oraciones de relativo
Anuncio

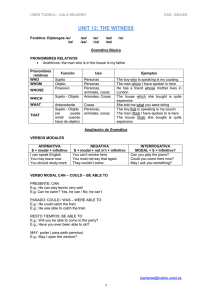
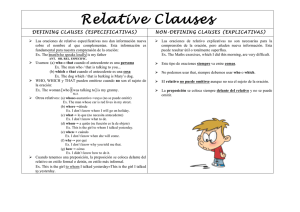
ORACIONES DE RELATIVO I) Oraciones de relativo: especificativas (defining) The woman who gave me a lift was from Romania Si la omitimos no sabemos de quién se trata. No lleva comas. Personas: Sujeto. The pickpocket who robbed you has been arrested. Objeto. The girl whom I saw told me to return today. Con preposición. The girl to whom I spoke (formal) The girl who I spoke to (informal) Posesivo. People whose houses have been destroyed can ask for special credits Cosas: Sujeto. This is the photo which/that caused so many problems. (También that). Objeto. The motorcycle which/that/Ø I hired broke down during the first week. Con preposición. The ladder on which I was standing began to slip. (Formal). The ladder that/Ø I was standing on began to slip. When puede sustituir a In/On which para tiempo. Where a In/At which para lugar y Why a For which. The hotel where I was satying…..The reason why he refused us.. Posesivo. Living in a flat whose walls were made of glass would be horrible (with glass walls) * Puede sustituirla un particip io de presente: People who are waiting for the bus often shelter in my doorway....(People waiting for the bus…) * It was Tom who helped us …. Tom helped us (Él y no otra persona) * The last man to leave the ship... The last man who left the ship.(Con un infinitive). II) Oraciones de relativo: explicativas (non-defining) Tras nombres que ya están definidos. No lo definen, sólo añaden información por lo que no son esenciales y pueden omitirse. Van separadas por coma s. No se puede omitir el pronombre y se usan más en inglés formal y escrito. Para personas: Para cosas: Sujeto WHO WHICH Objeto WHO/WHOM WHICH Posesivo WHOSE WHOSE/OF WHICH Para personas. Sujeto. WHO solamente: My son, who is very pessimistic, says there will be no strawberries this year. Objeto. WHOM/WHO. (El segundo más en conversación). John, whom everyone suspected, turned out to be innocent. Objeto de preposición. WHOM. (La preposición va delante en inglés formal) Mr Smith, for whom I was working, was very generous about overtime payments. Posesivo. WHOSE Liz, whose children are at school all day, is trying to get a job. Para cosas: Sujeto. WHICH (No se utiliza THAT) The 9.25 train, which is usually very punctual, was late today. Puede sustituir a una oración entera: She passed all her exams in June, which surprised me a lot. Objeto. WHICH (No se puede omitir ni se utiliza THAT) My daughter gave me this jumper, which she had knitted herself. Objeto de preposición. WHICH. (La preposición va delante en inglés formal) His apartment, for which he paid 50.000 € ten years ago, can cost now 6 times…. * Con verbos frasales no debemos separar la prep./adv. This machine, which I have looked after for 20 years, is still working perfectly. Posesivo. WHOSE (para animales y cosas) / OF WHICH (para cosas) His car, whose handbrake wasn’t very reliable, began to slide backwards. III) Oraciones de relativo: conectivas Pronombres: WHO, WHOM, WHOSE, WHICH. Tienen la misma forma que las explicativas, suelen ir tras el objeto del verbo principal (o tras preposición + nombre) y no describen a sus nombres, sino que continúan la historia, Por lo que pueden sustituirse por AND o BUT. I told Robert, who said it wasn’t his business. I threw the ball to Todd, who threw it to Mary. I threw the ball to Todd and he threw it to Mary. Importancia de las comas: The travellers who knew about the floods took another road (defining) The travellers, who knew about the floods, took another road (non-defining)