conjugation — giving the verb a subject
Anuncio

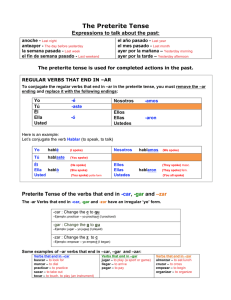
Preterite Congugation In Spanish, infinitives (to + a verb; ex: hablar—to talk) will end in –ar, –er, or –ir. conjugation — is giving the verb(infinitive) a subject preterite tense — is used to talk about a completed past event example: to swim—nadar I swam—nadé you swam—nadaste he swam—nadó she swam—nadó it swam—nadó you swam—nadó we swam—nadamos they swam—nadaron you(all) swam—nadaron example: to eat—comer I ate—comí you ate—comiste he ate—comió she ate—comió it ate—comió you ate—comió we ate—comimos they ate—comieron you(all) ate—comieron example: to live—vivir I lived—viví you lived—viviste he lived—vivió she lived—vivió it lived—vivió you lived—vivió we lived—vivimos hey lived—vivieron you(all) lived—vivieron A) conjugation endings yo tú él, ella, usted nosotros ellos, ellas, ustedes –ar –er –ir -é -aste -ó -amos -aron -í -iste -ió -imos -ieron -í -iste -ió -imos -ieron B) Stem Changing Preterite Verbs—verb conjugation where the stem of the verb changes. The stem of the verb is what remains when you remove the –ar, –er, or –ir ending from the infinitive form of the verb. There is NO stem changing for –ar and –er verbs in the preterite. ei ou ex: pedir ex: dormir *Note: The stem change only occurs in the el/ella/usted, and the ellos/ellas/ustedes forms. él, ella, usted ellos, ellas, ustedes sentir —to feel pedir—to ask for dormir—to sleep sentí sentiste sintió sentimos sintieron pedí pediste pidió pedimos pidieron dormí dormiste durmió dormimos durmieron C) Irregular Verbs—verbs that do not follow the conjugation pattern… ser—to be fui—I was fuiste—you were fue—he/she/it was, you were fuimos—we were fueron—they were, you were estar—to be estuve—I was estuvo—you were estuve—he/she/it was, you were estuvimos—we were estuvieron—they were, you were ir—to go fui—I went fuiste—you went fue—he/she/it went, you went fuimos—we went fueron—they went, you went hacer—to do/make hice—I made histe—you made hizo—he/she/it made, you made hicimos—we made hicieron—they made, you made dar—to give di—I gave diste—you gave dio—he/she/it gave, you gave dimos—we gave dieron—they gave, you gave tener—to have tuve—I had tuviste—you had tuvo—he/she/it had, you had tuvimos—we had tuvieron—they had, you had D) Irregular ―yo‖ form—verbs with the ―yo‖ conjugation that do not follow the conjugation pattern a. verbs ending in –car ex: buscar, explicar, tocar, practicar yo buscar—to look for busqué buscaste buscó buscamos buscaron tocar—to play toqué tocaste tocó tocamos tocaron explicar—to know expliqué explicaste explicó explicamos explicaron b. verbs ending in –zar ex: organizar, empezar, abrazar, alzar yo organizar—to organize organicé buscaste buscó buscamos buscaron empezar—to start empecé empezaste empezó empezamos empezaron abrazar—to hug abracé abrazaste abrazó abrazamos abrazaron c. verbs ending in –gar ex: jugar, apagar, pagar, llegar yo jugar—to play jugué jugaste jugó jugamos jugaron llegar—to arrive llegué llegaste llegó llegamos llegaron pagar—to pay pagué pagaste pagó pagamos pagaron E) –er and –ir verbs ending with a vowel ex: leer, oir, creer, traer él, ella, usted ellos, ellas, ustedes leer—to read leí leiste leyó leimos leyeron oir—to hear oí oiste oyó oimos oyeron creer—to believe creí creiste creyó creimos creyeron *Note: The change only occurs in the el/ella/usted, and the ellos/ellas/ustedes forms.