Defining Pronombres relativos Omisión del pronombre relativo Non
Anuncio

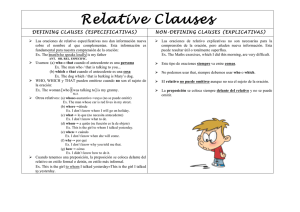
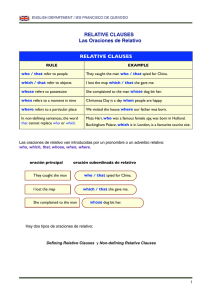
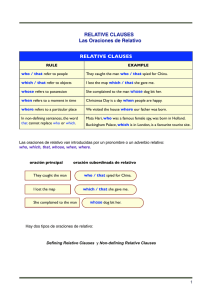
Las oraciones de relativo se dividen en 2: Defining Aportan información esencial para entender la frase Pronombres relativos Who/that (Personas) → I like the girl who works in the restaurant. Which/that (Animal/cosa) → I watched the film which you recomended. Where (Lugar) → This is the restaurant where we usually eat pizza. When/that (Tiempo) → That was the year when I was born. Why (Motivo) tiene “Reason” como antecedente → The reason why I am here is to convince you to come to the party. Whose (Cuyo) → That's the man whose car crashed into the wall. Omisión del pronombre relativo El pronombre relativo puede actuar de sujeto o de objeto (CD) de la oración de relativo. -Si el pronombre es sujeto de la oración de relativo, y por lo tanto va seguido de un verbo, NO SE PUEDE OMITIR. → I work with the man who drives the car. - Si el pronombre es objeto de la oración de relativo y por lo tanto va seguido por un nombre o pronombre, SI SE PUEDE OMITIR. → I like the shoes which you recomended. / I like the shoes you recomended. - El relativo whose NUNCA se omite. Non defining - Aportan información adicional - Van entre comas siempre - El pronombre relativo NO SE OMITE - El “that” no se usa Pronombres relativos Who (Personas) → Lisa, who is my best friend, is 18 years old. Which (Animal/cosa) → The dog, which I adopted last year, is playing in the park. Where (Lugar) → Cordoba, where I have many friends, is a beatifull city. When (Tiempo) → In 2001, when a plain crashed into the World Trade Center, I was living in New York. Whose (Cuyo) → Eminem, whose first album won a Grammy, is givining a concert next week Pronombres relativos y preposiciones - Podemos poner preposicones ante de los pronombres relativos (formal) Ejemplo: This is the city in which I was born - También podemos poner la preposición al final de la oración de relativo (informal) Ejemplo: This is the city which I was born in - Cuando usamos la preposición delante de “who” este se transforma en “whom” Ejemplo: He is Jack, with whom I went to school. (formal) He is Jack, who I went to school with. (informal) “Who” y “that” nunca se usa detrás de una preposición. What → Se puede usar en oraciones subordinadas de relativos. Actua como nombre + pronombre a la vez y significa “las cosas que” o “lo que”. Ejemplo: I don't like what you think What you did was horrible Is he going to do what I was asked?