Press Release - HOO.BOX Robotics
Anuncio

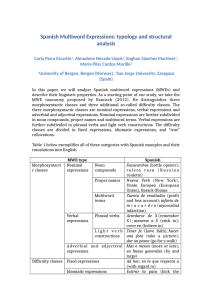
Smile, You Are Driving a Robotic Wheelchair Using Facial Expressions Paulo Pinheiro HOO.BOX (Press Release) ow about driving a robotic wheelchair using facial expressions? Meet Wheelie, the hands-free solution that can capture nearly 80 points from your face using TM technology to set up key R IntelRealSense expressions. Each key expression can control something on the wheelchair. Let’s take a ride! H we expect the user can talk while driving. What expressions were more comfortable to perform? After a stroke some patients may have different restrictions on controlling facial muscles. That’s why we have put available at least 7 key expressions ready to be picked up. Smile to drive the wheelchair Here are the options: full-smile, half-smile, wrinkle nose, eyebrows up, kiss movement, tongue out and puffed cheek. Pick up 5 of them, then we link these expressions to a command to drive the wheelchair: moving forward, backward, turning right, left and stop. Now you’re ready to go! Challenges The challenges were to create more comfortable facial key expressions, applying a little filtering to turn them more reliable. Also, what facial expressions Figure 1: Wheelie - Facial expressions can drive robotic wheelchairs. were the least used in a normal conversation? Yes, Page 1 of 3 How does it work? Put Wheelie into Action We manipulated the movement of nearly 80 facial TM camera to R points given by the IntelRealSense create the key expressions the Figure 2 shows up. Some of these expressions are variations of the RealSense ready provided expressions (e.g ., full-smile and tongue out) applied to the filter to maintain the reliability and comfortability. The Wheelie software constantly reads the points of the face extracting the expressions. When an expression hits the threshold of reliability and comfortability, the corresponding steering command is sent to the robotic wheelchair. Let’s put Wheelie into action where the user must drive his wheelchair over a real scenario with some trick obstacles. Figure 4 shows the user starting the ride from a room passing through obstacles that require fine-tune both in turns and moving straight ahead. Figure 4: Driving through narrow obstacles. Purposely this version does not include any kind Figure 2: Facial expressions available to drive the wheelchair. of shared control support. The user is the only responsible for all the fine movements to overcome Each person might pick up different expressions the obstacles. This way we could test the interface’s depending on the facial physical limitation or com- efficiency with no interference. Figure 5 shows the fort constraints. The following setup is the Wheelie user performing the full path. default one: Facial Expression Command Full-Smile Half-Smile Wrinkle Kiss Tongue out Stop Turn Right Turn Left Move Forward Move Backward Figure 3 shows a short example of using facial expressions to drive the wheelchair. Figure 5: Ride in a real office (7m × 6m). Figure 3: Facial expressions and actions. At this point you may be interested in some details of this ride. The total path covered was around 20 meters long. The user had to perform about 40 facial commands to complete it taking a total time of 2 minutes and 55 seconds. The transverse speed of the robotic wheelchair was set up to 180mm/s and the rotation speed to 100mm/s. If you want to watch this ride, the recorded video is available here on Youtube: http://bit.ly/drivingoffice Page 2 of 3 Setup Details Who we are The mentioned robotic wheelchair was designed and built by Prof. Dr. Eleri Cardozo (FEEC/UNICAMP) as part of the accessibility project supported by FINEP (Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos) research grant. HOO.BOX is the startup company heading the Wheelie hands-free project. AGEWELLBR is the HOO.BOX’s branch that concentrates projects related to accessibility. Experiments were held in LCA, at School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Campinas - BRAZIL. The researchers behind the project are Paulo Pinheiro (HOO.BOX), Ricardo Souza (HOO.BOX/FEEC) and Amadeu Junior (HOO.BOX/FEEC). • http://www.hoo-box.com • http://instagram.com/hooboxofficial • https://www.youtube.com/paulopine Figure 6: Robotic wheelchair and user’s laptop running TM R Wheelie with IntelRealSense . TM 3D Camera (Front F200) R The IntelRealSense is a stand-alone camera that uses depth-sensing technology and can be attached to a desktop or laptop computer. It consists of a conventional camera, an infrared laser projector, an infrared camera, and a microphone array. The camera features facial analysis tracking 78 points on the face inferring emotions, sentiments and calculating the roll, pitch and yaw of the head. The camera is available on Intel’s website. TM R Figure 7: IntelRealSense and Wheelie. Wheelie is the software package containing several hands free interfaces for controlling a wheelchair. Once you have the Wheelie installed on your comTM camera mounted R puter and an IntelRealSense on it, you can control a robotic wheelchair using facial expressions, head movement, eye tracking and voice commands. Wheelie is not available yet. Page 3 of 3