PARTE 1: EL PRESENTE PERFECTO – LOS VERBOS
Anuncio

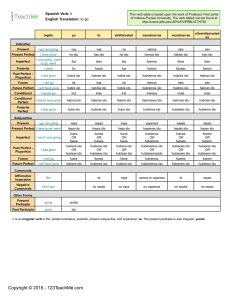
PARTE 1: EL PRESENTE PERFECTO – LOS VERBOS REGULARES The PRESENT PERFECT (presente perfecto) is used to express what someone HAS DONE (or has not done) in the recent past that may extend to the present moment. Example in English: I have studied. He has written a letter to María. We have been stranded for six days. How do you form the present perfect in Spanish? Just like in English, you need two parts (have eaten, have seen, etc.) The verb haber (he, has, ha, hemos, han) + verb root + ado (AR verbs) or ido (ER, IR verbs) EJEMPLO: Yo he hablado (hablar) à I have talked/spoken (haber) + HABLAR COMER VIVIR yo he hablado comido vivido tú has hablado comido vivido él,ella,ud. ha hablado comido vivido nosotros hemos hablado comido vivido ellos,uds. han hablado comido vivido LOS VERBOS REGULARES EN EL PRESENTE PERFECTO: (haber) + HABLAR DAR ESTAR SER COMER yo he hablado dado estado sido comido tú has hablado dado estado sido comido él,ella,ud. ha hablado dado estado sido comido nosotros hemos hablado dado estado sido comido ellos,uds. han hablado dado estado sido comido (haber) + TENER IR PODER yo he tenido ido podido tú has tenido ido podido él,ella,ud. ha tenido ido podido nosotros hemos tenido ido podido ellos,uds. han tenido ido podido ¡A practicar! ¿Cómo se dice en español? 1. You (tú) have been (estar) à 7. I have been (ser) à 2. We have given (dar)à 8. They all have gone (ir)à 3. You all have decided (decidir)à 9. You (usted) have had (tener) à 4. He has had (tener)à 10. They have left (salir) à 5. I have been able to (poder)à 11. We have wanted (querer) à 6. She has liked (gustar)à 12. She has found (encontrar) à VIVIR vivido vivido vivido vivido vivido PARTE II: EL PRESENTE PERFECTO – LOS VERBOS IRREGULARES Just like with other Spanish verbs, there are irregulars. Though the “haber” verb stays the same, the second part of the formation is different. There are many irregulars, but here are the ones that you will be expected to know. (haber) + HACER PONER VER DECIR yo he hecho puesto visto dicho tú has hecho puesto visto dicho él,ella,ud. ha hecho puesto visto dicho nosotros hemos hecho puesto visto dicho ellos,uds. han hecho puesto visto dicho ¡A practicar! ¿Cómo se dice en español? 1. You (tú) have done (hacer)à 5. I have seen (ver) à 2. He has seen (ver)à 6. She has done (hacer)à 3. You have put (poner)à 7. We have seen (ver)à 4. We have said (decir)à 8. They have put (poner) à PARTE III: EL PLUSCUAMPERFECTO (PAST PERFECT): This tense is used to express what someone “HAD DONE (or had not done)” prevously to another event that already occurred in the past. Example in English: I had studied all night, but I still failed the test. He had written a letter to María, but she never wrote back. We had been stranded for six days but finally got help. How do you form the past perfect in Spanish? Same as the present perfect but the verb haber changes to the past tense. (había, habías, había, habíamos, habían) + verb root + ado (AR verbs) or ido (ER, IR verbs) EJEMPLO: Yo había hablado (hablar) à I had talked/spoken Irregular irregular (haber)+ HABLAR COMER VIVIR HACER VER yo había hablado comido vivido hecho visto tú habías hablado comido vivido hecho visto él,ella,ud. había hablado comido vivido hecho visto nosotros habíamos hablado comido vivido hecho visto ellos,uds. habían hablado comido vivido hecho visto ¡A practicar! 7. She had been able (poder)à 1. I had seen (ver) à 8. He had made (hacer)à 2. You (tú) had been (estar)à 9. You had been (estar)à 3. We had said (decir)à 10. We had had (tener)à 4. They had put (poner)à 11. They had liked (gustar)à 5. He had gone (ir)à 12. They had given (dar)à 6. I had been (ser)à