Satellite Swarm Spots North Pole Drift : Discovery News
Anuncio
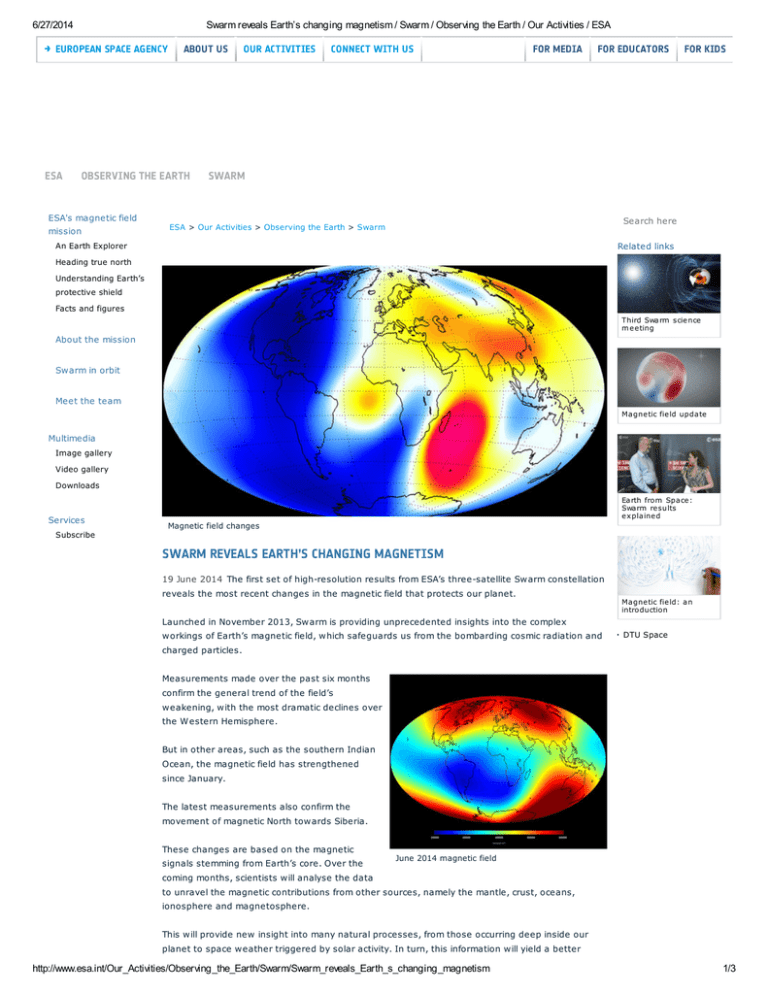
6/27/2014 Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism / Swarm / Observing the Earth / Our Activities / ESA → EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY ESA ABOUT US OBSERVING THE EARTH ESA's magnetic field mission OUR ACTIVITIES CONNECT WITH US FOR MEDIA FOR EDUCATORS FOR KIDS SWARM Search here ESA > Our Activities > Observing the Earth > Swarm Related links An Earth Explorer Heading true north Understanding Earth’s protective shield Facts and figures Third Swarm scie nce m e e ting About the mission Swarm in orbit Meet the team Magne tic fie ld update Multimedia Image gallery Video gallery Downloads Services Subscribe Earth from Space : Swarm re sults e x plaine d Magnetic field changes SWARM REVEALS EARTH’S CHANGING MAGNETISM 19 June 2014 The first set of high-resolution results from ESA’s three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. Magne tic fie ld: an introduction Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth’s magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and DTU Space charged particles. Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field’s weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the magnetic field has strengthened since January. The latest measurements also confirm the movement of magnetic North towards Siberia. These changes are based on the magnetic signals stemming from Earth’s core. Over the June 2014 magnetic field coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Observing_the_Earth/Swarm/Swarm_reveals_Earth_s_changing_magnetism 1/3 6/27/2014 Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism / Swarm / Observing the Earth / Our Activities / ESA understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening. “These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm,” said Rune Floberghagen, ESA’s Swarm Mission Manager. “With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm’s capability to map fine-scale features of the magnetic field.” The first results were presented today at the ‘Third Swarm Science Meeting’ in Copenhagen, Denmark. Earth's magnetic field Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Ørsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm’s core instrument – the Vector Field Magnetometer – was provided by the Technical University of Denmark. Denmark’s National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role – together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes – in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field. Swarm “I’m extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialised,” said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space. RATE THIS VIEWS 52351 SHARE Like Rating: 4.69/5 (123 votes Share Tw eet cast) 2.1k 434 90 29 points 137 RELATED ARTICLES Swarm’s precise sense of magnetism 07 May 2014 Swarm heads for new heights 06 February 2014 ESA’s Swarm trio on its way to watch over our planet’s magnetic shield 22 November 2013 @ESA_EO LATEST ARTICLES MOST-VIEWED ARTICLES MOST-VIEWED IMAGES http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Observing_the_Earth/Swarm/Swarm_reveals_Earth_s_changing_magnetism MOST-VIEWED VIDEOS 2/3 EARTH FROM SPACE: SPECIAL EDITION Earth from Space - Special ed1t1on Re leased: 03/ 04/ 2012 Rating ***** Earth from Space: Special edrt1on Re le ase d: 18/ 02/2014 Rating ***** RELATED LINKS Wa t chin: Ill f,!.!§ll!!.f.j,j. . Embe d Cod e . ~ .:irc=-• ht.t.p: //,,...,,,.,,.. esa . 'l.n t./ •p• C• 'l.n?'l.de o • / conee n~/ ?i e w/ embed.jv/ 43s ;•; • 1ll'l.dt.b.• • e40 • h.e l.9h.t.•_· •_•_o _· - - - --=A More 'Earth from Space' videos DETAILS T Titl e Earth from Space : Special edition Re le a sed 19/ 06/ 2014 Length 00 :05 : 58 Lan g u age English Foot a g e Type Interview Copyright ESA Description ESA Earth observation USING OUR VIDEOS Terms and Condrt:Jons Help Discover more about our planet with the Earth from Space video programme. Contact us In this special edition, Nils Olsen from DTU Space joins the show to discuss the la tes t measurements of Earth's magne tic field and changes observed over the last six months by ESA's Swarm mission. Our activities Observing the Carth [ Sea c r ESA > Our Activit ies > Soace News Human Spaceflight Launchers Navigation Space Science MOST VIEWED ARTICLES Article 1-10 of 3 51 page 1 o f 3 6 ............................................................................................................................................................................ l l 2 13 14 l 5 l 6 1718 19 l lO I > >> . ,_ Space Engineering Operations · Technology · Telecommunications & Integrated Applications Calendar ESA-sponsored conferences Dat e Views Art icle 19 Mar 20 13 268674 Black hole - star pair orbiting at dizzying speed 21 Mar2013 1677 13 Planck reveals an almost per fect Universe 20 Jan 20 14 84844 31Jan 20 13 689 15 Building a lunar base with 30 printing 17 Jan 20 13 66866 Reull Vallis: a river ran through it 19 Jun 20 14 52358 Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism .. SPACE IN VIDEOS I ESA's 'sleeping beauty' wakes up from deep space hibernation 10 Dec 20 13 52 196 Wake up, Rosetta! 02Apr 20 13 4 7605 Black hole wakes up and has a light snack 11 Nov 20 13 3759 1 GOCE gives in to gravity 10 Jan 20 14 35632 Suit up for Skinsuit Article 1-10 o f 3 51 page 1 o f 3 6 ············································································································································································ 1 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 110 1> >> Figures updated to 27/06/2014 - - - __ BBC News - Swarm mission makes magnetic maps News Sport Weather Capital Future Shop TV Radio More… Search SCIENCE & ENVIRONMENT Home UK Africa Asia Europe Latin America Mid-East US & Canada 20 June 2014 Last updated at 11:04 GMT Business Health Sci/Environment Share Tech Entertainment Video Top Stories EU signs pacts with ex-USSR states Swarm mission makes magnetic maps By Jonathan Amos Science correspondent, BBC News Summit set to snub UK over Juncker Sudan 'apostasy' woman freed again China 'denies food' to held academic Leukaemia clue in breast cancer Features & Analysis Forgotten flight The little-known story of one of the world's earliest hijackings Twice a day How Indian women manage without toilets Race against time Can Iraq sort itself out before it's too late to stop Isis? Best of frenemies Young Taiwanese protest against China, but also want to work there A field snapshot in June. Reds are strong; blues are weak. The view is dominated by the core contribution Europe's Swarm space mission has begun making maps of Earth's magnetic field. Related Stories Data just released shows how the field generated in the planet's liquid outer core varies in strength over the course of a few months. Swarm 'delivers on magnetic promise' Swarm's early assessment appears to support the prevailing view that this magnetic cloak in general is weakening. Many experts believe it heralds a flip in the poles, where north becomes south and vice versa, although it would take thousands of years to complete. The European Space Agency's Swarm mission was launched last November. It comprises three satellites that are equipped with a variety of instruments - the key ones being state-of-the-art magnetometers that measure field strength and direction. Satellites launch to map magnetism Mission to sense ocean magnetism Most Popular Shared Sudan death row woman freed again Amazon 'bullying' UK publishers Rooftop prisoners offered sun cream The long, dark walk to the toilet EU signs pacts with ex-USSR states Read EU signs pacts with ex-USSR states They fly in a configuration that offsets one platform from the other two. Pornographic videos flood YouTube The intention is that this should provide a three-dimensional view of the field, and make it easier to tease apart its various components. The long, dark walk to the toilet In the release this week from Esa, we get a view that is dominated by the EU summit set to confirm Juncker http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-27941557[27/06/2014 12:06:27] BBC News - Swarm mission makes magnetic maps contribution (95%) from the core. But eventually, Swarm will have the sensitivity to describe magnetism from other, more subtle sources, including that generated by the movement of our salt-water oceans. The story of a 60-year-old hijacking LaBeouf charged over theatre conduct The growing problem of Pablo Escobar’s hippos Bad review couple win compensation Maliki: Russian jets will turn tide Sudan death row woman freed again Video/Audio Harry visits Brazil's 'crack land' 'The most beautiful metro in the world' One-minute World News Putin aide calls Ukraine leader a Nazi Change in the field since January. Reds are a strengthening; blues are a weakening The maps on this page use the magnetic unit of a nanoTesla. Earth's field typically has a full strength of some 50,000nT. The moment Ukraine signed EU deal Obama congratulates Team USA Maliki: Russian jets purchased by Iraq The maps illustrate a snapshot (in June) and the change that occurs through time (January to June). In the latter, field strength is seen to drop over the western hemisphere but rise in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean. Who is the man leading Boko Haram? Webscape: Discover who takes Bitcoin Earth's magnetic field is worthy of study because it is the vital shield that protects the planet from all the charged particles streaming off the Sun. Without it, those particles would strip away the atmosphere, just as they have done at Mars. Investigating the magnetic field also has direct practical benefits, such as improving the reliability of satellite navigation systems which can be affected by magnetic and electrical conditions high in the atmosphere. "I started my career in magnetometry and the accuracy we had then in the laboratories was less than what we can fly in space now," explained Prof Volker Liebig, the director of Earth observation at Esa. "So what we have on Swarm is fantastic, but we need long time series to understand fully the Earth's magnetic field, and we will get that from this mission," he told BBC News. The alien brains living on Earth What creature has brains mostly in their arms? Read more... Programmes http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-27941557[27/06/2014 12:06:27] Date : 23/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Surface : 64 % Mots : 429 > Lire cet article sur le site web El Polo Norte magnético se desplaza hacia Siberia Los satélites de la misión Swarm confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético El Polo Norte magnético se desplaza ESA Copenhague. (Efe).- Los primeros resultados de la misión Swarm, el grupo de tres satélites lanzados en noviembre por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), confirman la tendencia general sobre el debilitamiento del campo magnético terrestre y el desplazamiento del Polo Norte magnético hacia Siberia. Según aseguraron los responsables del proyecto en una conferencia organizada por la ESA en Copenhague, el debilitamiento es mayor en el hemisferio occidental, aunque en otras áreas como el Índico sur se ha producido el fenómeno contrario. Las medidas registradas por Swarm desde enero pasado confirman también el desplazamiento progresivo del Polo Norte magnético hacia Siberia. Los expertos reunidos en Copenhague estimaron que en un plazo de entre 5.000 y 10.000 años habrá una inversión en el campo magnético, un fenómeno que se ha producido varias veces antes en la historia del planeta, la última hace 780.000 años. Nils Olsen, uno de los científicos al frente del proyecto, calificó de "excelentes" los datos preliminares aportados por la misión, aunque resaltó a Efe que ha pasado "demasiado poco tiempo" para sacar conclusiones más amplias sobre las mediciones de la operación, que durará cuatro años, y sus aplicaciones. Las alteraciones detectadas en los primeros resultados de Swarm están basadas en señales magnéticas del núcleo terrestre. Para las próximas observaciones se incluirán también otras fuentes de medición como el manto, la corteza, los océanos, la ionosfera y la magnetosfera, lo que permitirá un mayor conocimiento de diversos procesos naturales. La misión Swarm despegó del cosmódromo de Plesetsk (Rusia) en noviembre para estudiar los procesos en el interior de la Tierra, comprender mejor su campo magnético y por qué se está debilitando esta burbuja que protege el planeta de la radiación cósmica y las partículas cargadas que llegan a través del viento solar. La misión, que usa tecnología europea y canadiense, tiene también como objetivo aplicaciones prácticas, como mejorar la precisión de los sistemas de navegación por satélite y la predicción de terremotos o hacer más eficaz la extracción de recursos naturales. Los datos científicos -abiertos a toda la comunidad investigadora- se descargarán a través de la estación de seguimiento de Kiruna (Suecia) y se procesarán, distribuirán y archivarán en el Centro para la Observación de la Tierra de la ESA en Frascati (Italia). Te puede interesar: los usuarios que han consultado esto también han visto... Si todavía no estás registrado en LaVanguardia.com, regístrate ahora: El acceso se ha realizado correctamente. Muchas gracias. Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ALLEMAGNE Périodicité : Quotidien Surface : 40 % Mots : 340 (Zusammenfassung 1545) «Swarm»-Satelliten: Erdmagnetfeld wird nicht überall schwächer (Foto - Archiv und Foto-Illustration) Seit November sind die drei europäischen «Swarm»-Satelliten unterwegs im All. Sie nehmen das Magnetfeld der Erde unter die Lupe. Der Schutzschild wird schwächer - aber nicht überall. Kopenhagen (dpa) - Das lebenswichtige Magnetfeld der Erde wird zur Verblüffung von Weltraumforschern nicht überall schwächer. Das geht aus ersten Daten des europäischen Satelliten-Trios «Swarm» hervor, die Wissenschaftler der europäischen Weltraumagentur Esa am Donnerstag bei einer Konferenz in Kopenhagen vorstellten. Der Schutzschild vor gefährlichen Teilen aus dem All nimmt seit vielen Jahrzehnten langsam ab. «In manchen Regionen haben wir aber sogar eine Intensivierung, zum Beispiel südöstlich von Afrika», sagte der Forscher Nils Olsen. Am stärksten nimmt das Magnetfeld dagegen in der westlichen Hemisphäre ab. Mancherorts, wie etwa in der Südatlantik-Region, werde das Feld sogar bis zu zehn Mal so schnell schwächer als im globalen Durchschnitt, berichteten die Forscher. Die Satelliten «Alpha», «Bravo» und «Charlie» sind seit November 2013 in einer Höhe von rund 500 Kilometern unterwegs und liefern seitdem genaue Daten über Stärke, Richtung und Schwankungen des Magnetfeldes. Die große Errungenschaft, die sich die Forscher von dem Einsatz der Satelliten erhoffen, ist eine weltweite detaillierte Übersicht über das Magnetfeld und seine Veränderungen. Weil durch Teilchenschauer etwa Stromnetze gestört werden könnten, sei es «wichtig zu wissen, wie ein magnetisches Feld sich entwickelt», sagte Olsen. Die ersten Satellitendaten haben außerdem die Wanderung des magnetischen Nordens Richtung Sibirien bestätigt. Durch das «Swarm»-Trio wollen die Wissenschaftler auch Aufschlüsse etwa über das Weltraumwetter gewinnen. Die Satelliten könnten nach Einschätzung der Forscher viel länger im All bleiben als geplant. «Wir nehmen an, dass "Swarm" länger dauert als vier Jahre - alles sieht danach aus», sagte der Wissenschaftler Roger Haagmans. Bis zu zehn Jahre könnten die drei baugleichen Satelliten demnach den lebenswichtigen Schutzschild vor gefährlichen Teilchen aus dem All erkunden. # dpa-Notizblock Missing Internet [Esa](http://dpaq.de/8dJDY) [Die Swarm-Mission](http://dpaq.de/zYwQU) [Mitteilung Esa](http://dpaq.de/ASr4R) Missing Orte - [IDA Conference Center](Kalvebod Brygge 31, 1560 København V, Dänemark) dpa wbj xx z2 si 191549 Jun 14 Copyright: dpa Deutsche Presse-Agentur GmbH (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ALLEMAGNE Périodicité : Quotidien Surface : 22 % Mots : 178 Satelliten-Trio «Swarm» könnte viel länger im All bleiben als geplant (Foto - Archiv) Kopenhagen (dpa) - Das europäische Satelliten-Trio «Swarm» könnte das Magnetfeld der Erde vom All aus viel länger untersuchen als geplant. «Wir nehmen an, dass "Swarm" länger dauert als vier Jahre - alles sieht danach aus», sagte der Wissenschaftler Roger Haagmans am Donnerstag bei einer «Swarm»-Konferenz in Kopenhagen. Bis zu zehn Jahre könnten die drei baugleichen Satelliten der europäischen Weltraumagentur Esa demnach den lebenswichtigen Schutzschild vor gefährlichen Teilchen aus dem All unter die Lupe nehmen. «Alpha», «Bravo» und «Charlie» sind seit November 2013 in einer Höhe von rund 500 Kilometern unterwegs und liefern seitdem genaue Daten über Stärke, Richtung und Schwankungen des Magnetfeldes. Dieses wird wie von den Wissenschaftlern erwartet schwächer - aber nicht überall gleichermaßen, haben die Forscher schon herausgefunden. # dpa-Notizblock Missing Redaktionelle Hinweise - Zusammenfassung bis 1600 - ca. 30 Zl. Missing Internet - [Esa](http://dpaq.de/8dJDY) - [Die Swarm-Mission](http://dpaq.de/zYwQU) Missing Orte - [IDA Conference Center](Kalvebod Brygge 31, 1560 København V, Dänemark) dpa wbj xx n1 si 191432 Jun 14 Copyright: dpa Deutsche Presse-Agentur GmbH (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Page(s) : 1 Surface : 67 % (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Surface : 56 % efefuturo.com Mots : 379 > Lire cet article sur le site web Satélites de la misión Swarm confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético Copenhague (EFEfuturo).- Los primeros resultados de la misión Swarm, el grupo de tres satélites lanzados en noviembre por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), confirman la tendencia general sobre el debilitamiento del campo magnético terrestre. Jueves 19.06.2014 Según aseguraron hoy los responsables del proyecto en una conferencia organizada por la ESA en Copenhague, el debilitamiento es mayor en el hemisferio occidental, aunque en otras áreas como el Índico sur se ha producido el fenómeno contrario. Las medidas registradas por Swarm desde enero pasado confirman también el desplazamiento progresivo del Polo Norte magnético hacia Siberia. Los expertos reunidos en Copenhague estimaron que en un plazo de entre 5.000 y 10.000 años habrá una inversión en el campo magnético, un fenómeno que se ha producido varias veces antes en la historia del planeta, la última hace 780.000 años. Nils Olsen, uno de los científicos al frente del proyecto, calificó de "excelentes" los datos preliminares aportados por la misión, aunque resaltó a Efe que ha pasado "demasiado poco tiempo" para sacar conclusiones más amplias sobre las mediciones de la operación, que durará cuatro años, y sus aplicaciones. Las alteraciones detectadas en los primeros resultados de Swarm están basadas en señales magnéticas del núcleo terrestre. Para las próximas observaciones se incluirán también otras fuentes de medición como el manto, la corteza, los océanos, la ionosfera y la magnetosfera, lo que permitirá un mayor conocimiento de diversos procesos naturales. La misión Swarm despegó del cosmódromo de Plesetsk (Rusia) en noviembre para estudiar los procesos en el interior de la Tierra, comprender mejor su campo magnético y por qué se está debilitando esta burbuja que protege el planeta de la radiación cósmica y las partículas cargadas que llegan a través del viento solar. La misión, que usa tecnología europea y canadiense, tiene también como objetivo aplicaciones prácticas, como mejorar la precisión de los sistemas de navegación por satélite y la predicción de terremotos o hacer más eficaz la extracción de recursos naturales. Los datos científicos -abiertos a toda la comunidad investigadora- se descargarán a través de la estación de seguimiento de Kiruna (Suecia) y se procesarán, distribuirán y archivarán en el Centro para la Observación de la Tierra de la ESA en Frascati (Italia). EFE (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 20/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Page(s) : 40 Diffusion : (95855) Périodicité : Quotidien Surface : 13 % (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 20/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Surface : 56 % Mots : 375 > Lire cet article sur le site web Confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético de la Tierra - La Razón digital Los primeros resultados de la misión Swarm, el grupo de tres satélites lanzados en noviembre por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), confirman la tendencia general sobre el debilitamiento del campo magnético terrestre. Según aseguraron los responsables del proyecto en una conferencia organizada por la ESA en Copenhague, el debilitamiento es mayor en el hemisferio occidental, aunque en otras áreas como el Índico sur se ha producido el fenómeno contrario. Las medidas registradas por Swarm desde enero pasado confirman también el desplazamiento progresivo del Polo Norte magnético hacia Siberia. Los expertos reunidos en Copenhague estimaron que en un plazo de entre 5.000 y 10.000 años habrá una inversión en el campo magnético, un fenómeno que se ha producido varias veces antes en la historia del planeta, la última hace 780.000 años. Nils Olsen, uno de los científicos al frente del proyecto, calificó de «excelentes» los datos preliminares aportados por la misión, aunque resaltó a Efe que ha pasado «demasiado poco tiempo» para sacar conclusiones más amplias sobre las mediciones de la operación, que durará cuatro años, y sus aplicaciones. Las alteraciones detectadas en los primeros resultados de Swarm están basadas en señales magnéticas del núcleo terrestre. Para las próximas observaciones se incluirán también otras fuentes de medición como el manto, la corteza, los océanos, la ionosfera y la magnetosfera, lo que permitirá un mayor conocimiento de diversos procesos naturales. La misión Swarm despegó del cosmódromo de Plesetsk (Rusia) en noviembre para estudiar los procesos en el interior de la Tierra, comprender mejor su campo magnético y por qué se está debilitando esta burbuja que protege el planeta de la radiación cósmica y las partículas cargadas que llegan a través del viento solar. La misión, que usa tecnología europea y canadiense, tiene también como objetivo aplicaciones prácticas, como mejorar la precisión de los sistemas de navegación por satélite y la predicción de terremotos o hacer más eficaz la extracción de recursos naturales. Los datos científicos -abiertos a toda la comunidad investigadora- se descargarán a través de la estación de seguimiento de Kiruna (Suecia) y se procesarán, distribuirán y archivarán en el Centro para la Observación de la Tierra de la ESA en Frascati (Italia). (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ITALIE Surface : 61 % (1/2)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ITALIE Surface : 61 % (2/2)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Date : 19/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Surface : 98 % Mots : 663 > Lire cet article sur le site web España hace negocio en órbita Se situará en una órbita a 620 kilómetros de altitud desde donde tomará imágenes en alta resolución de la superficie terrestre Lanzamiento del Deimos-2 - El satélite español de observación de la Tierra se situará en una órbita a 620 kilómetros de altitud El satélite español de observación de la Tierra Deimos-2 está a punto para ser lanzado al espacio hoy jueves a las 21.11 (hora española) desde la base rusa de Dombarovsky. Construido por la empresa Elecnor Deimos, el satélite se situará en una órbita a 620 kilómetros de altitud desde donde tomará imágenes en alta resolución de la superficie terrestre. Las imágenes se comercializarán para, entre otros objetivos, mejorar la gestión de cosechas, la prevención de hambrunas, el control de la piratería en el Índico y la reacción ante incendios o inundaciones.Deimos-2 es el sucesor de Deimos-1, misión pionera que ha demostrado que un satélite español financiado únicamente con capital privado puede ser rentable. Lanzado hace cinco años, Deimos-1 ha conseguido como principales clientes al Gobierno de Estados Unidos -que le contrata para suministrar datos que permitan optimizar las cosechas- y la Unión Europea -que le contrata, por ejemplo, para monitorizar sequías en África y enviar ayuda humanitaria a tiempo-."Tenemos clientes en todo el mundo. Hacemos desde detección de cultivos ilegales en Colombia hasta control de inundaciones en Australia, terremotos en Japón o ayudar en la búsqueda del avión de Malasia", explica Miguel Belló, director general de Elecnor Deimos.Con el nuevo satélite, la empresa prevé mejorar su servicio. Si Deimos-1 capta imágenes de 650 kilómetros de lado y fotografía la superficie terrestre como un gran angular, Deimos-2 aumenta la resolución hasta los 12 kilómetros y la fotografía como un teleobjetivo. Tener los dos satélites simultáneamente en órbita permitirá a Elecnor Deimos ofrecer a sus clientes al mismo tiempo una visión de conjunto y una visión detallada de las zonas de más interés. "Cuando rastreamos piratas en el Índico, por ejemplo, nos interesa tener una resolución muy alta", señala Belló.La misión tiene un presupuesto total de 60 millones de euros -frente a los 25 millones de Deimos-1- y una duración prevista de siete años. Si el satélite sigue en buen estado en el año 2021, en principio se prorrogará la misión. También está previsto prolongar la de Deimos-1, que en principio debía retirarse en el 2015 pero se conserva en buen estado.Para el lanzamiento se ha contratado un cohete ruso Dnepr, un antiguo misil de la guerra fría al que se ha retirado la cabeza nuclear para reutilizarlo -y venderlo- con fines no militares. Unos quince minutos después del lanzamiento, el satélite se situará en una órbita que sobrevolará los polos y posteriormente desplegará sus cuatro paneles solares. Deimos-2 va equipado además con un motor de propulsión iónica alimentado con xenón para corregir su trayectoria cuando sea preciso. Con 300 kilos de peso, tres metros de longitud y uno de anchura (sin contar los paneles solares), se trata de un satélite pequeño para el que la propulsión iónica es ideal.Una vez en órbita, se comprobará que todos los dispositivos del satélite funcionan correctamente desde el centro de control de la misión ubicado en Puertollano (Castilla-La Mancha). Aunque las primeras imágenes llegarán en los próximos días, harán falta varios meses para calibrar la cámara antes de iniciar su explotación comercial. Con unos 350 trabajadores, la mayoría de ellos ingenieros, Elecnor Deimos es una empresa íntegramente española. Fue fundada en el 2001 y trabajó desde sus inicios en proyectos de la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), con lo que adquirió la experiencia necesaria para construir y comercializar sus propios satélites. En el 2006 incorporó al astronauta Pedro Duque, que acababa de obtener una excedencia de cinco años de la ESA, para dirigir la puesta en marcha del programa de satélites Deimos. Te puede interesar: los usuarios que han consultado esto también han visto... Si todavía no estás registrado en LaVanguardia.com, regístrate ahora: El acceso se ha realizado correctamente. Muchas gracias. (1/1)EARTH OBSERVATION Tous droits de reproduction réservés Il campo magnetico della Terra è sempre più debole. I risultati di Swarm | Effetto Terra Forum Scienza BLOG Ambiente EFFETTO TERRA Newsletter Cultura REGISTRATI Edicola Tecnologia Comportamento LOGIN Video iFocus GEOLOGIA CAMPO MAGNETICO SEMPRE PIÙ DEBOLE. CHE SUCCEDERÀ ALLA TERRA? Cerca Cerca GEOLOGIA Campo magnetico sempre più debole. Che succederà alla Terra? Il satellite europeo Swarm ha iniziato a mappare il campo magnetico terrestre. Confermando alcuni trend e aiutandoci a capire l’evoluzione del magnetismo terrestre. Su questo blog Questo blog ha il desiderio di raccontare la vita, le storie, il palpito del nostro Pianeta, la Terra. L'unico pianeta che, ad oggi, conosciamo possedere una vita intelligente. Il nostro pianeta è in continua evoluzione. Vulcani, terremoti, uragani e tornado, ma anche piccoli ruscielli di montagna, dolci colline e i grandi oceani ci dicono che il nostro pianeta è vivo. E come ogni essere vivente vivo, ogni giorno ha un nuovo racconto da rivelarci. E fin che sarà possibile cercheremo insieme, ossia anche con l'aiuto di chi legge, di raccontare le sue storie, i suoi palpiti e i suoi sussulti. Chi cercherà di tenere le fila di questo racconto è Luigi Bignami. Sono un geologo che ha come obiettivo di raccontare a chi ha poco tempo di seguire tutti gli avvenimenti che interessano la Terra, ma che ne è Il colore blu indica un indebolimento del campo magnetico terrestre, quello rosso un rafforzamento Il campo magnetico terrestre che ci protegge dalle radiazioni provenienti dal cosmo e che indirizza la bussola verso il Polo Nord si sta indebolendo. Lo si sapeva già da tempo, ma ora c’è una certezza assoluta. Lo ha stabilito il satellite Swarm dell’Esa. Lanciato nel novembre 2013, Swarm fornisce dati senza precedenti sul complesso funzionamento del campo magnetico della Terra. http://blog.focus.it/effetto-terra/2014/06/21/campo-magnetico-sempre-piu-debole-che-succedera-alla-terra/[27/06/2014 13:44:08] interessato, quel che avviene giorno dopo giorno al nostro pianeta e di vivere insieme a voi la grande avventura dell'esplorazione di questa "astronave", davvero rara, se non unica nel suo genere. Post più letti 1. Ecco il "primo extraterrestre" caduto sulla Terra Il campo magnetico della Terra è sempre più debole. I risultati di Swarm | Effetto Terra 2. Prime luci sulla misteriosa struttura del Mar Baltico 3. E se 2012 DA14... Le misurazioni effettuate nel corso degli ultimi sei mesi confermano la tendenza generale di indebolimento del campo magnetico, con un calo davvero drammatico che sta verificandosi nell’emisfero occidentale. In altre aree del pianeta, tuttavia, come sull’Oceano Indiano meridionale, il campo magnetico si sta rafforzato da gennaio. 4. Terremoto in Adriatico. C'è pericolo tsunami? 5. La colpa del freddo è la mancanza di ghiacci polari 6. Terremoto in Campania, non si fa così! 7. I terremoti che hanno colpito l'Italia 8. Terremoto in Emilia Romagna 9. Nuove scosse in Emilia: perché il terremoto non è E si sposta. Le ultime misurazioni, tra l’altro, confermano anche il movimento del Polo Nord magnetico verso la Siberia. Questi cambiamenti sono basati sui segnali magnetici che hanno il loro motore nel nucleo della Terra. In particolare nel nucleo esterno dove il movimento del ferro allo stato liquido produce il campo magnetico terrestre. terminato 10. Gli studi per prevedere i terremoti (parte prima) Archivio Seleziona mese Seleziona mese Nel corso dei prossimi mesi, gli scienziati analizzeranno i dati per svelare i contributi magnetici provenienti da altre fonti, vale a dire dal mantello, dalla crosta, dagli oceani, dalla ionosfera e dalla magnetosfera. Categorie Ciò fornirà una nuova visione di molti processi naturali, da quelli che si verificano in profondità all’interno del nostro pianeta fino a quelli prodotti dall’attività solare. A sua volta, questa informazione produrrà una migliore comprensione del perché il campo magnetico si sta indebolendo. «Questi primi risultati dimostrano l’ottima performance di Swarm», ha dichiarato Rune Floberghagen, Mission Manager di Swarm. «Con una risoluzione senza precedenti, i dati mostrano valori molto particolareggiati per ogni singola area del pianeta, fondamentale per capire cosa sta avvenendo a livello globale al campo magnetico». Blogroll Ambiente Documentation Animali Plugins Archeologia Suggest Ideas Clima Support Forum Curiosity Themes Energia WordPress Blog Esopianeti WordPress Planet Geologia Ghiacci Marte Misteri Natura Osservare la Terra dal I primi risultati sono stati presentati 19 giugno 2014 presso il terzo Swarm Science Meeting a Copenhagen, Danimarca. cielo Senza categoria Spazio I più colpiti saranno gli animali. Ma cosa significa un campo magnetico sempre più debole? Al momento gli scienziati non si sbilanciano, ma stando ad alcune previsioni potrebbe voler dire che siamo vicini ad un’inversione del campo medesimo. Questo potrebbe portare il Polo Nord a diventare il Polo Sud e viceversa. Tranquilli, ci metterà migliaia di anni e non sarà un evento così repentino. Terremoto Il fenomeno dell’inversione dei poli è già successo tante volte nel passato remoto della Terra, ma mai da che esiste l’ Homo sapiens e dunque non sappiamo esattamente si ci potrebbero essere delle ripercussioni. TUTTI I BLOG Uomini del Pianeta Terra Vulcani preistoria Focus su Twitter Certo è che ce ne potrebbero essere per molti animali, soprattutto uccelli, che utilizzano il campo magnetico per le migrazioni. Di luigibignami Pubblicato 21 giugno 2014 0 Tag: 250 22 3 5 Tweet Lascia un Commento L'oasi del Mar Morto L'indirizzo email non verrà pubblicato. I campi obbligatori sono contrassegnati * dead-sea-wonder-of-nature.com Nome * Il bacino più basso del mondo Sorgenti, piscine e piante uniche! Email * http://blog.focus.it/effetto-terra/2014/06/21/campo-magnetico-sempre-piu-debole-che-succedera-alla-terra/[27/06/2014 13:44:08] Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism -- ScienceDaily Mobile: iPhone ? Health Latest Headlines Android Web PhYsical/Tech Follow: Facebook Twitter EnVirOnment Health & Medicine Mind & Brain Featured Research Google+ SOcietY/EducatiOn Space & Time Matter & Energy Subscribe: RSS Feeds QuirKY Computers & Math Plants & Animals from universities, journals, and other organizations Search Earth & Climate Save/Print: Fossils & Ruins Share: Breaking News: Superconductor World Record Set Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism Date: June 20, 2014 Email Newsletters Enter keyword or phrase ... Share This Source: European Space Agency Summary: The first set of high-resolution results from ESA's three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth's magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field's weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. Email to a friend Facebook Twitter Google+ Print this page More options Related Topics Earth & Climate Atmosphere Geomagnetic Storms Related Stories Geology Earth Science How Solar Wind Can Break Through Earth's Magnetic Field Weather June 9, 2014 — Space is not empty. A wind of charged particles blows outwards from the Sun, carrying a magnetic field with it. Sometimes this solar wind can break through the Earth’s magnetic field. Researchers ... full story Environmental Awareness Related Articles Geophysics Tide Satellite Trio to Explore the Earth's Magnetic Field Earth Power station Radiant energy Temperature record of the past 1000 years Changes in Earth’s magnetic field from January to June 2014 as measured by the Swarm constellation of satellites. These changes are based on the magnetic signals that stem from Earth’s core. Shades of red represent areas of strengthening, while blues show areas of weakening over the 6-month period. Credit: ESA/DTU Space T [Click to enlarge image] he first set of high-resolution results from ESA's three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth's magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field's weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the magnetic field has strengthened since January. Studio sul colesterolo clinlife.it/Colesterolo… Cerchiamo persone con malattie cardiovascolari. Altre informazioni The latest measurements also confirm the movement of magnetic North towards Siberia. These changes are based on the magnetic signals stemming from Earth's core. Over the coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/06/140620115751.htm[27/06/2014 13:45:41] Nov. 22, 2013 — In a dense fog, a Russian Rockot rocket on 22 November 2013 cleared the launchpad of the Baikonur Cosmodrome on schedule at 13:02:15 CET. In the tip of the rocket: three identical satellites to ... full story Swarm Intelligence: New Collective Properties of Swarm Dynamics Uncovered Mar. 15, 2013 — A new study of animal swarms uncovers some new features of their collective behavior when overcrowding sets in. Swarming is the spontaneous organized motion of a large number of individuals. It is ... full story Rapid Changes in the Earth's Core: The Magnetic Field and Gravity from a Satellite Perspective Oct. 22, 2012 — Annual to decadal changes in Earth's magnetic field in a region that stretches from the Atlantic to the Indian Ocean have a close relationship with variations of gravity in this area. From this ... full story The Science Behind Those EyePopping Northern Lights Oct. 2, 2012 — Stormy weather on the sun drives the glistening aurorae Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism -- ScienceDaily other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. in our clear night ... full story This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening. more related stories "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen, ESA's Swarm Mission Manager. "With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm's capability to map finescale features of the magnetic field." The first results were presented June 19, 2014 at the 'Third Swarm Science Meeting' in Copenhagen, Denmark. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Ørsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm's core instrument -- the Vector Field Magnetometer -- was provided by the Technical University of Denmark. Denmark's National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role -- together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes -- in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field. "I'm extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialised," said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space. Trending Topics from the past week Plants & Animals Insects (including Butterflies) Story Source: The above story is based on materials provided by European Space Agency. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length. Zoology Cite This Page: Genetics Biotechnology and Bioengineering Microbiology MLA APA Chicago Soil Types European Space Agency. "Swarm reveals Earth’s changing magnetism." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 20 June 2014. <www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/06/140620115751.htm>. Bacteria Birds Earth & Climate Air Quality Share This Pollution Email to a friend Renewable Energy Facebook Water Twitter Geochemistry Google+ Energy and the Environment Print this page Geography More options Snow and Avalanches Fossils & Ruins Ancient DNA Cultures Early Climate Origin of Life Charles Darwin More Earth & Climate News Friday, June 27, 2014 Human Evolution Ancient Civilizations Featured Research Bloodsucking Mite Threatens UK Honeybees from universities, journals, and other organizations Bloodsucking Mite Threatens UK Honeybees Water-Cleanup Catalysts Tackle Biomass Upgrading Fossils In Other News ... from NewsDaily.com June 26, 2014 — Scientists have discovered how a bloodsucking parasite has transformed Deformed Wing Virus (DWV) into one of the biggest threats facing UK honeybees. Honeybees are a key pollinating insect, adding ... full story Geothermometer for Methane Formation Developed Science News Animals Built Reefs 550 Million Years Ago Ancient Ocean Currents: Effect On Ice Ages California scientists discover mouse-like mammal related to elephants How Electric Fish's Jolt Evolved: Genomic Basis Hawaii at center of battle over aquarium fish Foul Fumes Derail Dinner for Hungry Moths Virology; Agriculture and Food; Microbes and More; Pests and Parasites New Species of Elephant-Shrew Discovered Reef madness: scientists find oldest animal-built marine structure Optical Fibers for Use in Harsh Environments Organics Boosts Biodiversity On Farmlands newer top stories | older top stories Warning, high voltage: scientists solve mysteries of electric fish Russia to debut first new space rocket design since Soviet era Health News http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/06/140620115751.htm[27/06/2014 13:45:41] Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Free Newsletters - Space - Defense - Environment - Energy - Solar - Nuclear .. your email address . . ► NASA Space ► NASA Earth ► The Earth ► Earth First Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism by Staff Writers Paris (ESA) Jun 20, 2014 The first set of high-resolution results from ESA's three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth's magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field's weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the Changes in Earth's magnetic field from January to June 2014 as measured by the Swarm magnetic field has strengthened since constellation of satellites. These changes are January. based on the magnetic signals that stem from Earth's core. Shades of red represent areas of The latest measurements also confirm the strengthening, while blues show areas of movement of magnetic North towards Siberia. weakening over the 6-month period. Image courtesy ESA/DTU Space. For a larger version of These changes are based on the magnetic this image please go here. signals stemming from Earth's core. Over the coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. http://www.spacemart.com/reports/Swarm_reveals_Earths_changing_magnetism_999.html[27/06/2014 15:35:17] Space weather report for an subscribe free Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening. "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen, ESA's Swarm Mission Manager. "With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm's capability to map finescale features of the magnetic field." The first results were presented at the 'Third Swarm Science Meeting' in Copenhagen, Denmark. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Orsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm's core instrument - the Vector Field Magnetometer - was provided by the Technical University of Denmark. Denmark's National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role - together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes - in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field. "I'm extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialised," said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space. . alien world Paris (ESA) Jun 10, 2014 For the first time, ESA is providing regular space-weather reports for a spacecraft orbiting another planet. When your spacecraft is surfing deep into the atmosphere of an alien world, you need the latest information on conditions that could affect your trajectory. If that planet is Venus, that means knowing what's happening on our Sun in real time, because solar activity can greatly influ ... read more Scientists see Earth's most abundant mineral for the first time Researchers develop efficient approach to manufacture 3D metal parts Selex ES is upgrading RAT 31 DL radar in Turkey Defense against laser beam flashes at aircraft being tested Exelis enhancing communications for NATO country Chemring integrates new system with Resolve Northrop Grumman Receives Funding for Electronic Warfare Systems for US Army and Navy UK Connects with Allied Protected Communication Satellites European satellite chief says industry faces challenges Payload fueling begins for nexy Arianespace Soyuz flight Arianespace A World Leader In The Satellite Launch Market Airbus Group and Safran To Join Forces in Launcher Activities Soyuz Rocket puts Russian GLONASS-M navigation satellite into orbit Russia may join forces with China to compete with US, European satnavs Related Links ESA Swarm The latest information about the Commercial Satellite Industry ► Earth First ► Earth Ocean ► Earth World ► Earth Map http://www.spacemart.com/reports/Swarm_reveals_Earths_changing_magnetism_999.html[27/06/2014 15:35:17] Russia Says GLONASS Accuracy Could Be Boosted to Two Feet Northrop Grumman tapped for new miniature navigation system European Space Agency says magnetic north is drifting southward Free Newsletters - Space - Defense - Environment - Energy - Solar - Nuclear .. your email address . . ► NASA Space ► The Earth ► NASA Earth ► Esa European Space Agency says magnetic north is drifting southward by Brooks Hays London (UPI) Jun 23, 2013 The Earth's magnetic north pole is drifting southward towards Siberia, according to researchers at the European Space Agency (ESA). As part of ESA's Swarm mission, scientists have been mapping the planet's magnetic field with the help three satellites. Each satellite is equipped with several Earth-studying tools -including magnetometers, which measure the magnetic field's strength and direction. "I started my career in magnetometry and the accuracy we had then in the laboratories was disclaimer: image is for illustration purposes only less than what we can fly in space now," Volker Liebig, the director of Earth observation at ESA, recently told BBC News. "So what we have on Swarm is fantastic, but we need long time series to understand fully the Earth's magnetic field, and we will get that from this mission." Results from the Swarm mission suggest that not only is magnetic north on the move, but the entire magnet field is weakening, leaving Earth potentially exposed to additional cosmic radiation. This, however, is considered normal, with the magnet cloak likely to regain its strength in the near future. Analysis of ancient rocks buried deep in the Earth lead scientists to believe Earth's http://www.spacedaily.com/reports/European_Space_Agency_says_magnetic_north_is_drifting_southward_999.html[27/06/2014 15:37:07] Monitoring climate change subscribe free European Space Agency says magnetic north is drifting southward magnetic north and south poles switch every few million years. The latest from Swam suggests the poles may once again be preparing to trade sides; though the flip-flop itself takes several thousand years. A study published in 2011 surmised that the shifting magnetic poles are affected by the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. Currently, Swarm satellites have only honed in on the general magnetic field generated by Earth's molten core. But scientists expect to study more delicate magnetic fields in the future, such as the field generated by the movement of the world's oceans. "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen, ESA's Swarm Mission Manager. "With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm's capability to map fine-scale features of the magnetic field." Graphene Is The Future . from space Paris (ESA) Jun 16, 2014 How do measurements from satellites flying above Earth provide essential information on the effects of climate change on our planet? Scientific and political organisations considered the question in London. Held at the Royal Society, the 'Space: the new view on climate change' event focused on climate change monitoring by satellites and the achievements of ESA's Climate Change Initiative. ... read more NASA LRO's Moon As Art Collection Is Revealed Solar photons drive water off the moon 55-year old dark side of the moon mystery solved New evidence supporting moon formation via collision of 2 planets outsiderclub.com/Graphene Learn How It Will Change The World It's All In This Free Investor Rpt. Curiosity celebrates one-year Martian anniversary Aluminum-Bearing Site on Mars Draws NASA Visitor Mars Curiosity Rover Marks First Martian Year with Mission Successes NASA Invites Comment on Mars 2020 Environmental Impact Statement Orion Parachute Test Hits No Snags Related Links NASA has a Problem with Unauthorized Access to it's Technologies Earth Observation News - Suppiliers, Technology and Application ► Esa Recommend Recommend ► Map Earth ► New Earth ► More Space Share You and 21 others recommend this.21 people recommend this. Be the first of your friends. Elon Musk plans to take people to Mars within 10 years Tweet 16 Moon to see first tourists by 2017, single roundtrip ticket costs $150 mln Chinese lunar rover alive but weak China's Jade Rabbit moon rover 'alive but struggling' Comment on this article via your Facebook, Yahoo, AOL, Hotmail login. Chinese space team survives on worm diet for 105 days Moon rover Yutu comes closer to public Add a comment... ✔ A Laser Message from Space Also post on Facebook Posting as Mariangela D'Acunto (Not you?) http://www.spacedaily.com/reports/European_Space_Agency_says_magnetic_north_is_drifting_southward_999.html[27/06/2014 15:37:07] Comment Comment using... D-Day for the International Space Station Swarm Mission Reveals Earth's Weakening Magnetic Field : Space : Nature World News SECTIONS Swarm Mission Reveals Earth's Weakening Magnetic Field 4 Comments By Jenna Iacurci Like 26 Tweet 5 0 Share 1 E-mail Text Size Jun 24, 2014 10:13 AM EDT The European Space Agency's (ESA) Swarm mission recently revealed Earth's weakening magnetic field, which is necessary to protect our planet from bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. (Photo : ESA/DTU Space) The European Space Agency's (ESA) Swarm mission recently revealed Earth's weakening magnetic field, which is necessary to protect our planet from bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Launched in November 2013, the three-satellite Swarm constellation provided high-resolution insight into the complex workings of Earth's magnetic field, using instruments such as magnetometers that measure field strength and direction. Six months of measurements confirmed that the field is continuously weakening, with the most dramatic declines over http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/7731/20140624/swarm-mission-reveals-earths-weakening-magnetic-field.htm[27/06/2014 15:20:09] Swarm Mission Reveals Earth's Weakening Magnetic Field : Space : Nature World News the Western Hemisphere. SHARE THIS STORY 5 26 0 Tweet Like Though the general trend is a fading one, other areas like the southern Indian Ocean have actually strengthened since January. The latest measurements also confirm the shifting of magnetic North towards Siberia. 1 Share RELATED ARTICLES Evenly Matched: Magnetic Fields vs Black Holes' Pull Magnetic 'Fingerprint' of the Galaxy May Help Uncover Details of the Big Bang Results from the Swarm mission suggest that the magnetic cloak is once again switching sides, where north becomes south and vice versa. Although, experts note that this "flip-flop" could take thousands of years, BBC News reported. Researchers believe that the magnetic field will most likely regain its strength in the future - hopefully sooner rather than later because it is a vital shield from charged particles streaming off of the Sun. Without it, those particles would strip away the atmosphere, just as they have done to Mars. These changes are based on magnetic changes stemming from the Earth's core, but in the coming months researchers plan to investigate changes from other sources as well, such as the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere, according to the ESA press release. This will provide new insight into many natural processes, and also possibly explain why the field is weakening. Another practical benefit is improving the reliability of satellite navigation systems which can be affected by magnetic and electrical conditions high in the atmosphere. "I started my career in magnetometry and the accuracy we had then in the laboratories was less than what we can fly in space now," Professor Volker Liebig, the director of Earth observation at ESA, explained to BBC News. "So what we have on Swarm is fantastic, but we need long time series to understand fully the Earth's magnetic field, and we will get that from this mission," he said. The first results were presented June 19, 2014 at the 'Third Swarm Science Meeting' in Copenhagen, Denmark. Tags Magnetic field , Earth , ESA TV Das Original Clean Maxx AEG Electrolux Junior 2.0 1087 Aspirabriciole a … Aspirabriciole a batteria … €27,71 €24,98 http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/7731/20140624/swarm-mission-reveals-earths-weakening-magnetic-field.htm[27/06/2014 15:20:09] Satellite Swarm Spots North Pole Drift : Discovery News 8 Places Humans and Wild Animals Clash Earth Satellite Swarm Spots North Pole Drift Jun 22, 2014 03:33 AM ET // by Jason Major View Related Gallery » Swarm measurements of Earth’s magnetic field from June 2014. Blue areas show where it has weakened. ESA/DTU Space http://news.discovery.com/earth/satellite-swarm-spots-north-pole-drift-140622.htm[27/06/2014 15:04:26] Satellite Swarm Spots North Pole Drift : Discovery News Up Next Sea Turtles From Shell to Surf: Photos ‹› The North Pole is moving. Not the geographic axis around which Earth spins, of course, but rather its magnetic pole, the north end of which is slowly but steadily wandering across the Arctic Ocean toward Siberia. Scientists have known about our planet’s shifting magnetic field for a long time, since at least 1904 — and today we now have a “Swarm” of satellites investigating its many inconsistencies from orbit. NEWS: Satellite Swarm Maps Earth’s Magnetic Field Launched in November 2013, ESA’s Swarm mission consists of three 9-meter satellites orbiting the planet at altitudes of 300-530 km (186-330 miles). Their goal is to monitor Earth’s dynamic magnetic field, observing its changes over a period of four years. The data gathered by the Swarm satellites will help scientists better understand how our magnetic field works, how it’s influenced by solar activity, and why large parts of it are found to be weakening. Because the magnetic field is our planet’s first line of defense against radiation from both the sun and deep space, understanding what makes it tick is very important. ANALYSIS: Earth vs. Sun: Flipping Magnetic Face Off The first high-definition measurements from Swarm have been made and what’s become apparent are weakening regions within the core-generated magnetic field over the western hemisphere, while parts of the southern Indian Ocean show strengthening fields. Swarm measurements also confirm the march of the magnetic north pole toward Russia. http://news.discovery.com/earth/satellite-swarm-spots-north-pole-drift-140622.htm[27/06/2014 15:04:26] Satellite Swarm Spots North Pole Drift : Discovery News “These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm,” said Rune Floberghagen, ESA’s Swarm Mission Manager. “With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm’s capability to map finescale features of the magnetic field.” Watch a video of the Swarm compass findings below: It’s known that Earth’s magnetic poles occasionally reverse, a process that takes several thousand years to complete and creates a much more complex and unpredictable — but still protective — field during the interim. And while the weakening observed by Swarm could be a sign of a polarity reversal on the way, it’s an event that’s probably still thousands of years away. NEWS: Earth’s Magnetic Field Made Quick Flip-Flop Meanwhile, missions like Swarm will allow us to better understand the magnetic field we have today, in order to understand what it will do in the future. Read more about Earth’s moving magnetic field here, and find out what would happen during a magnetic reversal here. Source: ESA 100% MIND BLOWER DISCOVERYnewsletter Invalid Email Recommended for you 0% MUST KNOW 0% LOL 0% GENIUS SUBSCRIBE SUBSCRIBE http://news.discovery.com/earth/satellite-swarm-spots-north-pole-drift-140622.htm[27/06/2014 15:04:26] 0% WIN 0% REALLY? Date : 23/06/2014 Pays : ESPAGNE Surface : 77 % Mots : 520 > Lire cet article sur le site web El norte magnético se desplaza hacia Siberia Satélites europeos confirman la tendencia: el lugar al que apuntan las brújulas no será el mismo ESA Cambios en el campo magnético de enero a junio de 2014. Las áreas en rojo muestran las zonas donde se refuerza, y las azules donde se debilita El primer conjunto de resultados de alta resolución a partir de tres satélites de la constelación Swarm de la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) confirma una tendencia que ya se había observado en los últimos años: el movimiento del norte magnético desde Norteamérica, donde se encuentra en la actualidad, hacia Siberia. Este cambio, que podría acontecer en menos de medio siglo según anunciaron los geofísicos ya hace varios años, podría suponer que las auroras boreales dejaran de aparecer en los cielos de Alaska para hacerlo en Siberia y el norte de Europa. Donde apuntan las brújulas no será el mismo sitio. Lanzado en noviembre de 2013, Swarm proporciona conocimientos sin precedentes en el complejo funcionamiento del campo magnético de la Tierra, que nos protege de la radiación cósmica. Las mediciones realizadas durante los últimos seis meses confirman el movimiento del norte magnético desde la isla de Bathurst, en Canadá, hacia Siberia. Este conocimiento es fundamental en muchos campos, como para los marinos, que se fían de sus brújulas para dirigir la navegación. No hay que confundir los polos magnéticos con los geográficos. Los primeros no son constantes, y cambian ligeramente año a año. Los científicos consideran probable que estos movimientos sean oscilaciones cíclicas, por lo que después de desplazarse a Siberia es posible que vuelva de nuevo a Canadá. Los resultados también refuerzan la tendencia general de debilitamiento del campo magnético, con descensos más drásticos en el hemisferio occidental. Pero en otras áreas, tales como el sur del Océano Índico, el campo magnético se ha fortalecido desde enero. Estos cambios se basan en las señales magnéticas derivadas de núcleo de la Tierra. En los próximos meses, los científicos analizarán los datos para desentrañar las contribuciones magnéticas de otras fuentes, como el manto, la corteza, los océanos, la ionosfera y la magnetosfera. Esto proporcionará una nueva visión de muchos de los procesos naturales que se producen en el interior de nuestro planeta con el clima espacial provocado por la actividad solar. A su vez, esta información dará lugar a una mejor comprensión de por qué el campo magnético se está debilitando. Los primeros resultados han sido presentados en el III Encuentro de Ciencias del Swarm, en Copenhague, Dinamarca. Comentarios Imprimir Compartir En Vídeo Toda la actualidad de Ciencia En imágenes Toda la actualidad de Ciencia Noticias relacionadas Inversión de los polos magnéticos de la Tierra: ¿el regreso a la Edad de Piedra? Los perros prefieren defecar alineados con el campo magnético de la Tierra ¿Puede el campo magnético de la Tierra volverse loco de repente? El escudo protector de la vida en la Tierra El misterio de las auroras boreales de San Valentín El núcleo de la Tierra gira mucho más despacio de lo que se creía El Sol invierte su campo magnético Así funciona el escudo magnético de la Tierra Tous droits de reproduction réservés Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Sign In Top Send Feedback Physics Home Nanotechnology Astronomy & Space Earth Space Exploration Astronomy & Space Chemistry Biology Technology Other Sciences Register Medicine & Health June 20, 2014 Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Jun 20, 2014 Featured Popular Most shared Physicist suggests speed of light might be slower than thought Jun 26, 2014 73 Hydrogen breakthrough could be a game-changer for the future of car fuels Jun 24, 2014 18 Pesticides threaten birds and bees alike, study says Jun 24, 2014 4 Mysterious X-ray signal intrigues astronomers Jun 24, 2014 16 Tofu ingredient could revolutionise solar panel manufacture Jun 26, 2014 1 Earth's magnetic field. Credit: ESA/ATG Medialab (Phys.org) —The first set of high-resolution results from ESA's three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth's magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Phys.org on facebook Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field's weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. Relevant PhysicsForums posts But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the magnetic field has strengthened since January. Ratio of matter to radiation density 22 hours ago structure of galaxy and the laws behind it Jun 25, 2014 The latest measurements also confirm the movement of magnetic North towards Siberia. These changes are based on the magnetic signals stemming from Earth's core. Over the coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. http://phys.org/news/2014-06-swarm-reveals-earth-magnetism.html[27/06/2014 15:29:49] pulsating stars Jun 25, 2014 interaction of three black holes earth as a capacitor stability of black hole Jun 25, 2014 Jun 25, 2014 Jun 25, 2014 Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening. "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen, ESA's Swarm Mission Manager. June 2014 magnetic field. Credit: ESA/DTU Space "With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm's capability to map finescale features of the magnetic field." The first results were presented today at the 'Third Swarm Science Meeting' in Copenhagen, Denmark. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Ørsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm's core instrument – the Vector Field Magnetometer – was provided by the Technical University of Denmark. http://phys.org/news/2014-06-swarm-reveals-earth-magnetism.html[27/06/2014 15:29:49] More from Physics Forums - Astronomy & Astrophysics Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Swarm constellation over Earth. Credit: ESA/AOES Medialab Denmark's National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role – together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes – in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field. "I'm extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialised," said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space. Explore further: Swarm's precise sense of magnetism Provided by European Space Agency 4.6 /5 (30 votes) • Tweet 1 reddit http://phys.org/news/2014-06-swarm-reveals-earth-magnetism.html[27/06/2014 15:29:49] Swarm rivela cambiamenti del campo magnetico terrestre Contatti Pubblicità Chi siamo Prima Pagina Dati geografici Rilievo BIM CAD GIS Terra e spazio Scienze della terra Territorio Servizi Swarm rivela cambiamenti del campo magnetico terrestre 25 Giugno 2014 Renzo Carlucci La prima serie di risultati ad alta risoluzione dalla costellazione Swarm composta da tre satelliti dell'ESA rivela i più recenti cambiamenti nel campo magnetico che protegge il nostro pianeta. Lanciata nel novembre 2013, Swarm fornisce informazioni senza precedenti sul complesso funzionamento del campo magnetico della Terra, che ci protegge dal bombardamento di particelle e radiazioni cosmiche. Le misurazioni effettuate nel corso degli ultimi sei mesi confermano la tendenza generale di indebolimento del campo, con il calo più drammatici sopra l'emisfero occidentale. Ma in altre aree, come l'Oceano Indiano meridionale, il campo magnetico si è rafforzato. Le ultime misurazioni confermano anche un movimento del Nord magnetico verso la Siberia. Questi cambiamenti sono basati sui segnali magnetici derivanti dal nucleo della Terra. Nel corso dei prossimi mesi, gli scienziati analizzeranno i dati per svelare i contributi magnetici provenienti da altre fonti, vale a dire il mantello, la crosta, gli oceani, la ionosfera e la magnetosfera. Ciò fornirà una nuova visione di molti processi naturali, a partire da quelli che si verificano in profondità all'interno del nostro pianeta nello spazio innescato da attività solare. A sua volta, questa informazione produrrà una migliore comprensione del perché il campo magnetico si stia indebolendo. "Questi primi risultati dimostrano l'ottima performance di Swarm", ha dichiarato Rune Floberghagen, Swarm Mission Manager di ESA. "Con una risoluzione senza precedenti, i dati mostrano anche la capacità di Swarm di mappare caratteristiche del campo magnetico ad alta risoluzione." I primi risultati sono stati presentati alla terza Swarm Science Meeting a Copenhagen in Danimarca. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, ministro danese dell'Istruzione superiore e della Scienza, ha evidenziato il particolare contributo danese alla missione. Swarm continua l'eredità del http://www.rivistageomedia.it/20140625641/terra-e-spazio/swarm-rivela-cambiamenti-del-campo-magnetico-terrestre.html[27/06/2014 15:32:02] Swarm rivela cambiamenti del campo magnetico terrestre satellite danese Ørsted, che è ancora operativo, così come la missione Champ tedesca. Lo strumento principale di Swarm - il Vector Field Magnetometer - è stato fornito dalla Technical University of Denmark. (Fonte ESA) Copia qui lo "short link" a questo articolo www.geoforall.it/a6h9 Letto 315 volte Vota questo articolo Ultima modifica il Mercoledì, 25 Giugno 2014 08:41 (1 Voto) Etichettato sotto swarm satellite campo magnetico terra dimensione font Tweet Mi piace Piace a una persona. Di' c piace anche a te, prima d i tuoi amici. 6 Condividi http://www.rivistageomedia.it/20140625641/terra-e-spazio/swarm-rivela-cambiamenti-del-campo-magnetico-terrestre.html[27/06/2014 15:32:02] Stampa Email European Space Agency says magnetic north is drifting southward - UPI.com TERME DI AGNANO, INGRESSO PER 2 SPA PER 2 DA SALUS PER AQUAM € 60,00 68% Risparmia fino al 90% € 19,00 € 60,00 50% € 29,90 COMPRA! COMPRA! SCIENCE NEWS HOME / SCIENCE NEWS / MAGNETIC NORTH IS DRIFTING SOUTH TOWARDS SIBERIA Magnetic north is drifting south towards Siberia "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen. By Brooks Hays | June 23, 2014 at 6:20 PM | 4 Comments 39 12 0 4 Feedback Map of Earth's magnetic field. (ESA/Swarm) LONDON, June 23 (UPI) --The Earth's magnetic north pole is drifting southward towards Siberia, according to researchers at the European Space Agency (ESA). As part of ESA's Swarm mission, scientists have been mapping the planet's magnetic field with the help three satellites. Each satellite is equipped with several Earthstudying tools -- including magnetometers, which measure the magnetic field's strength and direction. "I started my career in magnetometry and the accuracy we had then in the laboratories was less http://www.upi.com/Science_News/2014/06/23/Magnetic-north-is-drifting-south-towards-Siberia/3531403559377/[27/06/2014 15:41:44] x European Space Agency says magnetic north is drifting southward - UPI.com than what we can fly in space now," Volker Liebig, the director of Earth observation at ESA, recently told BBC News. "So what we have on Swarm is fantastic, but we need long time series to understand fully the Earth's magnetic field, and we will get that from this mission." Results from the Swarm mission suggest that not only is magnetic north on the move, but the entire magnet field is weakening, leaving Earth potentially exposed to additional cosmic radiation. This, however, is considered normal, with the magnet cloak likely to regain its strength in the near future. Analysis of ancient rocks buried deep in the Earth lead scientists to believe Earth's magnetic north and south poles switch every few million years. The latest from Swam suggests the poles may once again be preparing to trade sides; though the flip-flop itself takes several thousand years. A study published in 2011 surmised that the shifting magnetic poles are affected by the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. Currently, Swarm satellites have only honed in on the general magnetic field generated by Earth's molten core. But scientists expect to study more delicate magnetic fields in the future, such as the field generated by the movement of the world's oceans. "These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm," said Rune Floberghagen, ESA's Swarm Mission Manager. "With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm's capability to map fine-scale features of the magnetic field." © 2014 United Press International, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Any reproduction, republication, redistribution and/or modification of any UPI content is expressly prohibited without UPI's prior written consent. Order reprints Previous Story Next Story May 2014 was Earth's warmest May on record, NOAA says YOU MAY LIKE YOU MAY LIKE UNESCO to send experts to Haiti to investigate possible Santa Maria shipwreck Sponsored Content by Taboola Sponsored Content by Taboola http://www.upi.com/Science_News/2014/06/23/Magnetic-north-is-drifting-south-towards-Siberia/3531403559377/[27/06/2014 15:41:44] Satélites de la misión Swarm confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético – Tecnología de los satélites – Noticias, última hora, vídeos y fotos de Tecnología de los satélites en lainformacion.com AVISO: Utilizamos cookies propias y de terceros para mejorar nuestros servicios y mostrarle publicidad relacionada con sus preferencias mediante el análisis de sus hábitos de navegación. Si continua navegando, consideramos que acepta su uso. Puede cambiar la configuración de su navegador u obtener más información aquí. Like 251k Secciones viernes, 27/06/14 - 15: 40 h Economía Bolsa Humor Observatorio Económico Vídeo Fotogalerías Fotos Tipos Gráficos Mis finanzas Blogs 365K seguidores Busca en miles de textos, vídeos y fotos 'El Intermedio' cierra por vacaciones lainformacion.com Seguir Huelga Lo último Lo más Vivienda Temas Tiempo Microsiervos Practicopedia TECNOLOGÍA DE LOS SATÉLITES Satélites de la misión Swarm confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético lainformacion.com [ jueves, 19/06/14 - 15:55 0 ] Los primeros resultados de la misión Swarm, el grupo de tres satélites lanzados en noviembre por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), confirman la tendencia general sobre el debilitamiento del campo magnético terrestre. Temas 2 0 2 0 Agencia Espacial Europea Ciencia y tecnología Copenhague Frascati Historia Investigación médica Italia Mundo Rusia Suecia Tecnología de los satélites El Gobierno reduce un 3,2% el techo de gasto para 2015, hasta 129.060 millones de euros Castro dice que Fiscalía tendría que querellarse contra él por prevaricación Copenhague, 19 jun.- Los primeros resultados de la misión Swarm, el grupo de tres satélites lanzados en noviembre por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), confirman la tendencia general sobre el debilitamiento del campo magnético terrestre. Según aseguraron hoy los responsables del proyecto en una conferencia organizada por la ESA en Copenhague, el debilitamiento es mayor en el hemisferio occidental, aunque en otras áreas como el Índico sur se ha producido el fenómeno contrario. Las medidas registradas por Swarm desde enero pasado confirman también el desplazamiento progresivo del Polo Norte magnético hacia Siberia. Los jueces se levantan contra Horrach por su crítico recurso hacia Castro La batalla por la presidencia de la Comisión pone sobre la mesa supuestos problemas con el alcohol de Juncker Los Obispos denuncian que la Religión con la Lomce reduce a la mitad las horas lectivas que con el PSOE Los expertos reunidos en Copenhague estimaron que en un plazo de entre 5.000 y 10.000 años habrá una inversión en el campo magnético, un fenómeno que se ha producido varias veces antes en la historia del planeta, la última hace 780.000 años. Nils Olsen, uno de los científicos al frente del proyecto, calificó de "excelentes" los datos preliminares aportados por la misión, aunque resaltó a Efe que ha pasado "demasiado poco tiempo" para sacar Lo más visto en Economía hoy esta semana este mes http://noticias.lainformacion.com/economia-negocios-y-finanzas/tecnologia-de-los-satelites/satelites-de-la-mision-swarm-confirman-el-debilitamiento-del-campo-magnetico_wMV19BrqQlPdPeUYCfWpr7/[27/06/2014 15:45:11] Satélites de la misión Swarm confirman el debilitamiento del campo magnético – Tecnología de los satélites – Noticias, última hora, vídeos y fotos de Tecnología de los satélites en lainformacion.com conclusiones más amplias sobre las mediciones de la operación, que durará cuatro años, y sus aplicaciones. 1 España empieza a generar empleo y ya hay siete regiones con más oferta que demanda 2 Las leches de Hacendado y Carrefour destacan por su buena relación calidad precio, según la OCU 3 Los españoles trabajan más que franceses, daneses y suecos, según un estudio La misión Swarm despegó del cosmódromo de Plesetsk (Rusia) en noviembre para estudiar los procesos en el interior de la Tierra, comprender mejor su campo magnético y por qué se está debilitando esta burbuja que protege el planeta de la radiación cósmica y las partículas cargadas que llegan a través del viento solar. 4 COMUNICADO: La comunidad de compras establece nuevos estándares con la Lyoness MasterCard® prepago 5 Tres respuestas básicas para entender el futuro de las pensiones La misión, que usa tecnología europea y canadiense, tiene también como objetivo aplicaciones prácticas, como mejorar la precisión de los sistemas de navegación por satélite y la predicción de terremotos o hacer más eficaz la extracción de recursos naturales. 6 Red Hat adquiereeNovance, líder en servicios de integración de OpenStack 7 Qué son las Sicav y qué se oculta tras ellas Los datos científicos -abiertos a toda la comunidad investigadora- se descargarán a través de la estación de seguimiento de Kiruna (Suecia) y se procesarán, distribuirán y archivarán en el Centro para la Observación de la Tierra de la ESA en Frascati (Italia). 8 ¿Buscas empleo en el extranjero? Éstos son los países que más oportunidades te ofrecen 9 Isla española quiere ser la primera del mundo autosuficiente en electricidad 10 Administración de Empresas e Ingeniería Industrial los estudios con mayor oferta de empleo Las alteraciones detectadas en los primeros resultados de Swarm están basadas en señales magnéticas del núcleo terrestre. Para las próximas observaciones se incluirán también otras fuentes de medición como el manto, la corteza, los océanos, la ionosfera y la magnetosfera, lo que permitirá un mayor conocimiento de diversos procesos naturales. (Agencia EFE) También te puede interesar más… Doña Letizia no podría solicitar el divorcio La nueva condición de inviolabilidad que implica la llegada al trono de Felipe VI tendrá también consecuencias para la reina Letizia. En caso de que decidiese divorciarse e interponer una demanda,... más Pérdida de peso que asusta médicos Científicos de Boston han descubierto un método para adelgazar chocante. 1 método extraño y ahora tiene 12kg menos... más La evolución física de Doña Letizia: del telediario a Reina de España Doña Letizia se ha convertido este jueves en Reina de España, más Los amigos de la Infanta Cristina confiesan que se siente psicológicamente... La revista Vanity Fair ha entrevistado al fiscal que lleva el caso, y a dos de los abogados del bufete de Miquel Roca, Pau Molins y Jesús-María Silva, que lleva la defensa de la Infanta. Muy seguros... más David Villa supera a Maradona como máximo goleador en los mundiales La despedida de David Villa de la selección no fue la soñada en lo colectivo, aunque siempre recordará que dejó la camis... más powered by plista Anúnciese Aquí Notificar Error Enviar 1 La indemnización por despido tributa desde el viernes 2 Los Técnicos de Hacienda creen que la reforma fiscal beneficia a los más ricos y la lucha contra el fraude es insuficiente 3 España empieza a generar empleo y ya hay siete regiones con más oferta que demanda 4 Las leches de Hacendado y Carrefour destacan por su buena relación calidad precio, según la OCU 5 Así te afecta la reforma fiscal de Montoro 6 Cómo diferenciar burka, chador, niqab y otras prendas musulmanas 7 El Ayuntamiento destaca que el ascenso del Córdoba CF a Primera tendrá "múltiples efectos beneficiosos" 8 ¿Buscas empleo en el extranjero? Éstos son los países que más oportunidades te ofrecen 9 La junta de Pescanova se celebrará el 1 de julio en segunda convocatoria 10 El mileurismo ya no es cosa de jóvenes y el sueldo más habitual es de 15.500 euros Leer más tarde más… Añade un comentario... ✔ 1 Rajoy anuncia que la próxima privatización será el transporte ferroviario de pasajeros 2 Cambio social bajo modelo de empresa, reto de colombiano reconocido en Forbes 3 El libro que devoran los economistas: 'Por qué fracasan los países' 4 ¿Buscas empleo en el extranjero? Éstos son los países que más oportunidades te ofrecen 5 Así te afecta la reforma fiscal de Montoro Publicar también en Facebook Publicar como Mariangela D'Acunto (¿No eres tú?) Plug -in social de Facebook Comentar Comentar http://noticias.lainformacion.com/economia-negocios-y-finanzas/tecnologia-de-los-satelites/satelites-de-la-mision-swarm-confirman-el-debilitamiento-del-campo-magnetico_wMV19BrqQlPdPeUYCfWpr7/[27/06/2014 15:45:11] Modifications spectaculaires du champ magnétique terrestre Recherchez sur tout Techno-Science.net Rechercher Vendredi 27 Juin 2014 Accueil News Dossiers Archives Boutique Librairie Glossaire A propos Techno-Science.net : Suivez l'actualité des sciences et des technologies, découvrez, commentez Forum 667 Catégories Techniques Aéronautique Transports Espace Energie Multimédia Architecture Sciences Mathématiques Physique Astrophysique Astronomie Vie et Terre Encore plus... Autres sujets Rétro Techno-Science.net Espace Membre Anti-spam Astronomie Posté par Publication le Vendredi 20/06/2014 à 12:55 Le point sur... Satellite naturel Étoile Lumière Couche d'ozone Modifications spectaculaires du champ magnétique terrestre modification champ magnétique 5 commentaires Like 330 mesure champ magnétique Tweeter 100 14 Les premiers résultats à haute résolution recueillis à partir des trois satellites de la constellation Swarm de l'ESA, révèlent les changements les plus récents dans le champ magnétique qui protège notre planète. Lancé en Novembre 2013, Essaim fournit un aperçu sans précédent dans les rouages complexes du champ magnétique de la Terre, qui nous protège du rayonnement cosmique et bombardant des particules chargées. Partenaires Organismes CEA CNES CNRS INSU-CNRS ESA Observatoire Paris Sites Web Analyse Bourse Sur la Toile HD-Numérique Allons-Sortir.fr Photo Mystérieuse Que représente cette image ? Juin 2014 champ magnétique. Illustration ESA Les mesures effectuées au cours des six derniers mois confirment la tendance générale de l'affaiblissement du champ, avec les baisses les plus spectaculaires dans l'hémisphère occidental. Mais dans d'autres domaines, tels que l'océan Indien, le champ magnétique s'est renforcé depuis Janvier. Les dernières mesures confirment également le déplacement du Nord magnétique vers la Sibérie. Ces changements sont basés sur les signaux magnétiques provenant du noyau de la Terre. Au cours des prochains mois, les scientifiques vont analyser les données et comparer avec les études provenant d'autres sources, à savoir le manteau, croûte, océans, ionosphère et magnétosphère. Cela fournira un nouvel éclairage sur de nombreux processus naturels, de ceux qui se produisent au fond de notre planète à la météorologie spatiale déclenchée par l'activité solaire. À son tour, cette information donnera une meilleure compréhension des raisons pour lesquelles le champ magnétique s'affaiblit. http://www.techno-science.net/?onglet=news&news=12899[27/06/2014 15:49:18] Modifications spectaculaires du champ magnétique terrestre Voir aussi Titan pourrait être antérieur à Saturne Modifications spectaculaires du champ magnétique terrestre Une avancée majeure pour le télescope géant EELT Nouvelle avancée pour la recherche de la vie extraterrestre Trois éruptions solaires classées X en deux jours Le champ magnétique de la Terre. Illustration ESA "Ces premiers résultats démontrent l'excellente performance de Swarm", a déclaré Rune Floberghagen, directeur Swarm, mission de l'ESA. "Avec une résolution sans précédent, les données montrent également la capacité de Swann à cartographier les caractéristiques à petite échelle du champ magnétique." Les premiers résultats ont été présentés à la réunion scientifique Swarm à Copenhague, au Danemark. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, ministre danois de l'Enseignement supérieur et de la Science, a souligné la contribution danoise à la mission. Essaim qui poursuit la tradition du satellite danois Ørsted, qui est toujours opérationnel, ainsi que la mission Champ allemande. L'instrument de base de Swarm, le magnétomètre, a été fourni par l'Université technique du Danemark. Essaim. Illustration ESA L'Institut National Space du Danemark, DTU espace, a un rôle de premier plan avec 10 instituts de recherche européens et canadiens dans la facilité Swarm application Constellation satellite et de la recherche, qui produit des modèles de pointe basés sur des données Swarm décrivant chacune des différentes sources du champ mesuré. http://www.techno-science.net/?onglet=news&news=12899[27/06/2014 15:49:18] Le rôle inattendu des galaxies naines dans la formation des étoiles Deux télescopes spatiaux canadiens exceptionnellement petits et économiques lancés Fin de la mission CoRot Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Space Newsfeed comprehensive free satellite, astronomy and space industry news Space Newsfeed Front Page Latest News Register for Free News Emails RSS Feeds Advertise on Space Newsfeed NASA ESA Space Patches space-boosters.co.uk From NASA space patches and pins to space,food,postcards,photos & more Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism (19 June 2014) The first set of high-resolution results from ESA’s three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet. http://www.spacenewsfeed.co.uk/index.php/news/1294-swarm-reveals-earth-s-changing-magnetism[27/06/2014 15:51:04] Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Changes in Earth’s magnetic field from January to June 2014 as measured by the Swarm constellation of satellites. These changes are based on the magnetic signals that stem from Earth’s core. Shades of red represent areas of strengthening, while blues show areas of weakening over the 6-month period. (courtesy: ESA/DTU Space) Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth’s magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. http://www.spacenewsfeed.co.uk/index.php/news/1294-swarm-reveals-earth-s-changing-magnetism[27/06/2014 15:51:04] Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism ‘Snapshot’ of the main magnetic field at Earth’s surface as of June 2014 based on Swarm data. The measurements are dominated by the magnetic contribution from Earth’s core (about 95%) while the contributions from other sources (the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere) make up the rest. Red represents areas where the magnetic field is stronger, while blues show areas where it is weaker. (courtesy: ESA/DTU Space) Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field’s weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the magnetic field has strengthened since January. The latest measurements also confirm the movement of magnetic North towards Siberia. These changes are based on the magnetic signals stemming from Earth’s core. Over the coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening. http://www.spacenewsfeed.co.uk/index.php/news/1294-swarm-reveals-earth-s-changing-magnetism[27/06/2014 15:51:04] Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism The magnetic field and electric currents near Earth generate complex forces that have immeasurable impact on our everyday lives. Although we know that the magnetic field originates from several sources, exactly how it is generated and why it changes is not yet fully understood. ESA’s Swarm mission will help untangle the complexities of the field. (courtesy: ESA/ATG Medialab) These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm,” said Rune Floberghagen, ESA’s Swarm Mission Manager. “With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm’s capability to map finescale features of the magnetic field.” The first results were presented today at the ‘Third Swarm Science Meeting’ in Copenhagen, Denmark. Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Ørsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm’s core instrument – the Vector Field Magnetometer – was provided by the Technical University of Denmark. http://www.spacenewsfeed.co.uk/index.php/news/1294-swarm-reveals-earth-s-changing-magnetism[27/06/2014 15:51:04] Swarm reveals Earth's changing magnetism Swarm is ESA's first Earth observation constellation of satellites. The three identical satellites are launched together on one rocket. Two satellites orbit almost side-by-side at the same altitude – initially at about 460 km, descending to around 300 km over the lifetime of the mission. The third satellite is in a higher orbit of 530 km and at a slightly different inclination. The satellites’ orbits drift, resulting in the upper satellite crossing the path of the lower two at an angle of 90° in the third year of operations. The different orbits along with satellites’ various instruments optimise the sampling in space and time, distinguishing between the effects of different sources and strengths of magnetism. (courtesy: ESA/AOES Medialab) Denmark’s National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role – together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes – in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field. “I’m extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialised,” said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space. (source: ESA) http://www.spacenewsfeed.co.uk/index.php/news/1294-swarm-reveals-earth-s-changing-magnetism[27/06/2014 15:51:04] Campo magnético da Terra está a enfraquecer - PÚBLICO Lisboa CIÊNCIA 23°C Campo magnético da Terra está a enfraquecer PÚBLICO 26/06/2014 - 18:32 A azul, regiões onde o campo magnético está a enfraquecer; a vermelho, as zonas onde está a reforçar-se ESA Recommend http://www.publico.pt/ciencia/noticia/campo-magnetico-da-terra-a-enfraquecer-1660653[27/06/2014 15:52:23] 4 Tweetar Share 2k 0 16 Campo magnético da Terra está a enfraquecer - PÚBLICO TÓPICOS Agência Espacial Europeia Os primeiros resultados recolhidos pelos três satélites Swarm da Agência Espacial Europeia (ESA), a funcionar em conjunto no espaço desde há seis meses, confirmam que, de um modo geral, o campo magnético da Terra, que protege o planeta da radiação cósmica e das partículas carregadas, está a enfraquecer, anunciou a ESA em comunicado. O declínio mais acentuado verifica-se ao longo do hemisfério ocidental. Contudo, noutras áreas, como a sul do oceano Índico, o campo magnético tem vindo a reforçar-se desde Janeiro. As medições também confirmam a deslocação do norte magnético para sul, em direcção à Sibéria. Ao longo dos próximos meses, os cientistas irão analisar os dados para tentar perceber as razões desse enfraquecimento. Notícia corrigida dia 27/06/2014 às 13h15. Recommend 4 Tweetar Share 0 16 2k RECOMENDADOS Esther foi retocada com Photoshop mais de 25 vezes. E ficou bonita? Um intruso convidado na Agência Espacial Europeia Cria de urso eutanasiada na Suíça vai servir para ensinar que a natureza é cruel Professores dizem que exame de Matemática A "é injusto" e vai "cortar as pernas" aos alunos COMENTÁRIOS NOS BLOGUES http://www.publico.pt/ciencia/noticia/campo-magnetico-da-terra-a-enfraquecer-1660653[27/06/2014 15:52:23]




