlenítés, a tisztítás és a sterilizálás minden eljárás előtt és után (az újrafelhasználható termékek esetében). 8. NEM STERIL ESZKÖZÖK TISZTÍTÁSA ÉS STERILIZÁLÁSA A fertőtlenítés és a tisztítási műveletek minden sterilizálási folyamat előtt elengedhetetlenek. - Az összetevők károsodásának megelőzése érdekében csak az anyagokkal kompatibilis tisztítószerek és fertőtlenítő termékek használhatók. Rozsdamentes acél és alumínium orvostechnikai eszközök esetén tilos lúgos és korrozív termékeket használni: a klór, nátrium-hipoklorit és nátrium-klorid vizes oldata elszínezi és/ vagy korrodálja a műszereket. - Az előfertőtlenítéshez, tisztításhoz, fertőtlenítéshez, öblítéshez és sterilizáláshoz használt víznek a vonatkozó rendelkezéseknek kell megfelelnie. - A felhasználónak különös figyelmet kell fordítania a műszerek minden részén (üregekben, hézagokban stb.) lévő szennyezés, maradék és lerakódások eltávolítására. Előfertőtlenítés: - az összes szétszerelt újrafelhasználható műszer esetén az eljárást követően a fertőtlenítést azonnal el kell végezni, - a korábban szétszerelt műszereket merítse teljesen egy aldehidet nem tartalmazó, semleges pH-jú fertőtlenítő oldatba, amelynek koncentrációja a műszerek kontaminációs fokától és szennyezettségük mértékétől függ. Áztassa 15-20 percig. Ultrahangos vízfürdős áztatás javasolt. - A fertőtlenítő oldatot a telítődés megelőzése érdekében minden egyes használat után meg kell újítani. Tisztítás: - ezt kefével és ultrahanggal lehet megtenni, és a szétszedett alkatrészeken kell elvégezni, - a kefés tisztítást puha kefével (például nylon) kell végezni, - legalább 15 perc áztatás szükséges. Bizonyos termékek esetében a több órás érintkezés az anyag korrózióját okozhatja (ne áztassa több mint 2 órán át). Öblítés - Szárítás: A tisztítást azonnali bőséges öblítésnek kell követnie, majd a termékeket a sterilizációs folyamat megkezdése előtt meg kell szárítani. Sterilizálás előtti becsomagolás: Az alkalmazott tisztítási módszertől függetlenül, a termékeket azonnal be kell csomagolni az újraszennyeződés elkerülése érdekében. Fémrácsos tálcákon való sterilizálás esetén kétrétegű csomagolópapírt kell használni a csomagoláshoz. Abban az esetben, ha a csomagolás később (>2 óra) történik, akkor egy további tisztítást is fontolóra kell venni az anyag sterilitása érdekében. Sterilizálás: A műszereket úgy kell előkészíteni, hogy minden felület közvetlenül érintkezzen a gőzzel. A javasolt ciklus a 134 °C-on 18 percig tartó Prion-ciklus. Visszatérjen: Miután a járulékos esetén a kölcsön, ezt vissza kell küldeni BIOTECH DENTAL miután megtisztították és fertőtlenítették megfelelően a vonatkozó előírásoknak. Az egészségügyi létesítmény és az orvos feladata annak biztosítása, hogy a hatékonyan végrehajtott (berendezés, anyagok és operátor) tisztítási/sterilizálási folyamat elérje a kívánt eredményt. A gyártó semmilyen körülmények között nem tehető felelőssé a sterilitással kapcsolatban. 9. KEZELÉS ÉS TÁROLÁS A termékeket a műtéti beavatkozás előtt gondosan kell kezelni és tárolni szennyeződés- és károsodásmentesség biztosítása érdekében. A tárolásnak gondosan, megfelelő, száraz és tiszta környezetben kell történnie. A termékeket nem szabad kitenni közvetlen napfénynek, ionizáló sugárzásnak, extrém hőmérsékletnek, meghatározott szennyeződésnek, korrozív hatású termékkel való érintkezésnek vagy azok közelségének. A eszközök elővigyázatosság nélküli kezelése vagy gyenge védelme veszélyezteti élettartamukat. 10. ÁRTALMATLANÍTÁS A gyógyászati hulladékok ártalmatlanításának meg kell felelnie a vonatkozó jogszabályoknak. A hulladékot termelő szakember felelős a fertőzés kockázatát magában hordozó és a háztartási hulladékkal kompatibilis hulladék szétválogatásáért. IT ISTRUZIONI PER L’USO BIOTECH DENTAL SISTEMI DI IMPIANTO DENTALE KONTACT®, B.I.S.®, B.I.S. Conic® e Weego.fr. Questo prodotto deve essere utilizzato da personale ESPERTO e QUALIFICATO che ABBIA LETTO le presenti istruzioni. 1. DESCRIZIONE GENERALE I sistemi di impianto dentale BIOTECH DENTAL sono costituiti da: - impianti dentali in titanio/lega di titanio conformi agli standard ISO 5832-2/ISO 5832-3 applicabili, - monconi ceramici, in titanio e in lega di titanio conformi agli standard applicabili, - ulteriori componenti protesici in titanio, lega di titanio o metallo e polimero conformi agli standard applicabili, - strumentazione accessoria in acciaio inox T40 e TA6V di grado medico. Per facilitarne l’identificazione, la maggioranza degli strumenti reca un numero di lotto di produzione e di riferimento ben visibile. I prodotti sterili sono indicati sulla confezione. Se la confezione non riporta espressamente la dicitura ‘sterile’, i prodotti non sono sterili e devono essere assolutamente sterilizzati prima dell’uso dal personale interessato. I sistemi di impianto dentale sono radiopachi. 2. CONDIZIONI D’USO GENERALI I sistemi di impianto dentale devono essere usati solo da chirurghi specializzati: - esperti di implantologia e delle tecniche d’uso dei dispositivi medicali BIOTECH DENTAL, - in conformità alle indicazioni, controindicazioni e precauzioni che devono essere riportate al paziente durante la fase post-operatoria e che sono menzionate in queste istruzioni nonché nei protocolli protesici e chirurgici disponibili su richiesta, - in strutture compatibili alle condizioni asettiche descritte in queste istruzioni, In nessuna circostanza i sistemi di impianto dentale possono essere usati con i dispositivi di un altro produttore. Nel periodo compreso tra il posizionamento dell’impianto e la sua gestione, BIOTECH DENTAL si impegna a sostituire qualsiasi impianto o componente protesico, a patto che siano state osservate le suddette condizioni. Il medico sarà responsabile di eventuali complicazioni risultanti dall’uso in caso di inosservanza delle raccomandazioni o dell’asepsi. Le complicazioni in questione in nessuna circostanza potranno essere attribuite a BIOTECH DENTAL e qualsiasi azione formulata contro BIOTECH DENTAL relativamente alla garanzia o alla sostituzione del prodotto sarà di conseguenza respinta. 3. INDICAZIONI Gli impianti dentali BIOTECH DENTAL sono usati come supporto per l’ancoraggio delle sostituzioni nella regione mandibolare e mascellare. I restauri variano dalla sostituzione singola alla sostituzione dell’intera dentatura al fine di riprodurre tutte o alcune delle funzioni dei denti naturali. Questa tecnica deve essere considerata solo laddove altre terapie meno invasive siano ritenute meno idonee. La qualità e il volume dell’osso devono essere sufficienti a sostenere gli impianti dentali. 4. CONTROINDICAZIONI Gli impianti dentali non devono essere usati in pazienti che presentano controindicazioni locali e/o generali agli interventi di chirurgia dentale. Queste controindicazioni devono essere valutate attentamente in sede decisionale dal chirurgo. Le controindicazioni sono costituite, tra le altre cose, da: - fattori che interferiscono con il processo di guarigione e rigenerazione del tessuto e dell’osso quali problemi del metabolismo osseo, del tessuto connettivo, diabete di tipo 2, terapia a base di steroidi, infezioni ossee e abuso di alcol e nicotina, - malattie o terapie immunosoppressive quali chemioterapia e radioterapia, - qualità e volume dell’osso non sufficienti ad accogliere un numero e una dimensione adeguata di impianti e a sostenerne i carichi funzionali, - bruxismo, abitudini parafunzionali, problemi di occlusione e/o delle articolazioni temporomandibolari, - infezioni e infiammazione orali quali parodontite e gengivite, - allergia al titanio o a leghe di titanio oppure scarsa igiene orale. 5. PRECAUZIONI D’USO - Per evitare di ingerire o inalare piccoli componenti, si raccomanda, laddove possibile, di fissarli. - BIOTECH DENTAL dovrà essere informata di qualsiasi incidente o problema relativo a un impianto o uno strumento. Precauzioni pre-operatorie: - prima dell’uso, l’utente deve verificare che il materiale sia in buone condizioni e funzioni correttamente. Il materiale non deve essere utilizzato in nessuna circostanza se la con - la superficie occlusale dell’impianto deve essere idealmente inferiore a quella della protesi dentale per garantire la dilatazione del tessuto molle e del profilo di emergenza della protesi, - è richiesto uno spazio minimo di 1,5 mm tra l’impianto e la radice adiacente e di 1,5 mm tra 2 impianti, nonché uno spessore dell’osso di 1 mm intorno alle superfici linguale e vestibolare dell’impianto (> in caso di grandi diametri), - In caso di sospetta o nota ipersensibilità ai corpi estranei, si raccomanda di controllare la tolleranza altitanio e al titanio TA6V ELI prima di procedere all’impianto del materiale. Per garantire la sicurezza completa è fondamentale predisporre un piano di trattamento clinico ed effettuare una valutazione radiografica e/o con TAC. Precauzioni perioperatorie: - la stabilità primaria dell’impianto è fondamentale, - la scelta del tipo e della dimensione dell’impianto sarà a discrezione del chirurgo, a seconda delle peculiarità del paziente e della rispettiva patologia. La dimensione e la natura delle strutture ossee saranno determinanti per la decisione del chirurgo. Il chirurgo dovrà altresì considerare gli sforzi sull’impianto dopo la procedura, - gli impianti non devono essere deformati. Per evitare di sottoporre l’impianto a sollecitazioni anomale, le manipolazioni dovranno essere progressive. Uno sforzo eccessivo sull’impianto potrebbe indurre sollecitazioni in grado di causare la rottura o la deformazione dell’impianto con conseguenti effetti secondari, - è responsabilità del medico definire la configurazione della sua attrezzatura a seconda del particolare caso clinico e verificare che l’attrezzatura funzioni correttamente prima di ogni procedura. Si raccomanda di eseguire le sequenze di perforazione a una velocità bassa e con abbondante e costante irrigazione esterna. La velocità di rotazione raccomandata varia da 700 a 1.200 giri nel caso della perforazione, senza mai superare in alcun caso i 1.500 giri, e da 200 a 400 giri per l’alesaggio, - essendo molto affilati, si raccomanda di fare attenzione quando si afferrano i trapani per evitare di tagliarsi. Dato che, inoltre, i trapani sono progettati con scanalature elicoidali, il loro utilizzo può dare luogo a un fenomeno di trascinamento che potrebbe influire negativamente sulla precisione della perforazione. Per evitare che ciò accada, si raccomanda di usare i fermi per trapano forniti a questo scopo, - gli strumenti di taglio (frese coniche, trapani, maschiatori e alesatori) non devono essere usati per oltre 20 volte al fine di prevenire problemi correlati all’usura. Per i trapani è disponibile uno speciale documento di monitoraggio. Precauzioni postoperatorie: Dopo l’inserimento dell’impianto, l’osteointegrazione avviene entro 4 mesi (mandibola) 6 mesi (mascella). Il chirurgo dovrà implementare il follow-up postoperatorio. Sarà responsabile di informare il paziente relativamente a: - attività da evitare dopo l’inserimento di un impianto e precauzioni da prendere nel corso delle normali attività quotidiane. Il paziente deve capire che, fino al completo consolidamento osseo, i materiali metallici non sono resistenti come le strutture ossee sane e possono rompersi se sottoposti a sollecitazioni intense o anomale, - comportamento e igiene orale del paziente ai fini dell’efficacia dell’impianto, - rischi ed effetti avversi potenziali associati all’inserimento di un impianto dentale, - possibilità di mancata osteointegrazione dell’impianto, - esigenza di segnalare qualsiasi sensibilità che interessi l’area operata, peri- o post-intervento, - potenziale interazione con altre procedure e dispositivi diagnostici o terapeutici. 6. POSSIBILI EVENTI AVVERSI Le tecniche di impianto sono accompagnate da controindicazioni e rischi d’uso che possono essere correlati all’utilizzo del dispositivo nonché all’intervento chirurgico e possono includere (a titolo non esaustivo): - sensibilità, difficoltà a parlare, edema o ematomi, - allentamento, rottura o perdita di un componente, - lesione nervosa locale, transitoria o permanente, - infezione, lesione dei denti adiacenti e problemi estetici, - reazione allergica ai vari materiali che costituiscono gli impianti BIOTECH DENTAL . 7. STERILITÀ E TRACCIABILITÀ Dispositivo consegnato sterile: Gli impianti dentali sono dotati di una vite di copertura e di una vite di guarigione nella confezione dell’impianto, sono sterili (sterilizzazione con raggi gamma). Qualsiasi prodotto fornito sterile è monouso e non deve essere risterilizzato. Prima dell’uso, controllare l’intera confezione per verificare che la sterilità dei contenuti non risulti alterata. In condizioni di conservazione adeguata, la confezione mantiene la sterilità fino alla data di scadenza. Non utilizzare se la confezione è danneggiata. Le etichette sui vari strati della confezione, nonché le etichette libere, consentiranno di garantire la perfetta tracciabilità sulla base del numero di riferimento e del numero di lotto dell’impianto. Sterili dispositivi monouso in nessun caso dovrei essere riutilizzati e ri-sterilizzati. In caso di ri-sterilizzazione di un dispositivo medico non ri-sterilizzabile, la mancanza di trasmissione iatrogena di patogeni da dispositivi tesi non è più garantito e incidenti nel settore del materiovigilance possono verificarsi. Dispositivo consegnato non sterile: La strumentazione accessoria e le parti protesiche sono fornite pulite, ma non sterili. Sarà responsabilità del personale interessato procedere alla decontaminazione, alla pulizia e alla sterilizzazione prima e dopo ogni procedura (per i prodotti riutilizzabili) ai sensi delle raccomandazioni applicabili. 8. PULIZIA E STERILIZZAZIONE DEI DISPOSITIVI NON STERILI Le attività di decontaminazione e pulizia sono obbligatorie prima di ogni processo di sterilizzazione. - Per prevenire il deterioramento dei componenti, usare solo prodotti per la pulizia e la decontaminazione compatibili con i materiali. I prodotti alcalini e corrosivi per i dispositivi medicali in alluminio e acciaio inox sono proibiti: candeggina, soluzioni acquose di ipoclorito di sodio e cloruro di sodio scolorano e/o corrodono gli strumenti. - L’acqua utilizzata per pre-disinfezione, pulizia, decontaminazione, risciacquo e sterilizzazione deve essere conforme alle normative applicabili. - L’utilizzatore deve prestare particolare attenzione alla rimozione di sporcizia, residui e depositi su tutte le parti degli strumenti (cavità, interstizi, ecc.). Pre-decontaminazione: - deve essere effettuata immediatamente dopo ogni procedura per tutti gli strumenti riutilizzabili disassemblati, - immergere completamente gli strumenti precedentemente disassemblati in una soluzione decontaminante con pH neutro, senza aldeide e con una concentrazione funzionale alla percentuale di contaminazione e al grado di sporcizia degli strumenti. Lasciare gli strumenti immersi per 15-20 minuti. Si raccomanda l’immersione in un bagno a ultrasuoni, - sostituire la soluzione decontaminante dopo ogni uso per evitarne la saturazione. Pulizia: - può essere eseguita mediante spazzolamento e ultrasuoni e deve essere svolta sui componenti disassemblati, - usare una spazzola con setole morbide (per esempio di nylon), - lasciare gli strumenti immersi per almeno 15 minuti. Il contatto prolungato con determinati prodotti per diverse ore può causare la corrosione del materiale (non superare le 2 ore). Risciacquo – Asciugatura: La pulizia deve essere immediatamente seguita da un risciacquo abbondante. I prodotti dovranno quindi essere asciugati prima di iniziare il processo di sterilizzazione. Confezionamento prima della sterilizzazione: Indipendentemente dal metodo di pulizia usato, il materiale deve essere confezionato immediatamente per evitare eventuali nuove contaminazioni. In caso di sterilizzazione su vassoi in griglia metallica, per il confezionamento usare una carta da imballo doppia. In caso di confezionamento tardivo (> 2 ore), considerare un’ulteriore procedura di pulizia al fine di accertarsi che il materiale sia sterile. Sterilizzazione: Preparare gli strumenti in modo che tutte le superfici siano a diretto contatto con il vapore. Si consiglia un ciclo Prion a 134 °C per 18 minuti. Restituzione: Se usati a titolo di prestito, gli accessori dovranno essere restituiti a BIOTECH DENTAL dopo adeguata pulizia e decontaminazione ai sensi delle normative applicabili. Spetta alla struttura sanitaria o al medico garantire che il processo di pulizia/sterilizzazione, correttamente svolto (attrezzatura, materiali e operatore), dia il risultato auspicato. In nessuna circostanza il produttore sarà responsabile della sterilità. 9. UTILIZZO E CONSERVAZIONE I prodotti devono essere trattati e conservati attentamente al fine di garantire che non vengano contaminati né che si deteriorino prima di qualsiasi intervento chirurgico. Conservare con cura in un ambiente appropriato, asciutto e pulito. Non esporre gli strumenti alla luce solare diretta, a radiazioni ionizzanti, a temperature estreme, a determinati agenti contaminanti né collocarli a contatto o in prossimità di prodotti che possano avere un effetto corrosivo. Il ciclo di vita dei dispositivi può essere compromesso dall’inosservanza delle precauzioni durante l’uso o da una scarsa protezione degli strumenti. 10. SMALTIMENTO Lo smaltimento dei rifiuti medici deve osservare la legislazione applicabile. I professionisti che producono rifiuti medici saranno responsabili di differenziare eventuali rifiuti a rischio di infezione da quelli compatibili con i rifiuti domestici. M Q G GAMME ANNÉE B S B S C KONTACT W O O