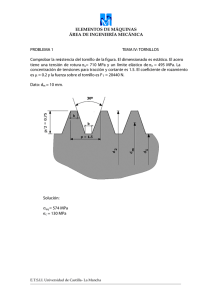
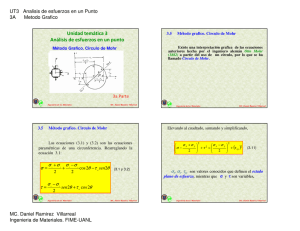
σx = σy = ( ) ( )2 - MC Daniel Ramirez Villarreal
Anuncio
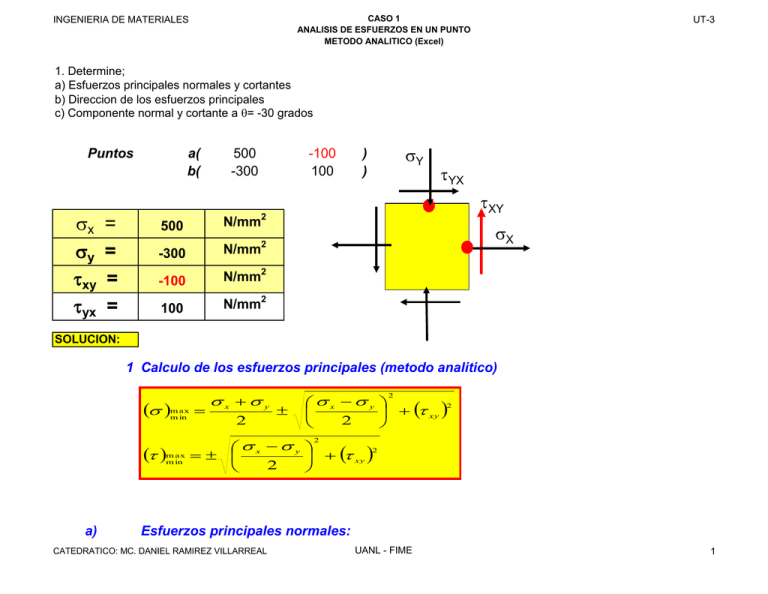
CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES UT-3 1. Determine; a) Esfuerzos principales normales y cortantes b) Direccion de los esfuerzos principales c) Componente normal y cortante a θ= -30 grados Puntos σx σy τxy τyx = = = = a( b( 500 -300 -100 100 σY ) ) τYX τXY 2 N/mm 500 σX 2 -300 N/mm -100 N/mm2 100 N/mm2 SOLUCION: 1 Calculo de los esfuerzos principales (metodo analitico) (σ ) m ax m in (τ ) m ax m in a) = σx +σy 2 σx −σ y 2 + (τ xy ) 2 2 ± σx −σ y 2 + (τ xy ) 2 2 =± Esfuerzos principales normales: CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL UANL - FIME 1 CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES (σ )max = min b) (τ )max min c) σ x +σ y 2 2 σ x −σ y + τ xy ± 2 ( ) 2 UT-3 σ maximo = 512.31 Mpa σ minimo = -312.31 Mpa Esfuerzos principales cortantes: σ x −σ y = ± 2 2 + τ xy ( )2 τ maximo τ minimo = 412.3 -412.3 Mpa Mpa = 100 Mpa = Calculo del esfuerzo normal: σn = σx +σ y 2 = σn 2 Direccion de los esfuerzos normales Principales: tan 2θ = − 2τ xy σ x −σ y CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL = UANL - FIME 2 CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES Tan 2 θ = 2θ = 14.04 UT-3 0.25 θ = grados σ maximo =????? 7.02 grados σ minimo =????? COMPROBACION Sustituyendo este angulo en las ecs. 1 para saber a quien pertenece si a σ 1 o ha σ 2 : σ = σ x +σ y 2 σ = + σ x −σ y 2 512.31 cos 2θ − τ xy sen 2θ Mpa Por lo que este valor le pertenece a σ 1 y el angulo obtenido le correspondera siendo: 2θ = 2θ1 = 14.04 grados θ1 = 7.02 grados Y la direccion de σ 2 sera: θ 2 = θ 1 +90 grados Para este caso sera: θ 2 = θ 1 +90 grados = 97.02 grados 2 Direccion de los esfuerzos cortantes principales: CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL UANL - FIME 3 CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES σ x −σ y tan 2θs = 2τ xy Tan 2 θ 2θ s= θ s= s -75.96 -37.98 UT-3 = -4 grados grados Sustituyendo este angulo en las ecs. 2 para saber a quien pertenece si a τ 1 o ha τ 2 : τ = σ x −σ y 2 τ= sen 2θ + τ xy cos 2θ -412.3 Mpa Por lo que este valor le pertenece a τ 2 y el angulo obtenido le correspondera siendo: 2θs = 2θs2 = -76.0 grados θs2 = -38.0 grados Y la direccion de τ 1 sera: θ s1 = θ s2 +90 grados Para este caso sera: θ s1 = θ s2 +90 grados = 52.02 grados 3 Orientacion de σ 1 y σ 2 : CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL UANL - FIME 4 CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES UT-3 2 y y σ1 θ1 θ2 1 x x σ1 1 σ2 σ2 2 3 Orientacion de σ n , τ 1 y τ 2 : 1' y σn τ1 σn θs1 x σn 1' y 2' τ2 τ1 x τ2 θs2 σn 2' 4 RESULTADOS PARA EL PUNTO A: CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL UANL - FIME 5 CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES Esfuerzos Mpa σ maximo = 512.31 σ minimo = -312.3106 τ maximo = 412.31 τ minimo = -412.31 σn = 100.00 CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL Direccion grados θ1 = θ2 = θs1 = θ s2 = 7.02 97.02 52.02 -37.98 UANL - FIME UT-3 6 INGENIERIA DE MATERIALES CATEDRATICO: MC. DANIEL RAMIREZ VILLARREAL CASO 1 ANALISIS DE ESFUERZOS EN UN PUNTO METODO ANALITICO (Excel) UANL - FIME UT-3 7