CATEGORÍAS Y FUNCIONES
Anuncio

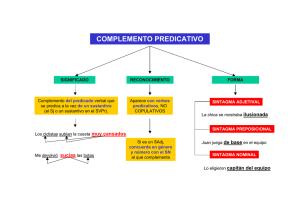
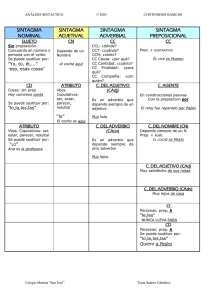
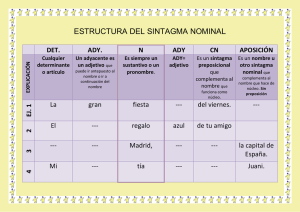
ANÁLISIS SINTÁCTICO o MORFOSINTÁCTICO DE LAS ORACIONES: CATEGORÍAS Y FUNCIONES El análisis sintáctico es la explicación de la forma, composición y función de las unidades morfosintácticas (palabras, sintagmas y oraciones ). tres pasos recurrentes: • Siempre se seguirán 1. Clasificar la unidad o categoría gramatical : simple (palabras) o compleja (sintagma y oración) 2. Segmentar las categorías complejas. 3. Indicar la función sintáctica de las categorías simples o complejas. No olvides que en el análisis morfosintáctico vas a utilizar una doble nomenclatura y con el orden adecuado: 1º( CATEGORÍA), 2º FUNCIÓN SINTÁCTICA. CATEGORÍAS SIMPLES ARTICULO- (Art) ADJETIVO DETERMINATIVO: POSESIVO, DEMOSTRATIVO,INDEFINIDO,NUMERAL,EXCLAMATIVO E INTERROGATIVO (A Pos), (A Dem), (A Ind), (A Num), (A Exc), (A Int) PRONOMBRE: PERSONAL, RELATIVO, REFLEXIVO, RECÍPROCO: (P PERS), (P Rel), (P REF), (P REC) PRONOMBRE DETERMINATIVO: POSESIVO, DEMOSTRATIVO,INDEFINIDO,NUMERAL,EXCLAMATIVO E INTERROGATIVO : (P Pos), (P Dem), (P Ind), (P Num), (P Exc), (P Int) ADJETIVO CALIFICATIVO –(ADJ) VERBO PREDIVATIVO (V), VERBO COPULATIVO (V COP) ADVERBIO O LOCUCIÓN ADVERBIAL- (Adv), ( Loc Adv) PREPOSICIÓN O LOCUCIÓN PREPOSICIONAL- (prep), (Loc prep) CONJUNCIÓN O LOCUCIÓN CONJUNTIVA- (conj), (Loc Conj) • • • • • CATEGORÍAS COMPLEJAS SINTAGMAS (S N) Sintagma Nominal (S ADJ) Sintagma Adjetival (S ADV) Sintagma Adverbial (S V) Sintagma Verbal (S PREP) Sintagma Preposicional ORACIONES • • Simples Compuestas PROPOSICIONES • • • 1 Yuxtapuesta- (P yux) Coordinada- (P coord) Subordinada- (p sub) FUNCIONES SINTÁCTICAS • • • • • FUNCIONES ORACIONALES (constituyentes de la oración) SUJETO-Suj PREDICADO NOMINAL-PredN PREDICADO VERBAL-PredV COMPLEMENTO ORACIONAL-COr ENUNCIADOS LIGADOS A LA ORACIÓN VOCATIVO-Voc INTERJECCIÓN-Intj • • • • • • • • • • FUNCIONES SINTÁCTICAS (constituyentes de los sintagmas) NÚCLEO-N DETERMINANTE-Det CUANTIFICADOR-Cuant COMPLEMENTO DEL NOMBRE-ADYACENTE-APOSICIÓN:CNAdy-Apo COMPLEMENTO DEL ADJETIVO-CAdj COMPLEMENTO DEL ADVERBIO-Cadv ENLACE-E NEXO-Nx TÉRMINO-T COMPLEMENTOS DEL VERBO: FUNCIONES RELACIONANTES (indican relaciones entre otros elementos) • COORDINADOR • SUBRDINADOR ATRIBUTO-Atr COMPLEMENTO DIRECTO-CD COMLEMENTO INDIRECTO-CI COMPLEMENTO CIRCUSTANCIAL-CC COMLPEMENTO DE RÉGIMEN -CR COMPLEMENTO PREDICATIVO-CPvo COMPLEMENTO AGENTE-CAg SINTAGMA: unidad sintáctica formada por una palabra o un conjunto de palabras que se aglutinan en torno a una de ellas, llamada NÚCLEO, y que desempeñan una función sintáctica dentro de la oración. Podemos distinguir los siguientes tipos según la categoría gramatical del núcleo: SINTAGMAS SINTAGMA NOMINAL – SN SINTAGMA ADJETIVAL – SAdj SINTAGMA ADVERBIAL – SAdv SINTAGMA VERBAL – SV SINTAGMA PREPOSICIONAL – SPrep 2 NÚCLEO SUSTANTIVO ADJETIVO ADVERBIO VERBO ENLACE (Prep o L prep) + TÉRMINO (SN o SAdj o SAdv) EJEMPLOS El árbol Muy amable Bastante lejos Llueve poco (En un lugar de la Mancha). (De blanco), (Por allí) SN : SINTAGMA NOMINAL FUNCIONES CATEGORÍAS (DETERMINANTE) concuerda en género y número ARTICULO- (Art) ADJETIVOS DETERMINATIVOS: (A Pos), (A Dem), (A Ind), (A Num), (A Exc), (A Int), El gato Mi gato Este gato Algún gato Primer gato ¿¡Qué gato!? Mi primer gato Todos los demás gatos NÚCLEO (ADYACENTE) SUSTANTIVO ( el gato) PRONOMBRE: (P PERS),(P Rel), (P REF), (P REC) (P Pos), (P Dem), (P Ind), (P Num), (P Exc), (P Int) PALABRA SUSTANTIVADA: ADJETIVO ( el bueno, el feo y el malo) VERBO ( fumar es malo) (“soy un fue, un será y un es cansado” Otras categorías con un artículo delante: (la y es una conjunción) ADJETIVO (el gato negro) S Adj ( el gato negro de patas) SUSTANTIVO-APOSICIÓN ( El gato Micifú) S Nom ( Micifú, el gato negro) S Prep ( El gato de mi hermano) Adjetivos determinativos pospuestos ( Un gato cualquiera) Proposición subordinada adjetiva(El gato que se llama Micifú) Proposición subordinada sustantiva (Tengo la ilusión de tener un gato ) S ADJ : SINTAGMA ADJETIVAL FUNCIONES CATEGORÍAS 3 (CUNTIFICADOR) ADVERBIOS DE INTENSIDAD: tan, muy, poco, bastante, demasiado, algo, nada, más, menos, etc. ( Muy listo) S. Adv ( Mucho menos agradable ) ADVERBIOS acabados en –mente (Extremadamente alto) Locuciones cuantificadoras ( El doble de caro, la mar de simpático NÚCLEO ADJETIVO ( guapo) (ADYACENTE O COMPLEMENTO ADJETIVAL) S Prep ( Muy ancho de espaldas) Proposición subordinada sustantiva (Soy capaz de correr 10 Km en una hora ) S ADV : SINTAGMA ADVERBIAL FUNCIONES CATEGORÍAS (CUNTIFICADOR) NÚCLEO ADVERBIOS DE INTENSIDAD: tan, muy, poco, bastante, demasiado, algo, nada, más, menos, etc. ( Muy lejos) S. Adv ( Mucho más cerca ) Locuciones cuantificadoras ( El doble de lejos ) ADVERBIO ( pronto) (ADYACENTE O COMPLEMENTO ADJETIVAL) S Prep ( Muy cerca de Arroyomolinos) Sustantivos ( hoy lunes), adverbios ( aquí abajo) y S Prep en aposición: luego, a las cuatro) Proposición subordinada caminos ) S PREP : SINTAGMA PREPOSICIONAL FUNCIONES CATEGORÍAS 4 ENLACE TÉRMINO PREPOSICIÓN- (Prep) Se sentó bajo el árbol LOCUCIÓN PREPOSITIVA (L Prep) No salió por culpa de la lluvia SUSTANTIVO ( viene de París) ADJETIVO (viene de negro) ADVERBIO ( Desde entonces no sale) S Nom ( Lo cambié por un gato negro) S Adj ( lo tienen por muy inteligente) S Adv ( Desde aquí mismo se ve la torre) S Prep ( Trabaja desde por la mañana) Proposición subordinada sustantiva (Tengo la ilusión de tener un gato ) (Allí donde se cruzan los