View PDF
Anuncio
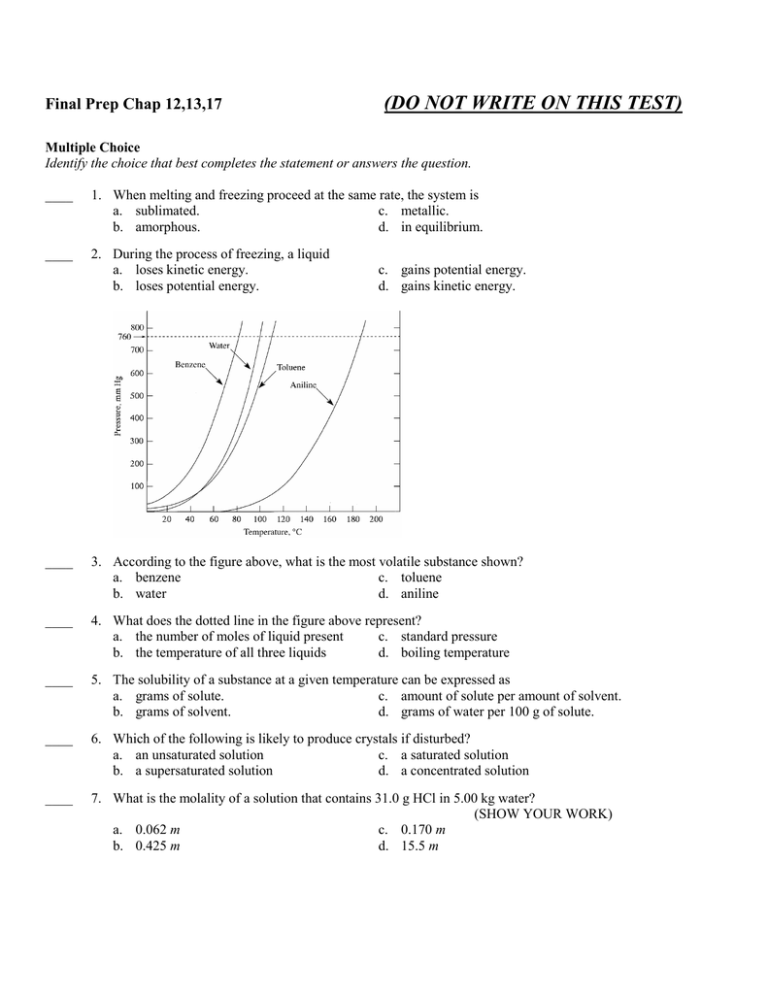
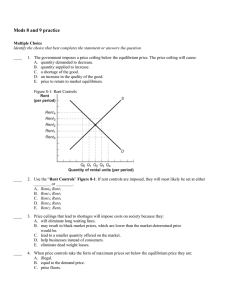
Final Prep Chap 12,13,17 (DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. When melting and freezing proceed at the same rate, the system is a. sublimated. c. metallic. b. amorphous. d. in equilibrium. ____ 2. During the process of freezing, a liquid a. loses kinetic energy. b. loses potential energy. c. gains potential energy. d. gains kinetic energy. ____ 3. According to the figure above, what is the most volatile substance shown? a. benzene c. toluene b. water d. aniline ____ 4. What does the dotted line in the figure above represent? a. the number of moles of liquid present c. standard pressure b. the temperature of all three liquids d. boiling temperature ____ 5. The solubility of a substance at a given temperature can be expressed as a. grams of solute. c. amount of solute per amount of solvent. b. grams of solvent. d. grams of water per 100 g of solute. ____ 6. Which of the following is likely to produce crystals if disturbed? a. an unsaturated solution c. a saturated solution b. a supersaturated solution d. a concentrated solution ____ 7. What is the molality of a solution that contains 31.0 g HCl in 5.00 kg water? (SHOW YOUR WORK) a. 0.062 m c. 0.170 m b. 0.425 m d. 15.5 m ____ 8. An NaOH solution contains 1.90 mol of NaOH, and its concentration is 0.555 M. What is its volume? (SHOW YOUR WORK) a. 0.623 L c. 1.05 L b. 0.911 L d. 3.42 L ____ 9. Which of the following is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter? a. chemical kinetics c. reaction rate b. thermochemistry d. temperature ____ 10. In what units is temperature measured? a. degrees Celsius b. kelvins c. both degrees Celsius and kelvins d. None of the above ____ 11. Reaction rate depends upon a. both collision frequency and efficiency. b. average kinetic energy. c. collision efficiency. d. average potential energy. ____ 12. Which of the following properties do solids share with liquids? a. fluidity c. definite volume b. definite shape d. slow rate of diffusion ____ 13. When heat is applied to a liquid-vapor system at equilibrium, a new equilibrium state will have a. a higher percentage of liquid. c. equal amounts of liquid and vapor. b. a higher percentage of vapor. d. all liquid. ____ 14. If the temperature of a closed liquid-vapor equilibrium system is raised, its vapor pressure a. decreases. c. remains the same. b. increases. d. shows no correlation. ____ 15. A volatile liquid a. has strong attractive forces between particles. b. evaporates readily. c. has an odor. d. is ionic. ____ 16. Which mixture contains visible particles that settle out unless the mixture is stirred? a. a colloid c. a solution b. a homogeneous mixture d. a suspension ____ 17. A substance whose water solution does NOT conduct a current is a(n) a. polar substance. c. electrolyte. b. nonelectrolyte. d. ionic substance. ____ 18. Which of the following decreases the average speed of solvent molecules? a. increasing the temperature c. adding more solvent b. stirring the solution d. decreasing the temperature ____ 19. The rule like dissolves like is used to predict a. solubility. b. equilibrium. c. reactivity. d. phase. ____ 20. The energy transferred between samples of matter because of a difference in their temperatures is called a. heat. c. chemical kinetics. b. thermochemistry. d. temperature. ____ 21. How much energy does a copper sample absorb as heat if its specific heat is 0.384 J/g·ºC, its mass is 8.00 g, and it is heated from 10.0ºC to 40.0ºC? (SHOW YOUR WORK) a. 0.0016 J/g·ºC c. 92.2 J b. 0.0016 J d. 92.2 J/g·ºC ____ 22. How much energy is absorbed as heat by 20. g of gold when it is heated from 25ºC to 35ºC? The specific heat of gold is 0.13 J/g·ºC. (SHOW YOUR WORK) a. 26 J c. 0.0006 J b. 26 J/g·ºC d. 0.0006 J/g·ºC ____ 23. The Greek letter ∆ stands for a. "heat stored in." b. "mass of." c. "rate of." d. "change in." ____ 24. Which of the following is a measure of the disorder in a system? a. entropy c. free energy b. enthalpy d. temperature ____ 25. Raising the temperature of reactants in a system a. increases the average molecular motion. b. decreases the average molecular motion. c. has no effect on the average molecular motion. d. disturbs the system so that the collision theory no longer applies. Problem (SHOW YOUR WORK) 26. What is the molarity of a solution of sucrose, C12H22O11, that contains 125 g of sucrose in 3.50 L of solution? 27. How many grams of NaOH are required to prepare 200. mL of a 0.450 M solution? 28. How many grams of NaC2H3O2 are needed to prepare 350. mL of a 2.75 M solution? 29. How many grams of Na2SO4 are needed to prepare 750. mL of a 0.375 M solution? 30. Iron(III) chloride can be produced by reacting Fe2O3 with a hydrochloric acid solution. How many milliliters of a 6.00 M HCl solution are needed to react with excess Fe2O3 to produce 16.5 g of FeCl3? Final Prep Chap 12,13,17 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D B A C C B C D D C A C B B B D B D A A C A D A A PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: I I III III I I III III I I I I I I I I I I I I III III I I I PROBLEM 26. ANS: 0.104 M sucrose PTS: 1 27. ANS: 3.60 g NaOH DIF: III OBJ: 13-3.1 OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 12-3.1 12-3.4 12-3.5 12-3.5 13-2.2 13-2.2 13-3.1 13-3.3 17-1.1 17-1.1 17-4.2 12-2.1 12-3.2 12-3.2 12-3.3 13-1.3 13-1.4 13-2.1 13-2.3 17-1.2 17-1.3 17-1.3 17-1.4 17-2.2 17-3.2 PTS: 1 28. ANS: 79.0 g NaC2H3O2 DIF: III OBJ: 13-3.2 PTS: 1 29. ANS: 40.0 g Na2SO4 DIF: III OBJ: 13-3.2 PTS: 1 DIF: III 30. ANS: 50.9 mL HCl solution OBJ: 13-3.2 Balanced equation for reaction: Fe2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2FeCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) PTS: 1 DIF: III OBJ: 13-3.3