PAST SIMPLE
Anuncio

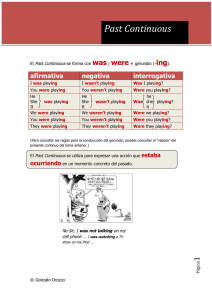
PAST SIMPLE AFFIRMATIVE (+) Subject pronoun +verb ended by -ed I played You played She/He/It played We played You played They played FORMS NEGATIVE (-) QUESTION (¿) Subject pronoun + auxiliary +not + Verb Auxiliary+ Subject pronoun + Verb I did not play = I didn’t play You did not play = You didn’t play She/He/It did not play = She/He/It didn’t play We didn’t play = We didn’t play You did not play = You didn’t play They did not play = They didn’t play Did I play? Did you play? Did she/he/it play? Did we play? Did you play? Did they play NOTA: En la tercera persona del singular no hay cambios. Sólo con el pasado del verbo to be: I was /I wasn’t/ Was I? You were /You weren’t/Were you? He/She/It was/ He/She/It wasn’t/ Was he/she/it? We were/We weren’t/Were we? You were /You weren’t/Were you? They were/ They weren’t/Were they? Para formar el pasado le añadimos –ed al verbo (cuando éste es regular): Play – played En los verbos terminados en –e añadimos una d: Like – liked Cuando el verbo termina en una consonante + y, la y cambia a –ied. Hurry – hurried Cuando un verbo monosílabo termina con una vocal y una consonante dobla la consonante: Plan - planned Hay algunos verbos que tienen los pasados irregulares, para aprenderlos hay que estudiarlos (ver listado de verbos): Become – became - become USOS: Para algo que sucedió en el pasado y ya ha terminado (una acción completa): Elvis Presley died in 1977 PAST CONTINUOUS AFFIRMATIVE (+) Subject pronoun +verb be+ verb ended by –ing I was playing You were playing She/He/It was playing We were playing You were playing They were playing FORMS NEGATIVE (-) Subject pronoun + verb be +not + verb ended by -ing I wasn’t playing You weren’t playing She/He/It wasn’t playing We weren’t playing You weren’t playing They weren’t playing QUESTION (¿) Verb be + Subject pronoun + Verb ended by -ing Was I playing? Were you playing? Was he/She/It playing? Were we playing? Were you playing? Were they playing? NOTA: Para ver cómo las reglas al añadir –ing mira los apuntes del present continuous. Recuerda que es el verbo to be en pasado + verbo acabado en –ing. USOS: Cuando estamos en un momento del pasado y estábamos en medio de una acción. I was cooking when the telephone rang. We were talking when she appeared. Se usa con acciones no con estados. Para estados utilizamos el past simple. I didn’t know where you were not I wasn’t knowing I was running through the forest. PAST CONTINUOUS OR SIMPLE? Normalmente utilizamos ambos tiempos juntos cuando una acción más corta sucede en la mitad de otra más larga. While Laura was sitting in the garden, it suddenly began to rain. Utilizamos el past continuous detrás de while, as o when. As we were driving down the hill, an strange object appeared in the sky. You drove right past me when I was waiting for the bus. While I was studying he prepared dinner. También podemos utilizar when delante del past simple. David was making lunch when the telephone rang. Usamos dos formas en past simple para una acción tras otra. When we saw the spaceship, we stopped the car. A menudo usamos el past continuous para describir circunstancias pasadas. The sun was shining Usamos el pasado simple para describir acciones en una historia. We arrived at the beach