unit_1.
Anuncio

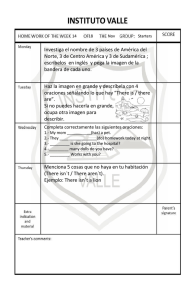
BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 UNIT 1. INTRODUCTIONS y MISCELLANEA y Presentaciones A continuación exponemos un listado de fórmulas de saludo y de presentación. ¿Sabrías qué responder a cada una de ellas? ¿Podrías ordenarlas de más a menos formal? 1. Pleased to meet you ____________________________________ 2. How are you? ____________________________________ 3. How do you do? ____________________________________ 4. Hi! ____________________________________ La expresión 'How do you do?' se utiliza en contextos muy formales cuando nos presentan a alguien por primera vez. La respuesta a esta fórmula es también 'How do you do?'. A veces ésta suele confundirse con la pregunta 'How are you?', que significa '¿Cómo está Ud?' y tiene por objeto interesarse por la persona a la que dirigimos esta pregunta. Las respuestas habituales a esta pregunta son: 'I'm fine, thanks. And you?' 'I'm OK, thanks. And you?' 'Not too bad, thanks. And you?' y Cómo formar nombres de profesiones Uno de los recursos lingüísticos para formar nuevo vocabulario es el empleo de afijos. Podemos añadir sufijos o prefijos a la raíz de una palabra para obtener otra nueva. Ejemplo: teach – teacher; science – scientist. Como se puede observar, al añadir los sufijos '-er', 'ist', se obtienen dos sustantivos referidos a profesiones. Los sufijos más comunes para formar nombres relacionados con los oficios profesiones son: '-er', '-or', '-ian', '-man', e '-ist’. Observe los ejemplos de profesiones que se obtienen de sustantivos y verbos. Página 1 Sustantivo y/o verbo act actor manage manager politics politician play player paint painter fire fireman chemistry chemist music musician Profesión BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 Cuando decimos a qué se dedica alguien, delante de la profesión hay que utilizar el artículo indeterminado a/an. Ejemplo: My mother works as a photographer. Mr Jones is a policeman. y Adjetivos de nacionalidad Los adjetivos de nacionalidad a menudo se forman añadiendo un sufijo al nombre del país. Los sufijos más utilizados son: '-ish', '-ian', '-ese.' Ejemplo: BritainÄBritish AustraliaÄAustralian JapanÄJapanese Escriba la nacionalidad correspondiente a los siguientes países: Vietnam Russia Argentina Poland Java Norway Yugoslavia France y TEXT y Verbo to be (ser/estar) Infinitivo Pasado Participio pasado Gerundio Be Was/were Been Being Afirmación Contracción Negación Contracción Interrogación I am I’m I am not I’m not Am I? You are You’re You are not You aren’t Are you? He is He’s He is not He isn’t Is he? She is She’s She is not She isn’t Is she? It is It’s It is not It isn’t Is it? We are We’re We are not We aren’t Are we? You are You’re You are not You aren’t Are you? They are They’re They are not They aren’t Are they? Página 2 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 Este verbo es auxiliar y puede hacer la negación y la interrogación sobre sí mismo. y Para hacer la negación, se le añade la partícula negativa 'not' al verbo. y Para interrogar, el verbo invierte su posición con el sujeto. y El uso de las formas contraídas denota un contexto más coloquial y, por lo tanto, no se consideran correctas en el lenguaje escrito formal. 1. LISTENING: “Introductions”. Escucha la siguiente conversación y después lee el diálogo. This is Lidia. She is an important business woman from Catalonia in Spain. She is in Britain on a business trip and to learn English. She meets John at the airport for the first time. This is John. He is the manager of a very important hotel in London. Lidia: Hello, I’m Lidia. John: Hello, Lidia. My name’s John. Lidia: Nice to meet you. John: Nice to meet you. Welcome to England. Lidia: Thank you. 2. Estudia el Grammar Box y construye frases verdaderas usando am, is, are, ‘m not, isn’t, o aren’t. 1. I _______ at work. 2. It _______ Wednesday today. 3. My father’s name _______ Peter. 4. My parents _______ at home. 5. I _______ married. 6. Cava _______ a drink from Catalonia. 7. Lidia and John _______ married. 8. Lidia _______ English. 9. A dog _______ a plant. It _______ an animal. 10. Diamonds _______ cheap. They _______ expensive. Página 3 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 3. Completa las siguientes frases con la forma correcta del presente del verbo ‘to be’. Ejemplo: My name is Claire 1. Where _______ you from? 2. I’_______ from Italy. 3. What’_______ your name? 4. Christina _______ 21 years old. 5. Mike and Rosie _______ from London but their parents _______ from Glasgow. 6. Clara _______ married. Her husband _______ a hotel manager. 7. His name _______ Stephen. 8. My friend and I _______ doctors. We _______ very interested in our profession. 4. Negación del verbo ‘to be’. Las siguientes frases son falsas. Escríbelas utilizando la forma negativa del verbo y corrígelas. Ejemplo: Britney Spears is an English football player. No, she isn’t. She is an American singer. 1. Paris is the capital of Spain. __________________________ . ____________________________ . 2. You’re English. __________________________ . ____________________________ . 3. Michael Jordan is white. __________________________ . ____________________________ . 4. Bananas are vegetables. __________________________ . ____________________________ . 5. The month after June is September. __________________________ . ____________________________ . 5. Escribe las formas verbales completas correspondientes a las formas contraídas del verbo ‘to be’ en las siguientes frases. Ejemplo: I’m a student. 1. What’s your name? 2. My name’s Tim. 3. He’s married. I am a student. Página 4 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 4. They’re from Belgium. 5. I’m eighteen. 6. She’s a nurse. 7. You’re Italian. 8. We’re teachers. y El artículo indeterminado – A /AN Este artículo se utiliza delante de los sustantivos contables en singular para hablar de un objeto o persona no especificada. Significa ‘un/a’ en español. Uso de A Uso de AN Delante de palabras que comienzan por consonante, excepto ‘h’ muda, ‘u’,‘eu’, ‘ew’ pronunciadas /ju:/ y ‘o’ pronunciada /u/. There’s a letter on the table. Delante de palabras que empiezan por vocal 'h' muda. I have got an American car. There is a horse in the farm. There is an envelope in the drawer. There’s a European student in the team. You are an hour late. He is a Union soldier 6. Escribe a o an delante de cada uno de los siguientes sustantivos. 1. ____ stamp 2. ____ egg 3. ____ bag 4. ____ notebook 5. ____ orange 6. ____ book 7. ____ key 8. ____ envelope 9. ____ dictionary 10. ____ newspaper 11. ____ letter 12. ____ umbrella 7. Usa el diccionario y escribe a o an delante de cada sustantivo. a. A boy b. An apple c. _____________ Página 5 d. _____________ BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 e. _____________ f. _____________ g. _____________ h. _____________ i. _____________ j. _____________ k. _____________ l. _______________ 8. Subraya la opción correcta. Ejemplo: He’s (a/an) accountant. 1. She’s (a/an) housekeeper. 2. John (is thirty years old/is thirty years). 3. I’m (not/no) married. 4. My sister (is/are) very beautiful. 5. My parents (are/is) rich. 6. There (are/is) a restaurant and two bars in the hotel. y Los adjetivos posesivos Los adjetivos posesivos siempre acompañan a un sustantivo y nos indican de quién es algo. Estos adjetivos tienen un antecedente, es decir, referencia a una persona o cosa nombrada con anterioridad y concuerdan en género y número con esta palabra. Ejemplo: Mr and Mrs Plough have a son. Their son lives in Jamaica. (El señor y la señora Plough tienen un hijo. Su hijo vive en Jamaica) Página 6 Como puede observar, el adjetivo posesivo 'their' es plural y acompaña a 'son', que es singular. Esto es así porque 'their' se refiere a Mr and Mrs Plough y nos indica que el hijo (‘son’) es de ambos (Mr and Mrs Plough). Pronombres personales I You He / She / It We Adjetivos posesivos My Your His / Her / Its Our You Your They Their BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 9. Completa las frases con my o your. 1. Hello. _____ name’s Sabina. 2. What’s _____ name? 3. Is Lynn _____ sister? 4. JENNY: Albert, this is _____ brother, Darren. ALBERT: Hello, Darren. DARREN: Hello. 10. Completa las frases con his o her. 1. ‘What’s _____ name?’ ‘Eugene’ 2. _____ name is Jim Burton. 3. I have a daughter. _____ name is Dorothy. 4. David is from France. _____ flat is in Paris. 5. My mother loves Spain. _____ father was Spanish. y There is / There are Ésta es una forma de verbo impersonal que significa 'hay'. A diferencia de nuestra lengua, el inglés distingue una forma para el singular 'there is' y otra para el plural 'there are'. - AFIRMATIVA - Usamos la forma there is para el singular. Ejemplo: “There is a computer in my room.” Hay un ordenador en mi habitación. - Usamos There are para el plural. Ejemplo: “There are three dogs in the park.” Hay tres perros en el parque. - NEGATIVA - There isn't (There is not) / There aren't (There are not) Ejemplos: “There isn't any water on the table.” No hay agua en la mesa. “There aren't many parks in this city.” No hay muchos parques en esta ciudad. - INTERROGATIVA - Is there? / Are there? Ejemplos: “Is there an English dictionary in the class?” ¿Hay un diccionario de inglés en la clase? “Are there any letters for me?” ¿Hay cartas para mi? Página 7 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 11. Ahora completa las siguientes oraciones con there is, there isn’t, is there, there are, there aren’t, o are there. 1. There _____ a big park in our town. There _____ a lake and ________________ a lot of trees. 2. ________________ a library in your school? Yes, ________________ one. 3. ________________ ten players in a football team? No, ________________. ________________ eleven players. 4. ________________ a train to the airport from the city centre? Yes, ________________ a train and ________________ two buses: number 7 and 27. 5. ________________ thirty-one days in November? 6. ________________ a computer in your house? Yes, ________________ two: one for me and one for my sister. 7. Is your coffee all right? - No, ________________ any sugar in it. 12. Responde las siguientes preguntas. 1. What’s your name? ________________________________________________________ 2. What’s your surname? ________________________________________________________ 3. How old are you? ________________________________________________________ 4. What’s your address? ________________________________________________________ 5. What’s your telephone number? ________________________________________________________ 6. Where are you from? ________________________________________________________ 7. What’s your job? ________________________________________________________ 8. Are you married? ________________________________________________________ Página 8 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 y VOCABULARY y y Numbers 1. ONE 11. ELEVEN 21. TWENTY-ONE 31. THIRTY-ONE 2. TWO 12. TWELVE 22. TWENTY-TWO 40. FORTY 3. THREE 13. THIRTEEN 23. TWENTY-THREE 50. FIFTY 4. FOUR 14. FOURTEEN 24. TWENTY-FOUR 60. SIXTY 5. FIVE 15. FIFTEEN 25. TWENTY-FIVE 70. SEVENTY 6. SIX 16. SIXTEEN 26. TWENTY-SIX 80. EIGHTY 7. SEVEN 17. SEVENTEEN 27. TWENTY-SEVEN 90. NINETY 8. EIGHT 18. EIGHTEEN 28. TWENTY-EIGHT 100. ONE HUNDRED 9. NINE 19. NINETEEN 29. TWENTY-NINE 200. TWO HUNDRED 10. TEN 20. TWENTY 30. THIRTY 1000. ONE THOUSAND Jobs Jobs Meanings Actor/Actress Actor/Actriz air stewardess /steward Azafata de vuelo Architect Arquitecto Shop assistant Dependiente Baker Panadero Barman / Barmaid / Bar Person Camarero/a Businessman / Businesswoman / Executive Empresario / Ejecutivo Butcher Carnicero Civil servant Funcionario Clerk Oficinista / Administrativo Computer Operator / Programmer Programador / Informático Cook Cocinero Dentist Dentista Designer Diseñador Director Director Doctor Doctor/Médico Bus / Taxi / Train driver Conductor de autobús/ Taxi/ Tren Página 9 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 Jobs Meanings Electrician Electricista Engineer Ingeniero Farmer Granjero Fisherman Pescador Fishmonger Pescadero Hairdresser Peluquero Head teacher Director de colegio Jeweler Joyero Journalist Periodista Judge Juez Lawyer Abogado Manager Director Miner Minero Musician Músico Nurse Enfermera Painter Pintor Photographer Fotógrafo Pilot Piloto Plumber Fontanero Police officer, policeman Oficial de policía, policía Politician Político Receptionist Recepcionista Sailor Navegante Salesman/ Saleswoman / Salesperson Vendedor/a, representante Secretary Secretaria Singer Cantante Surgeon Cirujano Teacher Profesor, maestro Travel agent Agente de viajes Waiter / waitress Camarero/a Writer Escritor Página 10 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 y Prepositions Prepositions (place) Meanings On encima, sobre Over por encima de, al otro lado de, sobre In front of delante Behind detrás In dentro Out fuera Of de At en, junto a Below debajo de y SELF-EVALUATION EXERCISES 13. What’s your name? Complete the conversation: A: Hello. What’s your name? B: Claire. What’s ______ ______? A: My name ______ George. Where ______ you ______Claire? B: I ______ from Dublin. And you...______ ______you from, John? A: ______ ______ New York. 14. Escribe acerca de las personas que aparecen en el siguiente ejercicio. Fíjate en el ejemplo: SURNAME: Roberts FIRST NAME: Alice FROM: The United States JOB: Dentist AGE: 25 SURNAME: Nolan FIRST NAME: Tom FROM: Australia JOB: Hairdresser AGE: 32 1. She’s Alice Roberts. 2. She’s from the United States. 3. She’s a dentist. 4. She’s twenty-five. 1. 2. 3. 4. Página 11 BÁSICO. UNIDAD 1 SURNAME: Smith FIRST NAMES: Ann and Tina FROM: Scotland JOB: Students AGE: 20 1. 2. 3. 4. y OPEN EVALUATION EXERCISES 15. Observa la imagen del siguiente ejercicio y descríbela. Usa el diccionario si lo necesitas, y escribe oraciones utilizando: there is, there are + a, an, one, two + nombres de objetos. Ejemplos: There is a scarf under the bed. There are three books on the floor. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________ . Página 12