Arquitecturas Paralelas
Anuncio
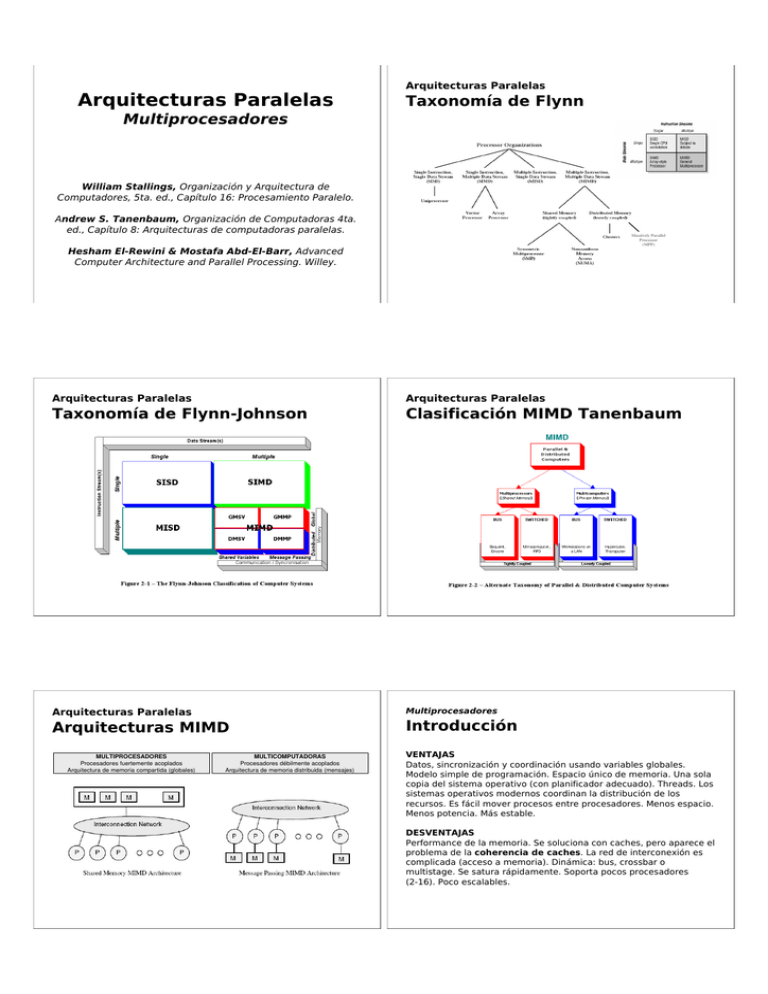
! Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) ! " # $ MULTIPROCESADORES Procesadores fuertemente acoplados Arquitectura de memoria compartida (globales) MULTICOMPUTADORAS Procesadores débilmente acoplados Arquitectura de memoria distribuida (mensajes) !"#$ !" # # "$!"#$ $ % ! " & # ' %#% ()*+$ %&$' ", ' %&$'(- % $ " # 12 " , , , /340 #%(.- )(/ !0- ! % & & '( ) )* + ,--. #% ) %$ 5 ##66 ! # # #% ! ! /.- ! ! 1 % / & (0 '( )1+ 2333 42' 56 '( 7)%8 $* +#% 3$07 -. / 8 #", %$ 4 % )-&.- -' /)0"12& $3' /' ! 9/' -3:- -/ % .03. ";% *!'</&<$=>&( & (% ?+<!# @.3/)A 66 ! &/ ' 4 $ # 6 " , 4 ! != ! , 2 1 .' BI N V 1h !'! !*)!' :' !J 4K 3' J !4 K A* C' J !4K :3' ! J !4K 93. '. C .*)!C .*)!CG:3 6 3?*:?*BB9C?DBB3$%!?EBF7.GDD H/#!D( 87 !AEEFI25 !28;8; & !% # ! #%! % ! 1"( '35( '3 6( , ( '3-( '3*( ), #"# $=$/$33 %3 & ")# ' & -5 - '( 6 ! /= I , ' & - '( " 1 ! - , / , , # 1 ! , "-"$ "-5 =)3 $3:$= ! '& %! 3%*+D "6 ' ' (M4& !=! '(# #& M ' M& 7 6 CLM %3 0%3 0%3 3$0%3N*BBD* *EE> - 8.3 !"#$%&'() * + $,+ -. ,/0$1 2/3 -4 "5, 66-4 7 ,-. " 8 !"#$%&'()94 34 ,:;4 !"#$%&'()4<<-. , 0/3-4 : " ,= 893 663 $3,+--4 , -. ,&%%>%4 " ,-0/3 -4 5,?-4 7 7 "5, 66-4 7 )-8.3 >! "" , 3 +89-. 3 4 +,-. :"" ",-4 ,$1 0/3-4 @ ,::;-. :""" ,-4 ,# 0 /3 -4 7 7 ;4 7 )- - 5( -$3 9L %L -.%3 8 / /@@ O & LN$ )! )-89 >! @ A; , 3 +89-. 3B:;3:?;;;;;;;4 @53C34 """ ,-4 +,353C3- ,<B ,:;44<<-. 5:,@- ,-%'("!'D4 C:,@- ,-%'("!'D4 :E ,55<CC-4 ,:?;-B<<4 7 ,F:0/3G;B-4 ;4 7 ! ! " # $ " # " # MULTIPROCESADORES Procesadores fuertemente acoplados Arquitectura de memoria compartida (globales) MULTICOMPUTADORAS Procesadores débilmente acoplados Arquitectura de memoria distribuida (mensajes) Massive Parallel Massively Processor (MPP) 5 ) -& 2 : 6 , !"#$ 6#% .# ! $# = % "$!"#$ $ 6&1 4 4 P 6 %0 1 O1 /#68 9 ; 1&5' # ,6 % G. &# )! & ' -, # #% 62 ' ' - + '$:*< + tiempo de cómputo Granularidad= tiempo de comunicación "2 # '-* 0 '7 & 6'N079 1 # 1 * : ; " 15&' & 35' ' '% ' '/ $' '6 6'# ',*66' '$* 2 6 ' 35( 6'1 '$3( '6 35'6, ,6 /, 0!$ 6' /$ ' 5 35'66 '5 35&35'' ,Q= QD(= 6 / 6,# 6'! $-- "-5 6 , 1 5 6 6 $ ' " & & 6,D=, $C$3' / 0% '"-)$3$3/9) . (3$-N<D(3:-%4<BB/ !9 3 / / =>>>/$ )0"1-?'L > $1 !F ,-. H3I4 !F"F,= 3= +-4 !F""I,!F">!!"1>%6(3=I-4 !F"" H,!F">!!"1>%6(3= H-4 ,$ 00/3 H3I-4 !F"JI,-4 ;4 7 $* + ## ":- /; +?5 @ <".33 23 4AB) :; .!3 4AB) :; 4 2 2./2./ C 2 ' <=5 : ( >$ )$; ## ## ":- 7% @. <".33 < 56 % )). # > 1?- 4 2 3:%>/*+BB >E> /N < -, /3: 62 N&D+B $D%L . :R*EES 2008 - Intel Core i7 Nehalem represents the largest architectural change in the Intel x86 family since the Pentium Pro in 1995. The Nehalem architecture has many new features. The ones that represent significant changes from the Core 2 include: FSB is replaced by QuickPath interface. Motherboards must use a chipset that supports QuickPath. As of November 2008, only the Intel X58 does this. The Intel QuickPath Interconnect is a point-to-point processor interconnect developed by Intel to compete with HyperTransport. It will replace the Front Side Bus (FSB) for Desktop, Xeon, and Itanium platforms. Intel will first deliver it in November 2008 on the Intel Core i7 desktop processor and the X58 chipset, and it will be used on new Nehalem-based Xeon processors and Tukwila-based Itanium processors. On-die memory controller: the memory is directly connected to the processor. Three channel memory: each channel can support one or two DDR3 DIMMs. Motherboards for Core i7 have four (3+1) or six DIMM slots instead of two or four, and DIMMs should be installed in sets of three, not two. Support for DDR3 only. Single-die device: all four cores, the memory controller, and all cache are on a single die. "Turbo Boost" technology allows the cores to intelligently clock themselves to 133MHz or 266MHz over the design clock speed so long as the CPU's thermal requirements are still met. This mode isn't enabled when the CPU is manually over-clocked by the user. Re-implemented Hyper-threading. Each of the four cores can process two threads simultaneously, so the processor appears to the OS as eight CPUs. This feature was present in the older Netburst architecture but was dropped in Core. On-die, shared, inclusive 8MB L3 cache. Only one QuickPath interface: not intended for multi-processor motherboards. 45nm process technology. 731M transistors. Sophisticated power management can place an unused core in a zero-power mode.